Introduction
Permethrin is a synthetic chemical that belongs to the class of insecticides known as pyrethroids. It is widely used to control various types of pests, including head lice, scabies mites, and other external parasites. Permethrin is also employed in agriculture and veterinary medicine for pest control. It works by disrupting the nervous system of insects, leading to paralysis and death. Permethrin is available in both prescription and over-the-counter formulations, including creams, lotions, shampoos, and sprays. Its use is considered safe when applied according to guidelines, but it is essential to be aware of potential side effects and precautions.
What is Permethrin?
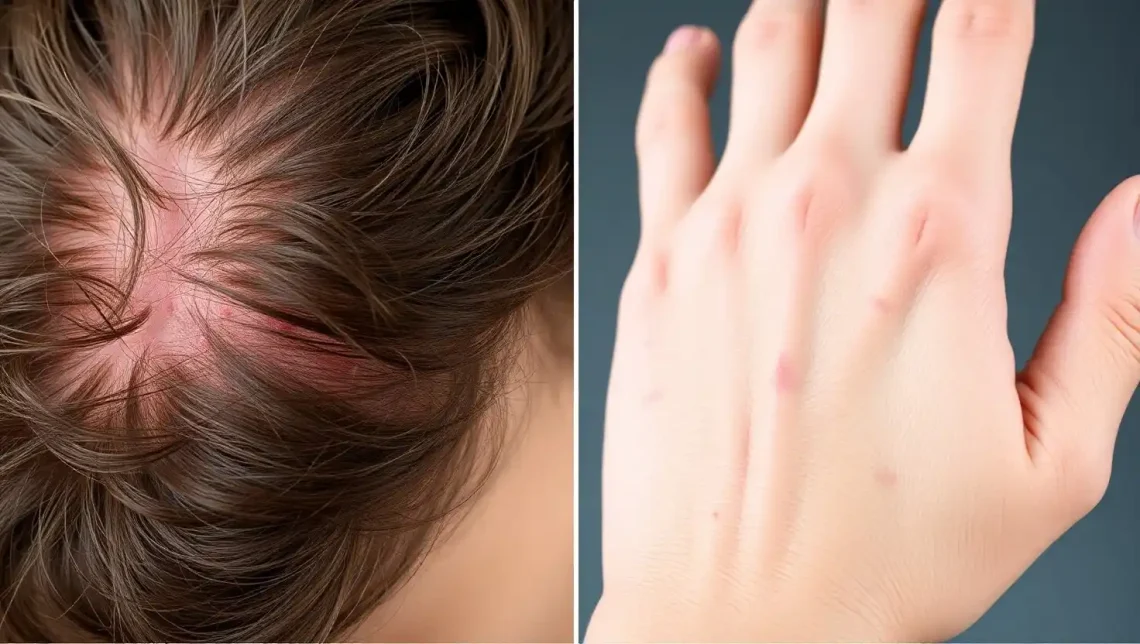
Permethrin is a synthetic version of pyrethrum, a natural insecticide derived from chrysanthemum flowers. It is primarily used to treat infestations of lice, scabies, and other parasitic infections. Permethrin is available in different strengths, with common concentrations being 1% for head lice treatment and 5% for scabies. It is designed to be applied topically to the skin or hair, where it exerts its effects on the pests by interfering with their nervous system.
Permethrin works by causing the insect’s nerve cells to become overstimulated, which leads to paralysis and eventual death of the insect. It is effective against a wide range of pests, including both adult and juvenile forms of lice and scabies mites.
How It Works
Permethrin works by targeting the nervous system of insects and other arthropods. When applied to the skin or hair, it binds to sodium channels in the insect’s nerve cells. This binding causes the channels to remain open, leading to an uncontrolled influx of sodium ions. As a result, the insect’s nerve cells become overstimulated, which causes paralysis and death.
In humans, permethrin has low toxicity due to its selective action on insect nerve cells and minimal absorption through the skin. This makes it an effective treatment for external parasitic infestations like lice and scabies.
Common Uses
Permethrin is primarily used to treat parasitic infections caused by insects or mites. Some of the most common uses include:
1. Head Lice Treatment:
Permethrin is often used in the treatment of head lice. A 1% permethrin lotion or shampoo is applied to the scalp and hair, where it works to kill adult lice and their eggs (nits). A second treatment may be required after 7 to 10 days to ensure that any newly hatched lice are also eliminated.
2. Scabies Treatment:
Permethrin 5% cream is the first-line treatment for scabies, a condition caused by an infestation of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. The cream is applied to the entire body, from the neck down, and left on for 8 to 14 hours before being washed off. A second application is often recommended a week later.
3. Pesticide in Agriculture:
Permethrin is also used as an insecticide in agriculture to protect crops from a variety of pests, including mosquitoes, flies, and beetles. It is commonly used in the treatment of grains, vegetables, and fruit crops.
4. Veterinary Use:
In veterinary medicine, permethrin is used to treat pets for external parasites such as fleas and ticks. It is often found in shampoos and sprays designed for animals.
Benefits and Effectiveness
Permethrin is considered highly effective for treating lice and scabies infestations. Here are the key benefits of using permethrin:
1. Effectiveness in Treating Lice and Scabies:
Permethrin is one of the most effective treatments for head lice and scabies, with studies showing it kills lice and mites on contact. It is often the first-line treatment recommended by healthcare providers due to its proven efficacy.
2. Low Toxicity in Humans:
Permethrin has a low toxicity profile when used as directed. It is generally well-tolerated by most individuals, with minimal systemic absorption. This makes it safer for use in children and adults, as long as the instructions are followed carefully.
3. Convenient Application:
Permethrin is available in various forms, including shampoos, creams, and lotions, making it convenient to apply for different types of infestations. Its ease of use contributes to its popularity in treating parasitic infections.
