Introduction
Pimples can be painful, inflamed, and hard to ignore—especially when they appear unexpectedly. In recent years, pimple patches, also known as hydrocolloid bandages, have become one of the most popular and effective spot treatments for reducing inflammation, absorbing pus, and speeding up healing. These tiny stickers may look simple, but they rely on medical-grade technology originally used for wound care.
This article explains what pimple patches are, how they work, their different types, when to use them, and important safety tips. Whether you’re dealing with an overnight breakout or want a cleaner way to manage pimples, hydrocolloid patches offer a gentle, science-backed solution.
What Are Pimple Patches?
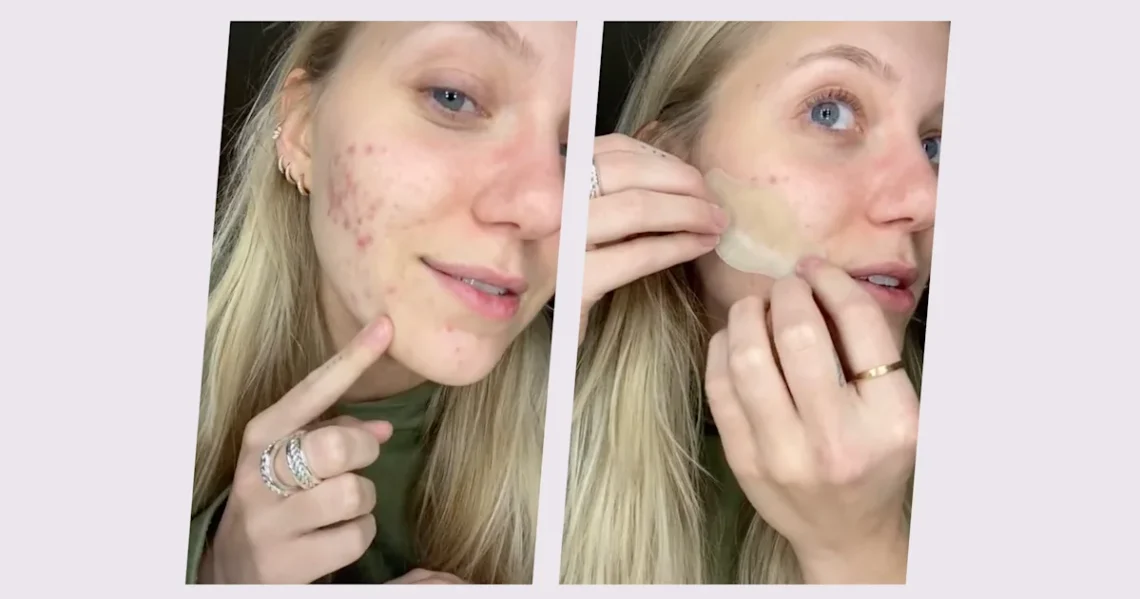
Pimple patches are small adhesive stickers designed to cover and treat acne spots. Most are made from hydrocolloid, a moisture-absorbing gel commonly used in hospitals for healing wounds and blisters.
They are designed to:
- Protect the pimple
- Absorb fluid (pus, oil)
- Reduce inflammation
- Prevent touching or squeezing
- Promote faster healing
How Hydrocolloid Technology Works
1. Absorbs Fluid from the Pimple
Hydrocolloid material pulls out pus, oil, and impurities from the acne lesion. As it absorbs fluid, the patch turns white and puffy, showing it has extracted gunk from the pimple.
This is especially effective for:
- Whiteheads
- Popped pimples
- Surface-level pimples
2. Creates a Moist Healing Environment
Hydrocolloid keeps the skin moist, which:
- Speeds up healing
- Prevents scabbing
- Reduces the chance of dark marks (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation)
3. Protects Against Bacteria and Dirt
A patch acts as a physical barrier, preventing:
- Bacteria from entering
- Dirt from worsening inflammation
- Fingers from touching and spreading germs
This stops the pimple from getting infected or inflamed.
