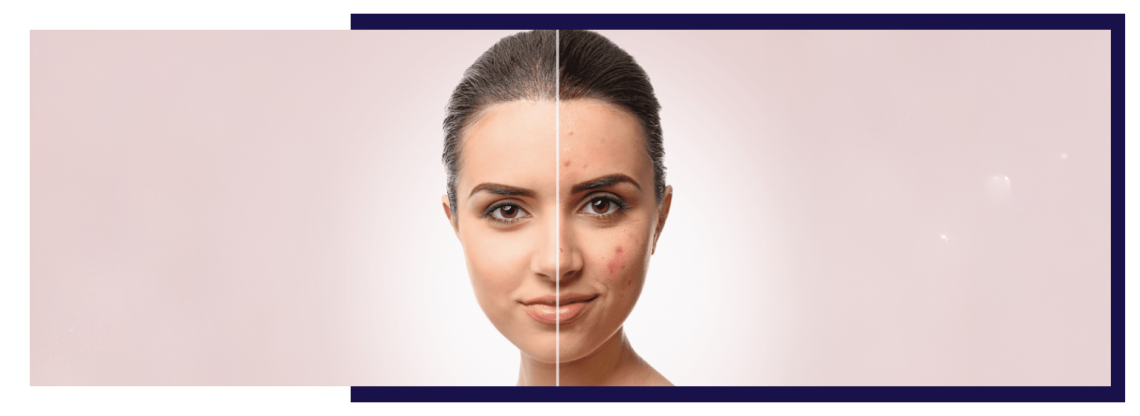
Introduction Acne is a common skin condition, but for many, its aftereffects linger long after active breakouts have faded. Acne scarring can impact confidence, texture, and skin tone, making the skin appear uneven or pitted. Understanding how scars form—and the wide range of treatments available today—can help you make informed decisions about prevention and correction.This comprehensive guide covers the types of acne scars, how to prevent them, and the most effective professional and at-home treatment options. What Causes Acne Scarring? Acne scarring occurs when inflammation damages the skin’s deeper layers. The healing process triggers collagen production, but if too much…
-
-
Introduction While topical products and oral medications form the foundation of acne treatment, professional in-clinic procedures can significantly enhance results—especially for stubborn, moderate, or persistent acne. Dermatologists and licensed estheticians offer targeted therapies that help reduce breakouts, unclog pores, minimize inflammation, and improve skin texture.This article explores the three most effective professional acne treatments: chemical peels, laser therapy, and extractions. Understanding how each works, who they’re suitable for, and what results to expect can help you choose the best treatment for your skin. Why Professional Acne Treatments Matter Professional treatments offer benefits that at-home skincare cannot achieve: They are especially…
-
Introduction For years, dermatologists believed diet and acne had little connection. Today, a growing body of scientific research shows that certain foods—especially those high in sugar, dairy products, and high-glycemic (fast-digesting) carbohydrates—may influence acne severity.Food alone doesn’t cause acne, but it can worsen or trigger breakouts in people who are genetically or hormonally prone. Understanding how diet affects skin inflammation, hormones, and oil production can empower you to make choices that support clearer skin.This article explores the evidence behind the main dietary factors linked to acne and offers practical recommendations. What Is the Link Between Diet and Acne? Acne is…
-
Introduction For many people, topical treatments alone are not enough to control moderate to severe acne. When breakouts are persistent, painful, widespread, or cause scarring, dermatologists often turn to oral prescription medications. These systemic treatments work from the inside out to reduce inflammation, regulate hormones, control bacteria, and shrink oil glands.The most commonly used oral medications include antibiotics, birth control pills, and isotretinoin (Accutane). Each targets acne differently and is recommended for specific situations.This comprehensive guide explains how each medication works, who needs it, how long treatment lasts, possible side effects, and when to consult a dermatologist. Why Oral Medications…
-
Introduction Topical retinoids are among the most effective and dermatologist-recommended treatments for acne. They are derived from vitamin A and work by targeting several root causes of acne—clogged pores, inflammation, and irregular skin cell turnover. Whether you struggle with blackheads, whiteheads, or recurring breakouts, topical retinoids can be a game-changer when used correctly.This article explores how retinoids work, the different types available, how to apply them safely, potential side effects, and tips for getting maximum results with minimal irritation. What Are Topical Retinoids? Topical retinoids are vitamin A derivatives used in skincare to increase cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.…
-
Introduction Acne is one of the most common skin concerns globally, affecting both teenagers and adults. While pimples may appear similar at first glance, acne actually comes in several types, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. Understanding your acne type is crucial to selecting the most effective skincare routine or medical treatment. The three primary categories of acne are comedonal, inflammatory, and cystic. Each type varies in severity, causes, and appearance, making accurate identification the first step in successful acne management. 1. Comedonal Acne: Blackheads and Whiteheads What It Is Comedonal acne is the mildest form of acne. It…
-
Introduction Acne is one of the most common skin concerns worldwide, affecting teens and adults alike. While occasional pimples are normal, frequent or stubborn breakouts require a targeted skincare routine. The foundation of an effective acne-fighting regimen relies on three essential steps: cleanser, treatment, and moisturizer. Each step plays a unique role in keeping pores clear, reducing inflammation, and preventing new pimples from forming. This article explains how to build a structured, evidence-based routine to tackle acne while keeping your skin healthy and balanced. Step 1: Cleansing – Removing Impurities Without Over-Drying Why Cleansing Is Crucial Cleansing removes: Without proper…
-
Introduction Pimples are extremely common, and most people experience breakouts at some point in their lives. Occasional pimples can usually be managed with simple skincare routines and over-the-counter (OTC) treatments. However, when pimples become persistent, painful, or start affecting your confidence, it may be time to involve a dermatologist. Dermatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating all types of acne, from mild comedones to severe cystic lesions. This article explains how to recognize when pimples need professional attention, what a dermatologist can do, and what to expect during your visit. Understanding Persistent Pimples Persistent pimples are breakouts that: Chronic or recurrent…
-
Introduction Under-the-skin pimples—also known as cystic pimples or cystic acne—are among the most painful and stubborn types of breakouts. Unlike surface pimples, they form deep within the skin, causing swelling, tenderness, and inflammation. These pimples often never develop a visible “head,” which is why they feel like hard, painful bumps under the surface. Cystic pimples can be emotionally frustrating because they last longer, resist simple treatments, and can leave behind scars or dark marks. Understanding why they form and how to manage them safely can make a huge difference in preventing damage and speeding up healing. Introduction: What Are Under-the-Skin…
-
Introduction Hormonal pimples are a frustrating yet extremely common type of acne that affects both teenagers and adults. These breakouts are closely linked to fluctuations in hormones—especially androgens—which can increase oil (sebum) production and trigger inflammation. Unlike occasional pimples caused by makeup or sweat, hormonal breakouts follow predictable patterns and often return in the same areas month after month. Understanding how hormonal pimples develop, when they occur, and how to manage them can help you take control of your skin and reduce flare-ups. This article explains the hormonal cycle, common triggers, treatment options, lifestyle changes, and prevention strategies. Introduction: Why…