4. Long-Lasting Results:
Permethrin is effective in eliminating adult lice and scabies mites after just one application, though a second treatment may be necessary to eliminate newly hatched pests. This reduces the need for repeated treatments and helps to break the cycle of reinfestation.
Side Effects and Risks
While permethrin is generally safe when used according to instructions, there are some potential side effects and risks associated with its use.
Common Side Effects:
- Skin Irritation: The most common side effect of permethrin is mild skin irritation, such as redness, itching, or a rash at the site of application.
- Burning or Stinging Sensation: Some people may experience a burning or stinging sensation when applying permethrin, particularly if there are broken or irritated areas on the skin.
- Dryness or Peeling: In some cases, permethrin can cause dryness or peeling of the skin.
Serious Side Effects (Rare):
- Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, individuals may experience severe allergic reactions, such as swelling, hives, or difficulty breathing. If any signs of an allergic reaction occur, medical attention should be sought immediately.
- Neurological Effects: Although uncommon, excessive use or improper application of permethrin can lead to neurological symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, or seizures.
Overuse and Toxicity:
- Overuse of permethrin or improper application can lead to toxicity, especially if it is absorbed into the bloodstream in large quantities. This is most likely to occur if the product is applied too frequently or to broken skin.
Dosage and Administration
For Head Lice:
- Form: 1% permethrin lotion or shampoo.
- Instructions: Apply to the scalp and hair, leaving it on for 10 minutes before rinsing. Repeat the treatment after 7 to 10 days if necessary to kill any newly hatched lice.
For Scabies:
- Form: 5% permethrin cream.
- Instructions: Apply the cream to the entire body, from the neck down, and leave it on for 8 to 14 hours before washing it off. A second application may be needed a week later.
For Pesticide Use:
- Permethrin formulations used for pest control in agriculture and veterinary applications should follow specific guidelines based on the pest being targeted and the type of crop or animal being treated. These instructions are available on the product packaging.
Strength and Available Forms
Permethrin is available in various strengths and forms, depending on its intended use:
- 1% Lotion/Shampoo: For head lice treatment.
- 5% Cream: For scabies treatment.
- Sprays and Aerosols: For agricultural and veterinary use.
- Shampoos/Sprays for Pets: For flea and tick control.
Drug Interactions
Permethrin has a low potential for drug interactions due to its minimal absorption into the bloodstream. However, caution should be exercised if using other topical products, especially those containing strong irritants or other insecticides. Combining permethrin with other pesticides or topical medications could increase the risk of skin irritation or toxicity.
Warnings and Precautions
- For External Use Only: Permethrin is intended for topical use only. It should not be ingested, inhaled, or applied to mucous membranes such as the eyes or mouth.
- Not for Use on Broken Skin: Permethrin should not be applied to areas of the skin that are severely damaged, as it may be absorbed into the bloodstream and cause toxicity.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: While permethrin is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, it should be used with caution and only if necessary. Consult a healthcare provider before using permethrin during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
- Children: Permethrin is safe for use in children older than 2 months when used as directed, but it should not be used on infants under 2 months unless specifically recommended by a healthcare provider.
Cost and Availability
Permethrin is available over-the-counter for the treatment of head lice in 1% formulations, while the 5% cream for scabies requires a prescription in most countries. The cost varies by formulation and brand, with typical prices ranging from $10 to $30 for a one-month supply of NRT products. Permethrin is widely available at pharmacies and online.
How to Use It Properly
To ensure the proper use of permethrin:
- Read Instructions Carefully: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions regarding dosage, application, and duration of use.
- Do Not Overuse: Overuse or improper application can lead to toxicity or skin irritation.
- Avoid Contact with Eyes and Mucous Membranes: If permethrin comes into contact with the eyes, rinse thoroughly with water. Avoid using permethrin on mucous membranes.
- Wash Hands After Application: Always wash your hands after applying permethrin to avoid accidental contact with your eyes or other sensitive areas.
- Monitor for Side Effects: If you experience severe irritation, allergic reactions, or other unusual symptoms, seek medical advice immediately.
Alternative Treatments
Several alternative treatments are available for lice and scabies infestations, including:
1. For Head Lice:
- Malathion: An alternative prescription treatment for head lice.
- Pyrethrins with Piperonyl Butoxide: Another over-the-counter option that works similarly to permethrin.
2. For Scabies:
- Ivermectin: An oral medication that can be used to treat scabies, particularly in cases where topical treatments are ineffective or unsuitable.
- Crotamiton: An alternative cream used to treat scabies infestations.
Conclusion
Permethrin is a highly effective treatment for head lice and scabies, with a proven track record of safety and efficacy when used as directed. It is available in various formulations, with options for both children and adults. However, it is essential to follow the recommended dosages and guidelines to avoid potential side effects and risks. With proper use, permethrin can help eliminate parasitic infestations and restore skin health. Always consult a healthcare provider before using permethrin, especially for young children, pregnant women, and individuals with sensitive skin.
FAQs:
What is Permethrin used for?
Permethrin is used to treat head lice and scabies infestations. It is also used as an insecticide in agriculture and veterinary medicine.
Can it be taken daily?
Permethrin is not taken daily. It is applied topically, typically as a one-time treatment, with a second application recommended after 7 to 14 days if needed.
What are the common side effects?
Common side effects include skin irritation, redness, itching, burning sensation, and dryness or peeling at the site of application.
Does it interact with other medications?
Permethrin has minimal systemic absorption, so it generally doesn’t interact significantly with other medications. However, caution should be used when applying it with other topical treatments.
What are the alternative treatments?
Alternatives include malathion, pyrethrins with piperonyl butoxide, ivermectin (for scabies), and crotamiton for lice and scabies treatment.