Introduction
Hormonal pimples are a frustrating yet extremely common type of acne that affects both teenagers and adults. These breakouts are closely linked to fluctuations in hormones—especially androgens—which can increase oil (sebum) production and trigger inflammation. Unlike occasional pimples caused by makeup or sweat, hormonal breakouts follow predictable patterns and often return in the same areas month after month.
Understanding how hormonal pimples develop, when they occur, and how to manage them can help you take control of your skin and reduce flare-ups. This article explains the hormonal cycle, common triggers, treatment options, lifestyle changes, and prevention strategies.
Introduction: Why Hormonal Pimples Happen
Hormones play a major role in regulating skin health. When hormonal levels shift—even slightly—they can cause:
- Increased oil production
- Enlarged pores
- clogged hair follicles
- Inflammation
- Bacterial growth under the skin
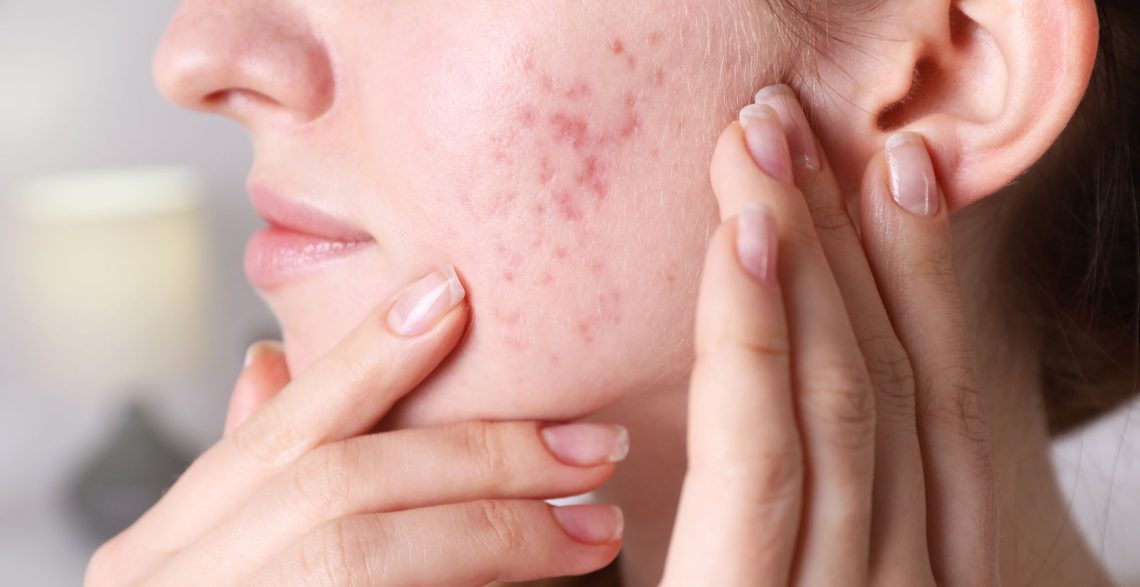
These changes make the skin more prone to painful, deep pimples, often concentrated around the lower face.
Hormonal pimples are especially common during:
- Puberty
- Menstrual cycles
- Pregnancy
- Postpartum period
- Perimenopause
- High-stress periods
- Stopping or starting birth control
While hormonal acne can be stubborn, the right management plan can significantly reduce flare-ups and improve skin clarity.
1. The Hormonal Cycle and Pimples: What’s the Connection?
How Hormones Trigger Breakouts
Hormonal pimples occur when certain hormones—especially androgens—increase activity in the oil glands. This leads to:
- Overproduction of sebum
- Clogged follicles
- Bacterial buildup
- Irritation and swelling
Androgens such as testosterone influence both men and women, but women experience more noticeable fluctuations.
Where Hormonal Pimples Usually Appear
Hormonal breakouts often show up in these areas:
- Chin
- Jawline
- Lower cheeks
- Neck
- Around the mouth
- Sometimes the chest and back
These regions are more sensitive to hormonal oil production.
2. The Menstrual Cycle: Week-by-Week Skin Changes
Female hormonal cycles create predictable acne patterns. Here’s how each phase affects the skin:
Week 1 – Menstruation
- Estrogen levels are low.
- Skin may feel dry, dull, and sensitive.
- Some pimples from the premenstrual week may still be healing.
Week 2 – Follicular Phase
- Estrogen rises.
- Skin looks clearer, softer, and more radiant.
- Oil production stabilizes.
Week 3 – Ovulation
- Estrogen and luteinizing hormone peak.
- Skin remains generally clear.
- Increased pheromonal activity may cause slight oiliness.
Week 4 – Premenstrual Week
This is when most hormonal pimples appear.
