Introduction
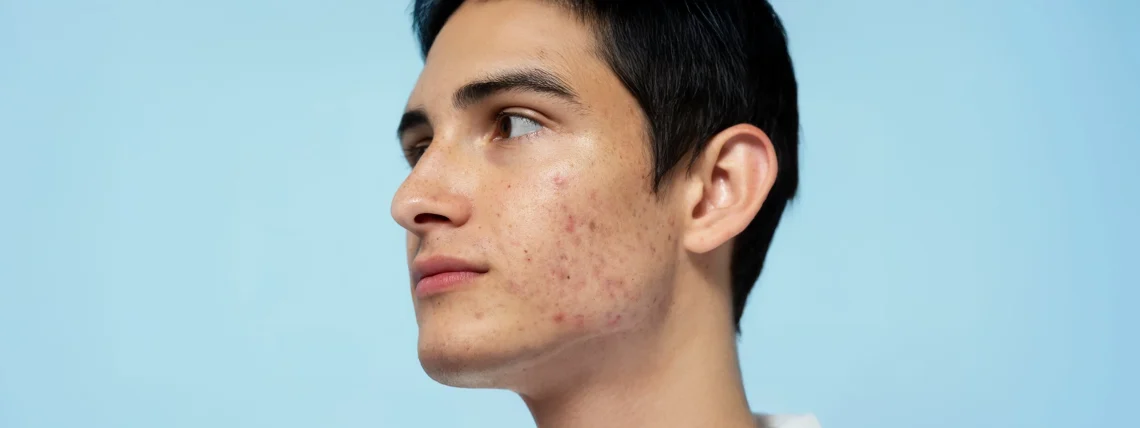
Acne is more than a skin-deep problem. While clogged pores, oil production, and bacteria are involved, many internal factors—including stress, gut health, diet, and micronutrient imbalances—can influence how often you break out and how your skin heals. A holistic approach doesn’t replace medical acne treatments but supports the body from within, helping reduce inflammation, balance hormones, and build skin resilience.
This comprehensive article explores three major holistic pillars—stress management, gut health, and supplements—that play a scientifically supported role in clearer, healthier skin.
Understanding Holistic Acne Management
A holistic approach focuses on the whole body, not just the skin. Acne can be affected by:
- Hormones
- Stress
- Gut health
- Diet
- Immune system
- Sleep patterns
- Inflammation
- Micronutrient levels
These internal factors can trigger oily skin, worsen inflammation, and slow healing—making breakouts more persistent.
Holistic strategies work best when combined with topical treatments such as retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and salicylic acid.
1. Stress and Acne
How Stress Causes Breakouts
When you’re stressed, your body produces:
Cortisol
- Increases oil (sebum) production
- Triggers inflammation
- Weakens skin barrier function
Androgens
Stress stimulates adrenal glands to release androgens, which worsen:
- Chin/jawline acne
- Cystic breakouts
- Hormonal flares
Inflammation
Chronic stress raises inflammation throughout the body, making acne lesions more severe and red.
Signs Your Acne Is Stress-Related
- Breakouts during exams, heavy workload, emotional stress
- More pimples on jawline, chin, and neck
- Acne flares during sleep deprivation
- Acne worsens during PMS due to combined stress + hormonal shifts
Holistic Stress-Management Techniques
1. Mindfulness & Meditation
Helps regulate cortisol and calm the nervous system.
Just 10 minutes a day can reduce stress-related breakouts.
2. Breathwork
Slow, deep breathing reduces cortisol and oil production.
3. Exercise
- Boosts blood circulation
- Lowers stress hormones
- Improves insulin sensitivity
But avoid overtraining, which can increase cortisol.
4. Yoga & Stretching
Balances the nervous system, lowers inflammation, and improves hormonal stability.
5. Sleep Optimization
Aim for 7–9 hours/night. Poor sleep increases:
- Oil production
- Inflammation
- Healing time
6. Healthy Boundaries
Work pressure, emotional stress, and burnout contribute heavily to adult acne—setting limits protects both mental and skin health.
2. Gut Health and Acne
The Gut–Skin Axis
Your skin reflects what’s going on inside your gut. A disrupted gut can lead to:
- Increased systemic inflammation
- Hormonal imbalance
- Poor skin healing
- Compromised immunity
Acne-prone individuals often show signs of:
- Dysbiosis (bad gut bacteria overgrowth)
- Leaky gut
- Low microbial diversity
How Gut Issues Affect Acne
1. Inflammation
Gut imbalances trigger inflammatory molecules that worsen acne severity.
