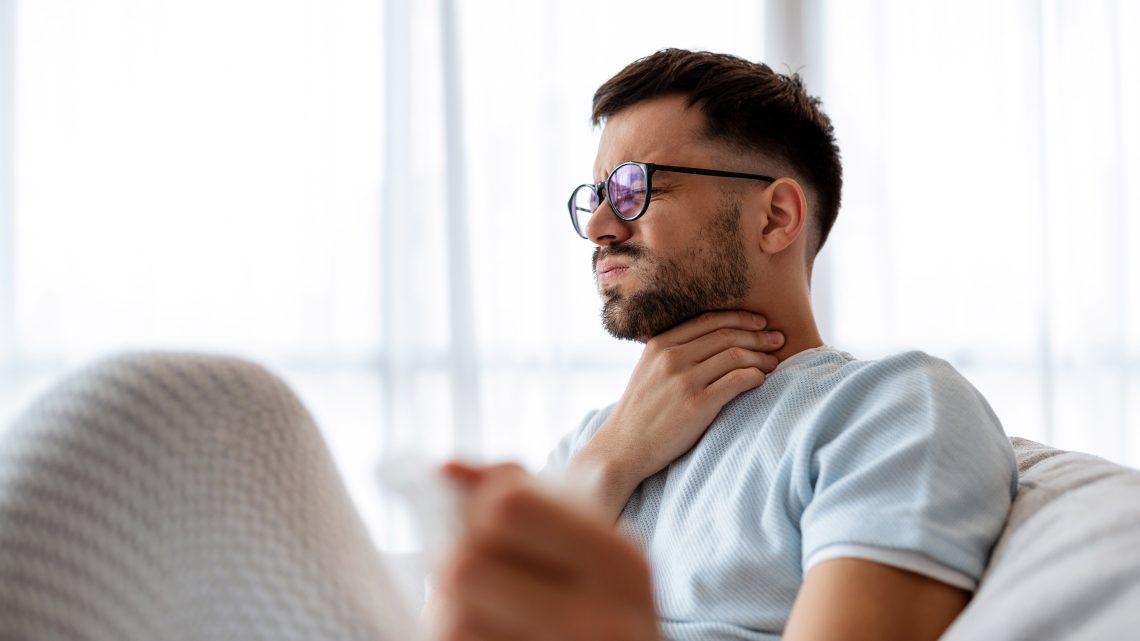
Introduction Sore throats are common, but not all are created equal. While most are caused by viruses and resolve on their own, bacterial infections, particularly strep throat, require medical attention and antibiotics. Distinguishing between viral and bacterial causes is crucial for proper treatment, preventing complications, and avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use. This guide outlines the key differences, symptoms, diagnosis, and management strategies for strep throat and viral sore throats. 1. Causes Viral Sore Throat Strep Throat (Bacterial) 2. Symptoms Viral Sore Throat Strep Throat Key point: Cough and runny nose are more common in viral infections, whereas high fever and pus…
-
-
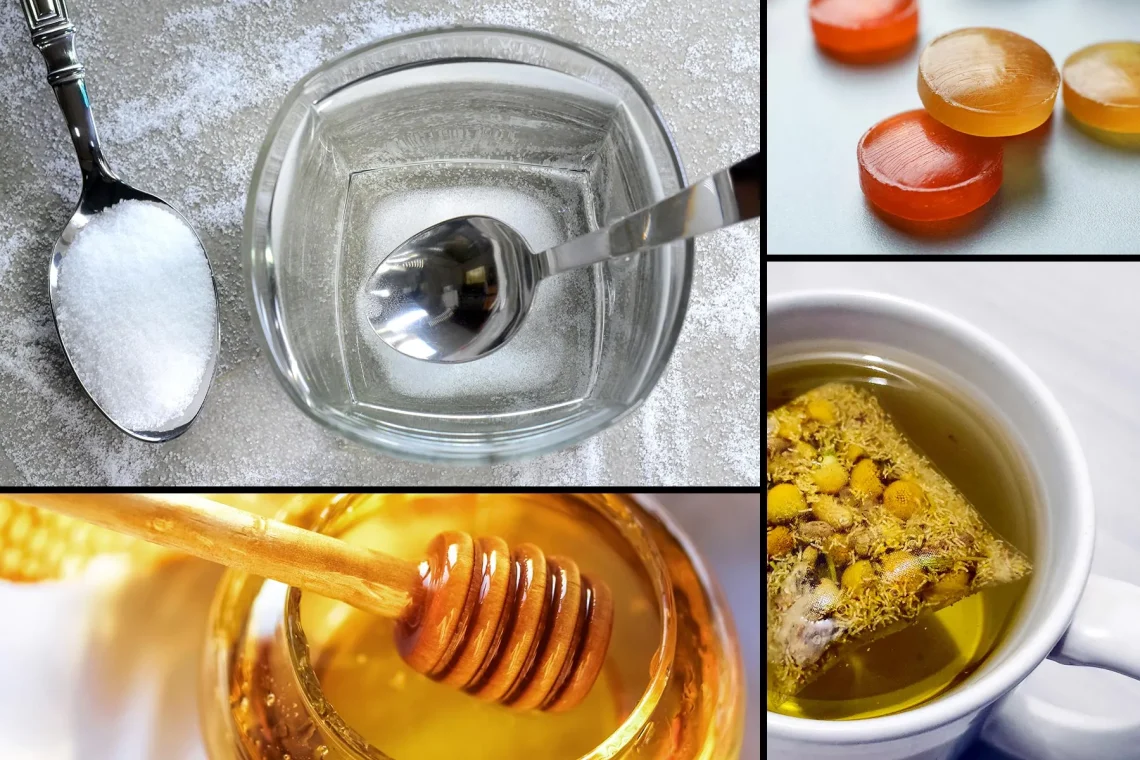
Introduction A sore throat is a common complaint that can range from mild irritation to a painful, inflamed throat making swallowing and speaking difficult. Causes vary from viral infections like the common cold or flu, bacterial infections such as strep throat, allergies, dry air, or even voice strain. While most sore throats resolve on their own, simple home remedies can provide relief, reduce discomfort, and speed up recovery. Among the most effective remedies are saltwater gargles, throat lozenges, and honey — all safe, natural, and widely accessible. 1. Saltwater Gargles Why It Works Saltwater gargles help by: How to Use…
-
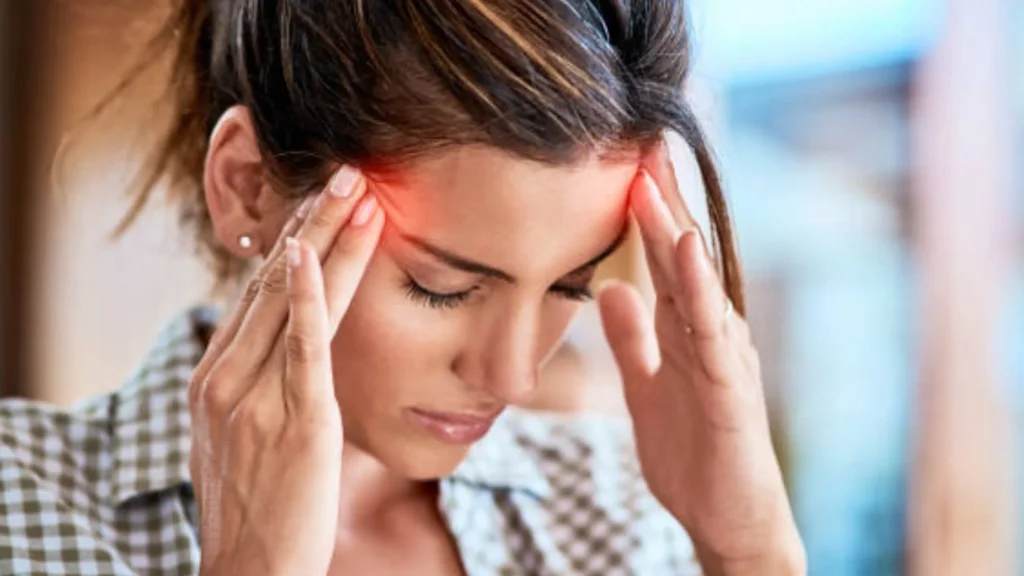
Introduction Headaches are common, ranging from mild tension headaches to severe migraines. Most are benign and manageable with rest, hydration, or over-the-counter medications. However, some headaches signal a serious underlying medical condition that requires immediate medical