- Progesterone increases and thickens the skin.
- Oil glands become more active.
- Pores clog easily.
- Inflammation increases.
- Painful chin or jawline cysts may form.
These breakouts often show up just 3–7 days before the period begins.
3. Other Causes of Hormonal Pimples
Hormonal acne isn’t limited to menstrual cycles. Other triggers include:
✔ Stress
Stress increases cortisol, which stimulates oil glands.
✔ Pregnancy
Hormonal shifts vary, causing either clear or breakout-prone skin.
✔ Postpartum Fluctuations
Hormone crashes after birth often lead to chin and jawline breakouts.
✔ Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
High androgen levels are a key feature, making acne more persistent.
✔ Birth Control (Starting or Stopping)
Hormonal contraceptives can improve or worsen acne depending on the formulation.
✔ Perimenopause
Declining estrogen allows androgens to have more impact, triggering adult acne.
4. Characteristics of Hormonal Pimples
Unlike regular surface-level pimples, hormonal ones often:
- Are deep, painful, and cyst-like
- Stay under the skin for days or weeks
- Appear in the same spots repeatedly
- Become inflamed and tender
- Leave dark marks or scars
They are less likely to come to a full “whitehead,” making them difficult to squeeze (and dangerous to pop).
5. Managing Hormonal Pimples: Treatment Options
A. Skincare-Based Treatments
1. Salicylic Acid
- Unclogs pores
- Best for preventing buildup
- Use daily (0.5%–2%)
2. Benzoyl Peroxide
- Kills acne-causing bacteria
- Reduces inflammation
- Ideal for occasional hormonal flare-ups
- Use as a spot treatment
*3. Retinoids (Adapalene)
- Regulate cell turnover
- Reduce clogged pores
- Best for long-term management
- Helps with dark marks
*Available OTC (adapalene 0.1%) or via prescription (tretinoin).
4. Niacinamide
- Reduces inflammation
- Controls oil
- Strengthens skin barrier
B. Prescription Treatments
1. Spironolactone
A widely used treatment for adult female hormonal acne.
- Blocks androgen receptors
- Reduces oil production
- Works best for jawline/chin pimples
2. Prescription Retinoids (Tretinoin, Tazarotene)
- Stronger than OTC retinoids
- Clear deeper pimples
- Smooth texture and fade marks
3. Hormonal Birth Control Pills
Combo pills can regulate hormones and reduce acne.
4. Oral Antibiotics
Short-term use for severe inflammation.
5. Isotretinoin (Accutane)
Reserved for chronic, scarring, or severe hormonal acne.
6. Lifestyle and Habit-Based Management
Stress Management
- Meditation
- Exercise
- Deep breathing
- Journaling
Reduces cortisol-related flare-ups.
Balanced Diet
Avoid excessive:
- High sugar
- Dairy (if sensitive)
- Fast food
- Refined carbs
Include:
- Omega-3 rich foods
- Fiber
- Hydration
- Antioxidant-rich fruits & veggies
Sleep
Poor sleep increases hormonal imbalance and inflammation.
Avoid Touching and Picking
Prevents deeper inflammation and scarring.
Clean Pillowcases & Makeup Tools
Reduces bacterial transfer.
Limit Heavy Makeup
Choose non-comedogenic formulas.
7. Prevention Strategies for Monthly Breakouts
1. Start Retinoids Before Your Premenstrual Week
Helps prevent clogged pores.
2. Use Salicylic Acid Cleansers During Week 4
Controls excess oil.
3. Apply Spot Treatments Early
At the first sign of soreness under the skin.
4. Use Oil-Free Sunscreen
Prevents product-induced clogging.
5. Track Your Cycle
Helps you anticipate breakouts and adjust your routine.
Conclusion
Hormonal pimples can be persistent, predictable, and painful—but they are also highly manageable. By understanding your hormonal cycle, recognizing triggers, and following consistent skincare and lifestyle strategies, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of breakouts.
Whether you choose over-the-counter treatments, prescription medications, or hormonal therapies, a personalized and proactive approach often brings the best results. With patience and the right routine, long-term improvement is absolutely possible.
FAQs
1. Are hormonal pimples preventable?
Yes—while not entirely avoidable, breakouts can be minimized with consistent skincare and lifestyle management.
2. Why do hormonal pimples appear mostly on the chin and jawline?
These areas have more hormone-sensitive oil glands, making them prone to deep pimples.
3. Does birth control help hormonal acne?
Some combination pills reduce acne, but results vary by individual and pill type.
4. How long do hormonal pimples usually last?
Typically 5–10 days, but deeper cysts may last weeks if not treated.
5. Can diet affect hormonal pimples?
Yes. High sugar, dairy, and processed foods may worsen acne in some people.