2. Insulin and Blood Sugar
Poor gut health increases insulin resistance, which:
- Raises IGF-1 (growth hormone)
- Increases oil production
- Worsens acne
3. Hormonal Balance
The gut helps metabolize hormones. If gut flora is imbalanced, androgen levels can spike, causing breakouts.
4. Nutrient Absorption
A damaged gut can lead to deficiencies in:
- Zinc
- Vitamin D
- B vitamins
- Omega-3s
All crucial for healthy skin.
Signs Your Acne Is Linked to Poor Gut Health
- Bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea
- Food sensitivities
- Fatigue
- Brain fog
- Eczema or rosacea
- Acne worsens after certain foods (sugar, dairy, gluten)
Gut-Friendly Approaches for Clearer Skin
1. Eat More Whole Foods
Include:
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Lean proteins
- Whole grains
- Healthy fats
These reduce inflammation and support a diverse microbiome.
2. Include Fermented Foods
These add probiotics naturally:
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Kimchi
- Sauerkraut
- Kombucha
- Miso
3. Increase Prebiotic Fiber
Feeds beneficial bacteria:
- Oats
- Bananas
- Onions
- Garlic
- Beans
- Asparagus
4. Reduce Sugar and Refined Carbs
High-glycemic foods spike insulin and worsen acne.
5. Watch Dairy Intake
Some people are sensitive to milk proteins and hormones. Try reducing:
- Skim milk
- Whey protein
- Excess cheese
6. Treat Digestive Disorders
If you have IBS, SIBO, or food intolerances, addressing them can dramatically improve skin.
3. Supplements for Acne
Supplements should support medical treatment—not replace it. Always consult a healthcare professional, especially if pregnant, breastfeeding, or on medication.
Key Supplements Backed by Science
1. Zinc
One of the most effective supplements for acne.
Benefits:
- Reduces inflammation
- Regulates oil production
- Helps heal acne lesions
Common dose: 15–30 mg/day
(Do not exceed 40 mg without medical guidance.)
2. Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Fish Oil or Algal Oil)
Omega-3s reduce inflammation and stabilize hormones.
Benefits:
- Improves inflammatory acne
- Supports gut health
- Enhances skin healing
3. Vitamin D
Low vitamin D is linked to acne and inflammation.
Helps with:
- Immune regulation
- Skin healing
- Lower inflammation
4. Probiotics
Support gut-skin axis and reduce systemic inflammation.
Beneficial strains:
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus
- Bifidobacterium longum
- Lactobacillus paracasei
5. Myo-Inositol (especially for women with PCOS)
Balances insulin levels and reduces androgen-driven acne.
Useful for:
- Irregular cycles
- PCOS
- Hormonal acne
6. Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
May reduce oil production in some people.
7. Evening Primrose Oil
Helps regulate hormones and inflammation.
Useful in:
- PMS-related acne
- Perimenopause acne
8. DIM (Diindolylmethane)
Supports estrogen metabolism.
Helpful for:
- Chin/jawline acne
- Hormonal imbalance
- Acne flares during cycle
Avoid without medical supervision.
Supporting Lifestyle Practices
1. Hydration
Helps flush toxins and supports skin healing.
2. Movement
Boosts circulation, reduces stress, and improves gut motility.
3. Sun Protection
Prevents PIH (dark marks) and supports skin barrier health.
4. Clean Skincare Routine
Use:
- Non-comedogenic products
- Gentle cleansers
- Lightweight moisturizers
When Holistic Approaches Are Not Enough
Seek medical or dermatological care if:
- Acne is cystic or very painful
- Scarring is developing
- Acne affects confidence or mental health
- Over-the-counter + holistic methods aren’t helping
Medication may be needed alongside holistic support.
Conclusion
Holistic acne management focuses on the internal factors that influence skin health—stress hormones, gut function, and micronutrient balance. By lowering stress, supporting the gut, optimizing nutrition, and using targeted supplements, many people experience significant improvements in breakouts and skin clarity. While holistic strategies may not replace prescription treatments, they complement them powerfully and address underlying causes that topical products alone cannot fix.
Combining internal and external approaches creates the strongest foundation for long-term acne control and healthier skin from the inside out.
FAQs
1. Can stress alone cause acne?
Yes—stress increases cortisol and androgens, which trigger inflammation and oil production.
2. Does gut health really affect acne?
Absolutely. Poor gut health increases inflammation and hormone imbalance, both linked to acne.
3. What supplements are best for acne?
Zinc, omega-3s, probiotics, vitamin D, and myo-inositol (for PCOS) are most effective.
4. Should I stop dairy if I have acne?
Some people are sensitive to dairy—especially skim milk. A 4-week trial dairy reduction can help identify triggers.
5. Can holistic approaches replace medical treatments?
No—they work best alongside proper dermatological care, especially for moderate to severe acne.