Introduction
Bleeding hemorrhoids are a common source of rectal bleeding and discomfort, affecting many people worldwide. While hemorrhoidal bleeding is often benign and manageable with simple treatments, it can also signal more serious underlying conditions. Understanding the causes of bleeding hemorrhoids, recognizing when the bleeding requires urgent medical attention, and knowing how to manage symptoms are essential to maintaining digestive and overall health.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of why hemorrhoids bleed, how to identify when bleeding is serious, and practical guidance on when to see a healthcare professional.
What Are Hemorrhoids?
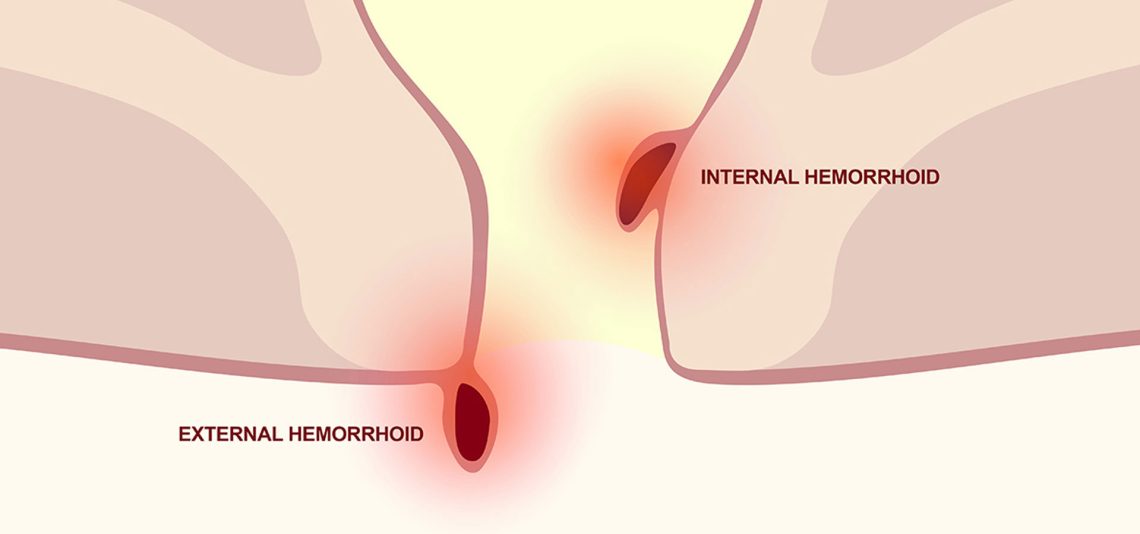
Hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels located in the lower rectum or anus. They can be:
- Internal hemorrhoids: Found inside the rectum; usually painless but prone to bleeding.
- External hemorrhoids: Located under the skin around the anus; can cause pain, swelling, and bleeding.
Why Do Hemorrhoids Bleed?
Bleeding from hemorrhoids occurs because the swollen veins become irritated, inflamed, or damaged. Common triggers include:
1. Straining During Bowel Movements
- Hard or large stools cause excessive straining, which puts pressure on hemorrhoidal veins.
- This pressure can rupture tiny blood vessels, leading to bright red bleeding.
2. Constipation or Diarrhea
- Both conditions increase irritation and trauma to hemorrhoids.
- Frequent diarrhea can cause repeated wiping, worsening inflammation.
3. Pregnancy
- Increased pelvic pressure and hormonal changes make hemorrhoids more susceptible to bleeding.
4. Prolonged Sitting
- Sitting for long periods, especially on the toilet, increases pressure on anal veins.
5. Heavy Lifting or Strenuous Activity
- Increases abdominal and pelvic pressure, aggravating hemorrhoids.
Characteristics of Hemorrhoidal Bleeding
- Usually bright red blood is seen on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
- Blood typically coats the stool but does not mix with it.
- Bleeding is often painless.
- May be intermittent or occasional, especially during or after bowel movements.
When Is Bleeding From Hemorrhoids Serious?
While bleeding hemorrhoids are often mild, certain signs suggest the bleeding might be serious or caused by another condition:
1. Heavy or Persistent Bleeding
- Large amounts of blood or bleeding that do not stop may lead to anemia.
- Requires urgent evaluation.
2. Dark or Black Stools
- Indicates bleeding higher up in the digestive tract, not typical of hemorrhoids.
- Requires immediate medical attention.
3. Blood Mixed with Stool
- Could suggest conditions other than hemorrhoids, such as colorectal polyps or cancer.
4. Painful Bleeding
- Hemorrhoids are usually painless; pain with bleeding may indicate thrombosis or anal fissures.
5. Associated Symptoms
- Unexplained weight loss, changes in bowel habits, abdominal pain, or fatigue.
- These warrant prompt investigation.
Other Causes of Rectal Bleeding
Not all rectal bleeding comes from hemorrhoids. Other causes include:
- Anal fissures: Small tears causing sharp pain and bleeding.
- Diverticulosis: Small pouches in the colon that can bleed.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
- Colorectal polyps or cancer.
- Gastrointestinal infections.
Proper diagnosis is critical.
Diagnosing Bleeding Hemorrhoids
Your healthcare provider may perform:
- Physical examination: Visual inspection and digital rectal exam.
- Anoscopy: A small tube with a light to view internal hemorrhoids.
- Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy: To rule out other causes, especially if you’re over 45 or have risk factors.
Managing Bleeding Hemorrhoids
1. Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
- Eat a high-fiber diet to soften stools.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Avoid straining and prolonged sitting.
2. Home Remedies
- Warm sitz baths to relieve irritation.
- Use moist wipes instead of dry toilet paper.
- Apply over-the-counter creams or suppositories as advised.
3. Medical Treatments
- Rubber band ligation for persistent internal hemorrhoids.
- Sclerotherapy or infrared coagulation.
- Surgery for severe cases.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical care if you experience:
- Heavy or continuous rectal bleeding.
- Symptoms of anemia (fatigue, dizziness).
- Blood mixed with stool or dark stools.
- Severe pain or swelling.
- Changes in bowel habits or unexplained weight loss.
Conclusion
Bleeding hemorrhoids are common and often manageable with proper care and lifestyle changes. However, it’s important to recognize when bleeding may signal a more serious condition requiring professional evaluation. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
If you experience rectal bleeding, don’t ignore it—consult your healthcare provider for a thorough assessment and peace of mind.
FAQs:
What causes hemorrhoids to bleed?
Straining during bowel movements, constipation, pregnancy, and irritation of swollen veins can cause bleeding.
Is bright red blood on toilet paper always from hemorrhoids?
Not always. While hemorrhoids often cause bright red bleeding, other conditions can too—consult a doctor if unsure.
When should I worry about bleeding hemorrhoids?
If bleeding is heavy, persistent, or accompanied by pain, dark stools, or other symptoms, see a healthcare provider.
Can hemorrhoidal bleeding lead to anemia?
Yes, chronic or heavy bleeding can cause anemia, leading to fatigue and dizziness.
How are bleeding hemorrhoids treated?
Treatment includes dietary changes, topical creams, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery in severe cases.