attention. Recognizing the warning signs of an emergency headache can prevent complications and save lives. This guide outlines the types of headaches that should never be ignored, what symptoms to watch for, and what to do in urgent situations. Types of Emergency Headaches Certain headache patterns or accompanying symptoms indicate that urgent medical evaluation is necessary: 1. Thunderclap Headache 2. Headache With Neurological Symptoms…
-
Introduction For many people suffering from frequent headaches or migraines, over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications seem like a lifeline. However, frequent or excessive use of these medications can paradoxically lead to Medication Overuse Headaches (MOH) — a condition where the very drugs used to relieve pain end up causing more headaches. MOH is sometimes called a “rebound headache” and is a common but often overlooked cause of chronic headaches. Understanding the causes, recognizing the warning signs, and knowing how to break the cycle are essential steps toward regaining control and reducing headache frequency. What Are Medication Overuse Headaches? Medication…
-
Introduction Caffeine is one of the most widely consumed stimulants in the world, found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and certain medications. It has a complex relationship with headaches: for some, it provides relief, while for others, it may trigger or worsen headaches. Understanding how caffeine affects the nervous system and blood vessels can help individuals use it wisely — either as a tool for relief or to avoid headache triggers. This article explores the dual role of caffeine, its mechanisms, benefits, risks, and practical tips for managing headaches effectively. How Caffeine Affects the Head Caffeine impacts headaches primarily through…
