Introduction
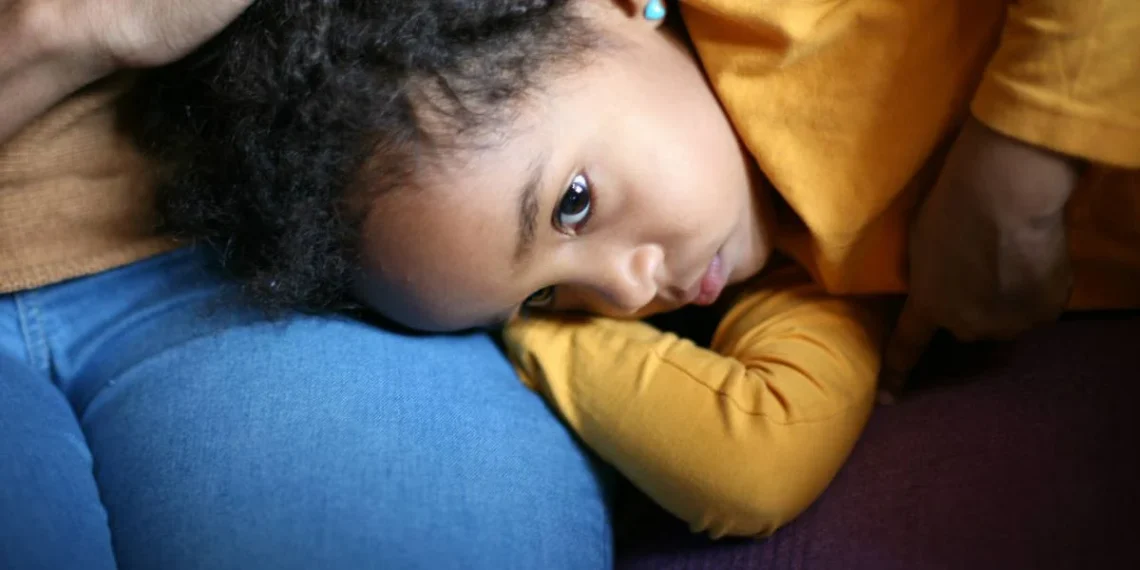
Abdominal pain is one of the most frequent complaints in children and a leading reason for pediatric doctor visits. While it is often caused by minor and temporary issues like indigestion or constipation, sometimes abdominal pain can signal something more serious that requires urgent medical care. Parents and caregivers often struggle to determine when to wait, when to treat symptoms at home, and when to seek professional help. Understanding the common causes of abdominal pain in children, as well as the warning signs of serious illness, can help ensure timely and appropriate care.
Common Causes of Abdominal Pain in Children
1. Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Caused by viral or bacterial infection.
- Symptoms: cramping, diarrhea, vomiting, low-grade fever.
- Usually self-limiting, but hydration is crucial.
2. Constipation
- A very common cause in school-aged children.
- Signs include infrequent, hard stools and straining.
- Pain often improves after passing stool.
3. Gas and Indigestion
- Can result from overeating, eating too quickly, or consuming gas-producing foods.
- Usually mild and resolves on its own.
4. Food Intolerance or Allergy
- Lactose intolerance, gluten sensitivity, or other food-related issues can cause bloating, cramps, and diarrhea.
- Allergic reactions may also involve skin rashes or breathing difficulties.
5. Stress and Anxiety
- Emotional stress, exams, or social issues may trigger abdominal pain without physical disease.
- Often called “functional abdominal pain.”
6. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Abdominal or lower belly pain, often with painful urination, urgency, or bedwetting.
- Needs medical evaluation and antibiotics.
7. Appendicitis
- Starts as vague pain near the belly button, later shifting to the lower right side.
- Pain worsens with movement, coughing, or jumping.
- Often associated with nausea, vomiting, and fever.
- Medical emergency.
8. Other Causes
- Hernias, gallstones (rare in children), inflammatory bowel disease, or even pneumonia can present as abdominal pain.
When to Worry: Red Flag Symptoms in Children
Parents should seek immediate medical care if their child has abdominal pain accompanied by:
- Severe, persistent, or worsening pain.
- Pain localized to one area (e.g., lower right abdomen in appendicitis).
- High fever.
- Repeated vomiting or inability to keep fluids down.
- Blood in vomit or stool (black, tarry, or bright red).
- Distended or swollen abdomen.
- Pain after an injury or trauma.
- Unexplained weight loss or poor growth.
- Pain that wakes the child from sleep regularly.
Supporting Your Child at Home
- Encourage rest and offer small, frequent sips of water or oral rehydration solution if vomiting or diarrhea is present.
- Avoid fatty, spicy, or heavy foods until symptoms improve.
- Use a warm compress for cramping discomfort.
- Keep a symptom diary noting the timing, location, triggers, and associated symptoms to help the doctor.
When to See a Doctor
- If abdominal pain persists beyond 24 hours without improvement.
- If red flag symptoms appear.
- If you suspect appendicitis or UTI.
- If the child appears very unwell, weak, or lethargic.
Conclusion
Abdominal pain in children is common and often harmless, but it can also signal serious illness that requires urgent attention. Parents should watch closely for red flag symptoms such as persistent severe pain, fever, vomiting, blood in stool, or localized pain. When in doubt, it’s always safer to have a child evaluated by a healthcare professional. Prompt recognition and treatment can prevent complications and provide peace of mind.
FAQs
1. Is stomach pain in children usually serious?
Most cases are mild, due to gas, indigestion, or constipation, but some may indicate conditions like appendicitis or infection.
2. How can I tell if my child’s abdominal pain is from appendicitis?
Pain starting near the belly button and moving to the lower right side, worsening with movement, often with fever and vomiting, suggests appendicitis.
3. Can stress really cause abdominal pain in kids?
Yes. Emotional stress or anxiety can trigger functional abdominal pain even without a physical cause.
4. When should I take my child to the ER for stomach pain?
If the pain is severe, persistent, associated with vomiting blood, blood in stool, high fever, or abdominal swelling, go to the ER.
5. What should I give my child for mild stomach pain?
Offer fluids, rest, and light food. Avoid strong painkillers without medical advice—acetaminophen may help if needed.