Introduction
Arthritis, a group of conditions characterized by joint inflammation and degeneration, affects millions worldwide, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. While medications and lifestyle changes are critical components of arthritis management, physical therapy (PT) plays a pivotal role in reducing symptoms, improving function, and enhancing quality of life.
This article explores how physical therapy helps manage arthritis, the techniques used, benefits, and how to work with a physical therapist effectively.
Understanding Arthritis and Its Impact on the Body
Arthritis encompasses many forms, with osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) being the most common. Both result in joint damage, but OA stems from wear and tear, while RA is an autoimmune inflammatory disease.
Symptoms include:
- Joint pain and tenderness
- Stiffness, especially in the morning
- Swelling and inflammation
- Decreased range of motion
- Muscle weakness around affected joints
These symptoms impair daily activities and reduce overall mobility.
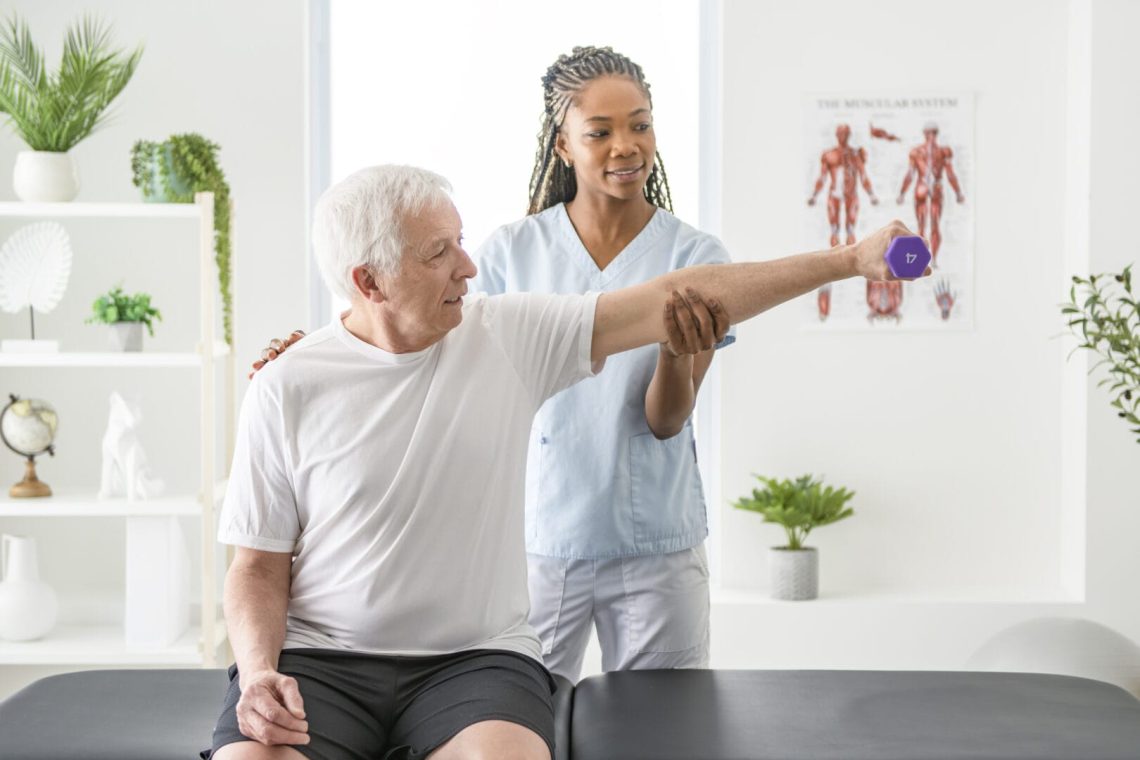
What is Physical Therapy?
Physical therapy is a healthcare specialty focusing on restoring movement, strength, and function through targeted exercises, manual techniques, education, and assistive devices.
Physical therapists evaluate each patient’s condition and tailor treatments to individual needs, aiming to:
- Relieve pain
- Restore joint function
- Improve muscle strength and flexibility
- Enhance balance and coordination
- Prevent disability
How Physical Therapy Helps Manage Arthritis
1. Pain Relief
- Therapeutic exercises strengthen muscles supporting joints, reducing stress on damaged cartilage.