-
Introduction Headaches are one of the most common ailments, ranging from mild tension headaches to severe migraines. While medications are often effective, many people seek natural remedies to relieve pain, reduce frequency, and minimize side effects. Among the most researched natural options are peppermint oil, magnesium supplementation, and adequate hydration. These remedies are accessible, generally safe, and can be combined with lifestyle changes for better headache management. Understanding how they work and how to use them effectively can help reduce headache intensity and improve overall quality of life. 1. Peppermint Oil for Headache Relief How It Works Peppermint oil contains…
-
Introduction Headaches are one of the most common health complaints, affecting millions worldwide. From mild tension headaches to debilitating migraines, identifying the underlying triggers can make a world of difference in managing pain and preventing future episodes. A headache diary is a simple yet powerful tool that helps you track when, how, and why your headaches occur. By recording daily details such as timing, symptoms, food intake, and stress levels, you and your healthcare provider can uncover patterns that lead to better diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies. Whether you experience occasional headaches or chronic migraines, keeping a headache diary is…
-
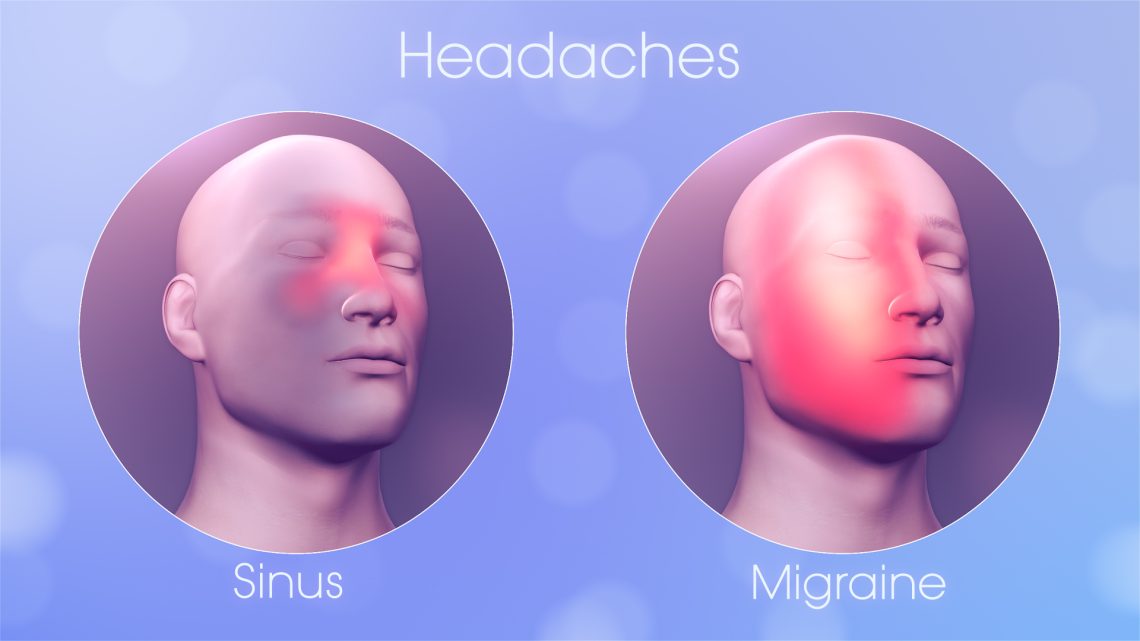
Introduction Headaches are a common ailment that many people experience, but not all headaches are created equal. Two types of headaches that are often confused are sinus headaches and migraines. Both can cause significant discomfort and disrupt daily activities, but they have distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding the differences between a sinus headache and a migraine is crucial for seeking the most appropriate treatment and finding relief. