Introduction
Swelling, or edema, is a common occurrence during pregnancy, especially in the feet, ankles, and hands. Hormonal changes, increased blood volume, and fluid retention contribute to this condition. While mild swelling is usually harmless, sudden or severe edema can signal underlying complications such as preeclampsia.
This article explores the causes of swelling during pregnancy, normal patterns, warning signs, and strategies for relief.
Why Swelling Occurs During Pregnancy
1. Increased Blood Volume
- Blood volume increases by up to 50% during pregnancy to support the growing fetus.
- The body retains extra fluid, leading to mild swelling in extremities.
2. Hormonal Changes
- Progesterone relaxes blood vessel walls, which can cause fluid to leak into surrounding tissues.
3. Pressure from the Growing Uterus
- The uterus exerts pressure on pelvic veins, slowing blood return from the legs and causing fluid buildup.
4. Dietary and Lifestyle Factors
- High salt intake, long periods of standing or sitting, and dehydration can worsen swelling.
When Swelling is Normal
- Gradual swelling in the feet, ankles, and hands by the third trimester
- Mild puffiness that improves after rest or elevation of legs
- Swelling that comes on slowly and is symmetrical
- Often worse in hot weather or after standing all day
When Swelling Could Be a Concern
Seek medical attention if swelling is sudden, severe, or accompanied by other symptoms, such as:
- Swelling of the face, around the eyes, or hands
- Sudden weight gain over a few days
- Headaches, blurred vision, or dizziness
- Pain in the abdomen or upper right side
- Decreased urine output or high blood pressure
These may indicate preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication requiring urgent evaluation.
Tips to Manage Normal Pregnancy Swelling
1. Elevate Your Legs
- Raise legs above heart level several times a day to encourage fluid return.
- Lie on your side with pillows under your legs for comfort.
2. Wear Comfortable Shoes
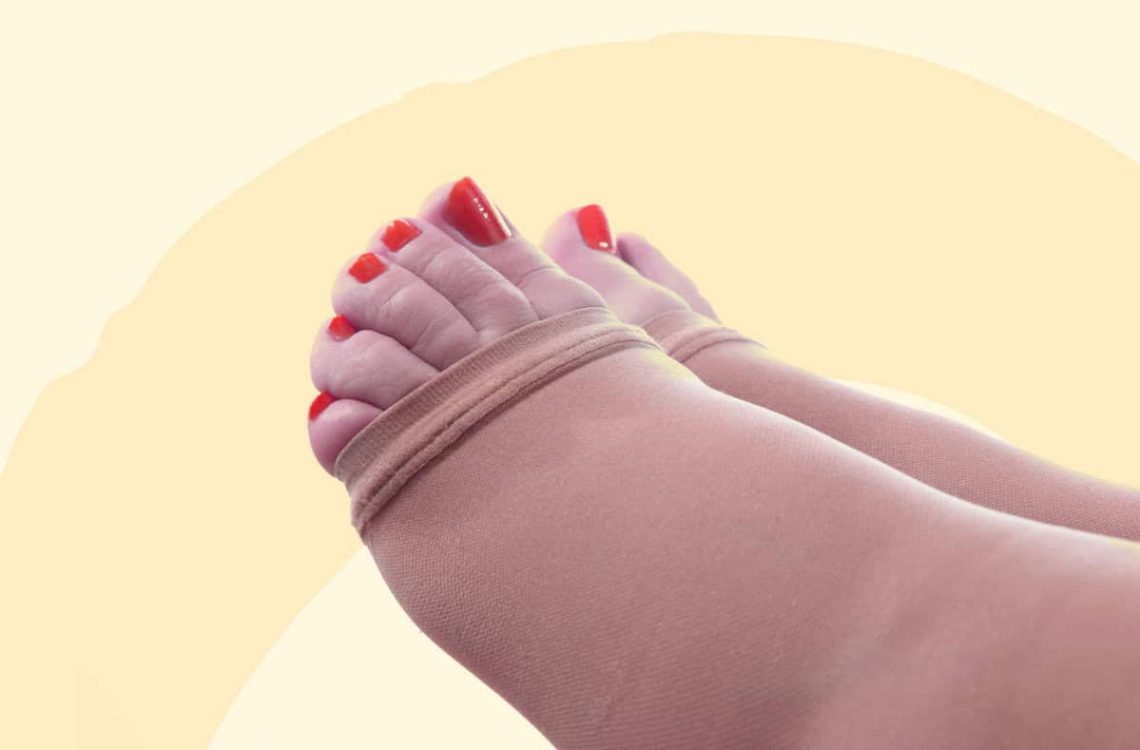
- Avoid tight socks or shoes that restrict blood flow.
- Consider compression stockings to reduce leg swelling.
3. Stay Active
- Walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga improve circulation.
- Avoid long periods of standing or sitting without moving.
4. Reduce Salt Intake
- Limit processed and salty foods, but maintain balanced electrolytes.
5. Stay Hydrated
- Drinking enough water can reduce fluid retention by supporting kidney function.
6. Avoid Hot Environments
- High temperatures can worsen swelling, so stay cool when possible.
When to Seek Medical Advice
- Rapid or severe swelling of hands, face, or feet
- Persistent headaches or vision changes
- High blood pressure readings
- Painful or red swollen legs (could indicate a blood clot)
- Any sudden changes in swelling pattern
Early detection is critical for conditions like preeclampsia, which can affect both mother and baby.
Conclusion
Mild swelling in pregnancy is common and usually harmless, caused by fluid retention, hormonal changes, and uterine pressure. Lifestyle strategies like leg elevation, moderate activity, proper footwear, hydration, and reduced salt intake can help manage edema. However, sudden, severe, or unusual swelling requires prompt medical evaluation to rule out complications such as preeclampsia. Awareness and early intervention ensure maternal comfort and fetal safety.
FAQs
1. Is swelling in pregnancy normal?
Yes, mild swelling in feet, ankles, and hands is common, especially in the third trimester.
2. How can I reduce swelling at home?
Elevate legs, wear comfortable shoes, stay active, limit salt intake, and stay hydrated.
3. When is swelling dangerous?
Sudden or severe swelling in hands, face, or around the eyes, especially with headache or vision changes, may indicate preeclampsia.
4. Can compression stockings help?
Yes, they improve blood circulation and reduce leg swelling.
5. Should I see a doctor for mild swelling?
Routine mild swelling is usually fine, but consult a healthcare provider if swelling is sudden, severe, or accompanied by other symptoms.