4. Reduces Picking and Popping
A major cause of acne scars is picking. Patches prevent this by covering the pimple and reducing the urge to touch it.
5. Minimizes Redness and Swelling
By keeping the area moisturized and protected, swelling gradually decreases, making the pimple look smaller.
Types of Pimple Patches
1. Pure Hydrocolloid Patches
These contain no active ingredients and simply absorb fluid.
Best for whiteheads or popped pimples.
2. Hydrocolloid + Active Ingredients
Some patches include ingredients like:
- Salicylic acid
- Tea tree oil
- Niacinamide
- Centella asiatica
These help reduce inflammation and unclog pores in early-stage pimples.
3. Microdart / Microneedle Patches
These patches have tiny dissolving micro-needles that deliver active ingredients deeper into the skin.
Suitable for:
- Early-stage pimples
- Deep, painful bumps
When to Use Pimple Patches
Best For:
- Whiteheads
- Pus-filled pimples
- Popped pimples
- Small inflamed bumps
- Preventing picking or touching
Not Effective For:
- Deep cysts
- Nodular acne
- Blackheads
- Severe acne
Hydrocolloid cannot reach deep inflammation beneath the skin.
How to Use Pimple Patches Correctly
Step-by-Step
- Clean the area with a gentle cleanser
- Pat dry (patches won’t stick on damp skin)
- Apply the patch directly on the pimple
- Keep it on for 6–12 hours or until it turns white
- Remove gently and replace if needed
Avoid applying thick creams under the patch—this stops it from sticking properly.
Benefits of Using Pimple Patches
1. Fast Healing
They accelerate healing by creating the ideal environment for skin repair.
2. Prevent Scars and Dark Marks
By stopping picking and keeping the wound moist, they reduce hyperpigmentation risks.
3. Hygienic and Safe
Hydrocolloid is widely used in medical wound care and is gentle enough for most skin types.
4. Easy to Use
Just apply and forget—great for overnight use.
5. Invisible Options
Clear or ultra-thin patches allow daytime wear and can even be worn under makeup.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Applying over unclean or oily skin
- Using on deep cystic acne (won’t work)
- Touching or pressing the patch repeatedly
- Pulling it off aggressively
- Applying after heavy moisturizers
- Using after harsh exfoliants (skin may be irritated)
Side Effects and Risks
Pimple patches are generally safe, but may cause issues if:
- Skin is extremely sensitive
- You’re allergic to adhesives
- You apply to broken, painful skin
If redness, itching, or irritation occurs, discontinue use.
Combining Patches With Other Acne Treatments
Before Applying the Patch:
- Cleanser
- Toner (alcohol-free)
After Removing the Patch:
- Niacinamide
- Hydrating products
- Sunscreen in the morning
Avoid:
- Retinoids
- Exfoliating acids
- Benzoyl peroxide before applying (do these at night when not using patches)
Conclusion
Pimple patches and hydrocolloid bandages offer a gentle, effective, and scientifically backed method for managing whiteheads, inflamed pimples, and newly popped blemishes. By absorbing fluid, preventing infection, and stopping the urge to pick, they promote faster healing and reduce the risk of scarring. Although not suitable for deep or cystic acne, they’re an excellent addition to any skincare routine for surface-level breakouts.
Used correctly, pimple patches can be a simple but powerful tool to help keep your skin clearer, calmer, and healthier.
FAQs
1. How long should I leave a pimple patch on?
6–12 hours, or until it turns white.
2. Do pimple patches work on cystic acne?
No, hydrocolloid cannot reach deep inflammation.
3. Can I put a pimple patch on after popping a pimple?
Yes, it helps absorb fluid and speeds healing.
4. Can I wear a pimple patch under makeup?
Yes—thin, clear patches are designed for daytime wear.
5. Do pimple patches prevent scars?
They help reduce scabbing and picking, which lowers the chance of dark marks and scars.