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between these two types of headaches, their causes, symptoms, triggers, and how to properly diagnose and manage them. What is a Sinus Headache? A…
-
Introduction Cluster headaches are among the most painful types of headaches, often described as “suicide headaches” due to their extreme intensity. Unlike migraines or tension headaches, cluster headaches strike in repetitive cycles — or “clusters” — of frequent attacks followed by remission periods. These headaches are short-lived but excruciating, usually affecting one side of the head and often centered around the eye. Understanding the symptoms, cyclical pattern, and treatment options can help patients manage the condition and reduce the disruption it causes in daily life. What Are Cluster Headaches? Cluster headaches are a neurological disorder involving sudden, severe pain on…
-
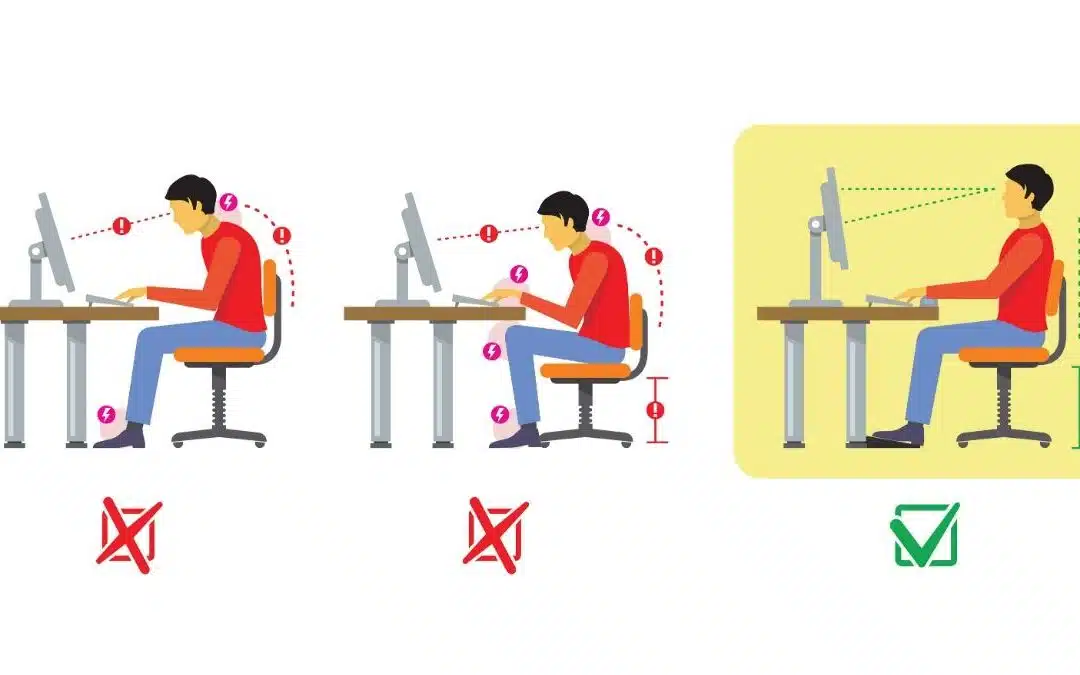
Introduction Tension headaches are among the most common types of headaches, affecting millions of people around the world. These headaches can range from mild to severe and can be debilitating, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life. Often described as a dull, aching pain, tension headaches are usually associated with tightness around the forehead, temples, or the back of the head and neck. While the exact cause of tension headaches is not always clear, they are often triggered by stress, poor posture, and muscle tension. Thankfully, there are numerous ways to alleviate the pain and prevent the onset of…