Introduction
Strep throat, caused by the bacterium Group A Streptococcus (GAS), is a common infection that usually resolves quickly with proper antibiotic treatment. However, if left untreated or inadequately managed, strep throat can lead to several serious complications. These complications include scarlet fever, peritonsillar abscess, and post-streptococcal kidney issues, among others.
Understanding these complications, their symptoms, and prevention is essential for timely treatment and avoiding long-term health problems. This article delves into the major complications associated with strep throat and how they can be managed.
What Is Strep Throat?
Strep throat is a contagious bacterial infection characterized by a sudden sore throat, pain when swallowing, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and red, inflamed tonsils often with white patches. It is confirmed via rapid strep test or throat culture and treated with antibiotics.
Common Complications of Strep Throat
1. Scarlet Fever
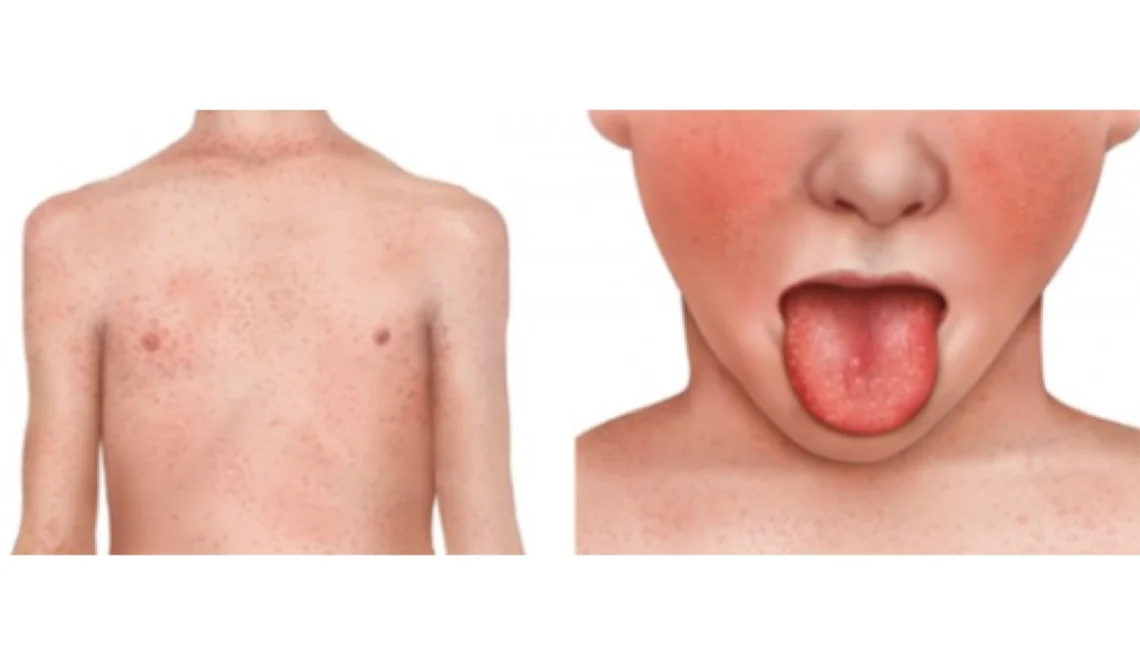
What Is Scarlet Fever?
Scarlet fever is a condition that occurs in some people with strep throat due to toxins released by certain strains of GAS bacteria. It mainly affects children aged 5 to 15.
Symptoms of Scarlet Fever
- Red rash: Appears within 1-2 days after the sore throat, starting on the chest and spreading over the body. It feels like sandpaper.
- Strawberry tongue: The tongue looks red and bumpy with a white coating early on.
- High fever: Often above 101°F (38.3°C).
- Flushed face with a pale area around the mouth.
- Headache, nausea, and vomiting may also occur.
Treatment and Prevention
- Scarlet fever is treated with antibiotics, usually penicillin or amoxicillin.
- Early treatment prevents spread and complications.
- Good hygiene practices reduce transmission.
2. Peritonsillar Abscess
What Is a Peritonsillar Abscess?
A peritonsillar abscess (quinsy) is a painful collection of pus near the tonsils, developing as a complication of untreated or severe tonsillitis or strep throat.
Symptoms
- Severe sore throat, often worse on one side.
- Difficulty opening the mouth (trismus).
- Swollen, red area near one tonsil.
- Fever and chills.
- Difficulty swallowing and muffled “hot potato” voice.
- Drooling due to painful swallowing.
Treatment
- Medical emergency requiring prompt attention.
- Drainage of the abscess by needle aspiration or surgery.
- Antibiotic therapy to clear infection.
- Pain management and supportive care.
3. Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
What Is PSGN?
PSGN is a kidney inflammation that can develop 1-3 weeks after a strep throat or skin infection. It results from an abnormal immune reaction to streptococcal bacteria.
Symptoms
- Dark, tea-colored or cola-colored urine (blood in urine).
- Swelling (edema) in the face, hands, feet, and abdomen.
- High blood pressure.
- Reduced urine output.
- Fatigue and general illness.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnosis involves urine tests, blood tests, and sometimes kidney biopsy.
- There is no specific antibiotic treatment once PSGN develops, but antibiotics may be given if strep infection is still present.
- Treatment focuses on managing symptoms:
- Controlling blood pressure.
- Reducing fluid retention.
- Close monitoring of kidney function.
- Most children recover fully, but severe cases may require hospitalization.
Other Possible Complications
- Rheumatic fever: A serious inflammatory condition affecting the heart, joints, skin, and brain that can occur weeks after untreated strep throat.
- Otitis media (ear infection)
- Sinusitis
- Scar tissue formation on tonsils
- Spread of infection to deeper neck tissues
How to Prevent Strep Throat Complications
Early Diagnosis and Treatment
- Prompt diagnosis through rapid strep testing or throat culture.
- Full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve early.
Follow-up Care
- Monitor symptoms after treatment.
- Return to the doctor if symptoms worsen or new symptoms appear.
Hygiene and Infection Control
- Wash hands frequently.
- Avoid sharing utensils, cups, or towels.
- Cover coughs and sneezes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical care if:
- Severe throat pain prevents swallowing or breathing.
- Swelling causes difficulty opening the mouth.
- High fever persists despite treatment.
- Urine becomes dark or decreases significantly.
- New rashes or joint pain develop after strep throat.
Conclusion
While strep throat is typically straightforward to treat, it can lead to serious complications like scarlet fever, peritonsillar abscess, and kidney inflammation if untreated. Early diagnosis and completing the full antibiotic course are crucial in preventing these outcomes. Awareness of symptoms and timely medical intervention can ensure effective treatment and recovery.
If you or your child shows signs of complications, do not delay seeking medical care.
FAQs:
What is scarlet fever, and how is it related to strep throat?
Scarlet fever is a rash-causing illness triggered by toxins from strep bacteria, often developing shortly after strep throat.
What are the signs of a peritonsillar abscess?
Severe one-sided throat pain, difficulty opening the mouth, muffled voice, fever, and swelling near the tonsils.
Can strep throat cause kidney problems?
Yes, it can lead to post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, an immune-related kidney inflammation occurring weeks after infection.
How can complications from strep throat be prevented?
Early diagnosis and completing the full antibiotic course are key to preventing complications.
When should I seek urgent medical care for strep throat?
If you experience severe throat pain, trouble swallowing or breathing, high fever, or dark urine, seek medical attention immediately.