- Manual therapy (joint mobilization and soft tissue massage) decreases stiffness and improves circulation.
- Modalities like heat, cold, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation can reduce pain and inflammation.
2. Improving Joint Mobility and Flexibility
- Stretching exercises prevent or reduce joint contractures (permanent stiffness).
- Range-of-motion exercises help maintain or restore joint movement.
- Techniques may vary depending on arthritis type and severity.
3. Strengthening Muscles
- Strong muscles support and protect arthritic joints.
- Strength training can slow disease progression and reduce joint pain.
- Exercises target specific muscle groups around affected joints.
4. Enhancing Balance and Coordination
- Arthritis may impair balance, increasing fall risk.
- PT incorporates balance training to improve stability.
- Coordination exercises help in performing daily tasks safely.
5. Education and Joint Protection
- Physical therapists teach patients about joint-friendly techniques.
- Advice on activity modification reduces joint overload.
- Training on assistive devices helps maintain independence.
Common Physical Therapy Techniques for Arthritis
Exercise Therapy
- Aerobic exercises: Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling improve cardiovascular health without stressing joints.
- Range of motion exercises: Gentle movements maintain flexibility.
- Strength training: Using weights, resistance bands, or body weight.
- Functional training: Mimics daily activities to improve real-world function.
Manual Therapy
- Joint mobilizations improve joint mechanics.
- Soft tissue massage reduces muscle tension and swelling.
Modalities
- Heat therapy: Loosens muscles and relieves stiffness.
- Cold therapy: Reduces inflammation and swelling.
- Ultrasound: Promotes tissue healing.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Manages pain signals.
Special Considerations for Different Types of Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis: Focus on improving joint mechanics, muscle strengthening, and weight management.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Tailor PT to manage inflammation, protect joints, and maintain function during flare-ups.
- Other types: PT programs adjusted to address specific symptoms and limitations.
Benefits of Physical Therapy in Arthritis Management
- Reduced pain and inflammation
- Increased joint flexibility and muscle strength
- Enhanced ability to perform daily activities
- Lower risk of falls and injuries
- Reduced reliance on medications and surgery
- Improved mental well-being and confidence
How to Work Effectively with a Physical Therapist
1. Initial Assessment
- Discuss symptoms, medical history, and goals.
- Physical exam to assess joint mobility, muscle strength, and function.
2. Setting Realistic Goals
- Short-term (e.g., reduce pain)
- Long-term (e.g., improve walking ability)
3. Customized Treatment Plan
- Exercises, manual therapy, and education tailored to individual needs.
4. Regular Follow-Up
- Monitor progress and adjust treatments as needed.
- Address new symptoms or challenges promptly.
5. Home Exercise Program
- Commitment to exercises outside therapy sessions is crucial.
- Therapists provide guidance and modifications.
Tips for Maximizing the Benefits of Physical Therapy
- Stay consistent with prescribed exercises.
- Communicate openly about pain or difficulties.
- Use assistive devices as recommended.
- Combine PT with other lifestyle changes like diet and weight management.
- Maintain a positive mindset and be patient.
Conclusion
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of effective arthritis management, offering a non-invasive, drug-free way to reduce pain, improve joint function, and enhance quality of life. By working closely with a skilled physical therapist and committing to personalized treatment plans, individuals with arthritis can regain mobility, maintain independence, and lead active, fulfilling lives.
FAQs:
How does physical therapy help with arthritis pain?
PT reduces pain by strengthening muscles, improving joint mobility, and using techniques like heat or massage.
Can physical therapy improve joint flexibility?
Yes, stretching and range-of-motion exercises help maintain and increase joint flexibility.
How often should I do physical therapy for arthritis?
Frequency varies; typically 1–3 times per week initially, plus daily home exercises.
Is physical therapy safe during arthritis flare-ups?
Yes, but exercises and intensity may be modified to avoid worsening symptoms.
Do I need a referral to see a physical therapist?
This depends on your location and insurance; check with your healthcare provider.