Introduction
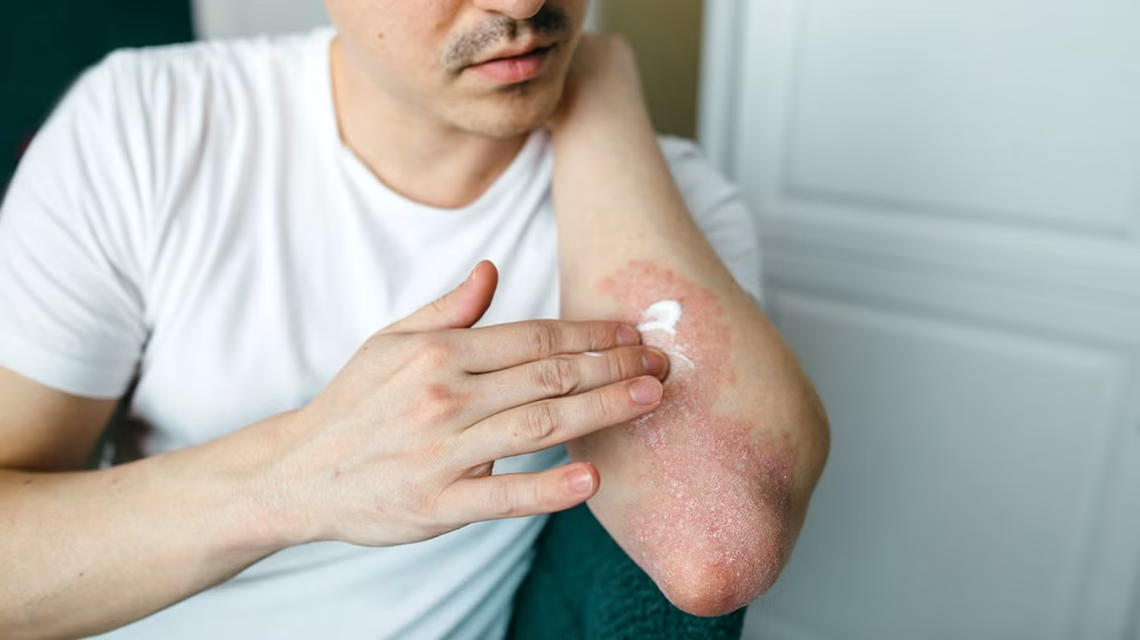
Psoriasis is a chronic, immune-mediated skin disorder characterized by rapid skin cell turnover, leading to thick, scaly plaques. It affects about 2–3% of the global population and can range from mild, localized patches to widespread, severe involvement.
Beyond physical symptoms, psoriasis can impact mental health, self-esteem, and quality of life. Understanding the different types of psoriasis and treatment options helps manage symptoms effectively and reduce flare-ups.
Types of Psoriasis
1. Plaque Psoriasis (Most Common)
- Appearance: Raised, red patches with silvery-white scales
- Common Locations: Scalp, elbows, knees, lower back
- Symptoms: Itching, burning, cracking of skin
2. Guttate Psoriasis
- Appearance: Small, drop-like red spots
- Common Triggers: Often triggered by infections such as strep throat
- Common Locations: Trunk, arms, legs
3. Inverse Psoriasis
- Appearance: Smooth, shiny red patches
- Common Locations: Skin folds (armpits, groin, under breasts)
- Notes: Often worsened by friction and sweating
4. Pustular Psoriasis
- Appearance: White pus-filled blisters surrounded by red skin
- Types: Localized (palms/soles) or generalized
- Symptoms: Painful, may be accompanied by fever
5. Erythrodermic Psoriasis
- Appearance: Widespread redness with scaling, affecting most of the body
- Symptoms: Severe itching, pain, systemic symptoms (fever, chills)
- Urgency: Requires immediate medical attention
Treatment Approaches
Psoriasis management depends on type, severity, and location of lesions. Treatments aim to reduce inflammation, slow skin cell turnover, and relieve symptoms.
1. Topical Treatments
Ideal for mild to moderate psoriasis or localized plaques.
- Corticosteroid creams and ointments: Reduce inflammation and itching
- Vitamin D analogs (calcipotriol, calcitriol): Slow skin cell growth
- Coal tar preparations: Reduce scaling and inflammation
- Moisturizers and emollients: Maintain skin hydration, reduce itching and cracking
- Salicylic acid: Helps remove scales for easier absorption of other topicals
2. Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
Used for moderate to severe psoriasis or when topical treatments are insufficient.
- UVB therapy: Slows skin cell growth, reduces inflammation
- PUVA (psoralen + UVA): Combines medication with UVA exposure
- Home light therapy units are available under medical supervision
- Benefits: Effective for widespread psoriasis with fewer systemic side effects than medications
- Risks: Skin aging, sunburn, increased risk of skin cancer with long-term use
3. Systemic and Biologic Therapies
For severe or resistant psoriasis, systemic treatment may be required.
Traditional Systemic Medications
- Methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin
- Reduce immune system overactivity and inflammation
- Requires regular monitoring for liver and kidney function
Biologic Therapies
- Target specific immune pathways (TNF-alpha, IL-12/23, IL-17)
- Examples: Adalimumab, Etanercept, Secukinumab, Ustekinumab, Dupilumab
- Advantages: Highly effective for moderate-to-severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
- Monitoring: Increased risk of infections; requires screening before use
Lifestyle Measures
- Moisturize regularly to reduce dryness and scaling
- Avoid triggers: stress, alcohol, smoking, certain medications
- Maintain healthy weight to reduce severity and improve response to treatment
- Protect skin from injury and sunburn (Koebner phenomenon can worsen psoriasis)
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition with multiple types and varying severity. Management includes topical therapies for mild cases, light therapy for moderate disease, and systemic or biologic therapies for severe cases. A combined approach of medical treatment and lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce flare-ups, improve symptoms, and enhance quality of life.
FAQs
1. What is the most common type of psoriasis?
Plaque psoriasis, characterized by thick, scaly patches.
2. Can psoriasis go away completely?
Psoriasis is chronic, but symptoms can be well-controlled with treatment.
3. Are biologics safe?
Biologics are generally safe but require monitoring for infections and other side effects.
4. Can stress trigger psoriasis flare-ups?
Yes, stress is a known trigger for worsening psoriasis.
5. Is light therapy effective?
UVB and PUVA therapies are effective for moderate-to-severe psoriasis, but must be done under supervision to prevent skin damage.