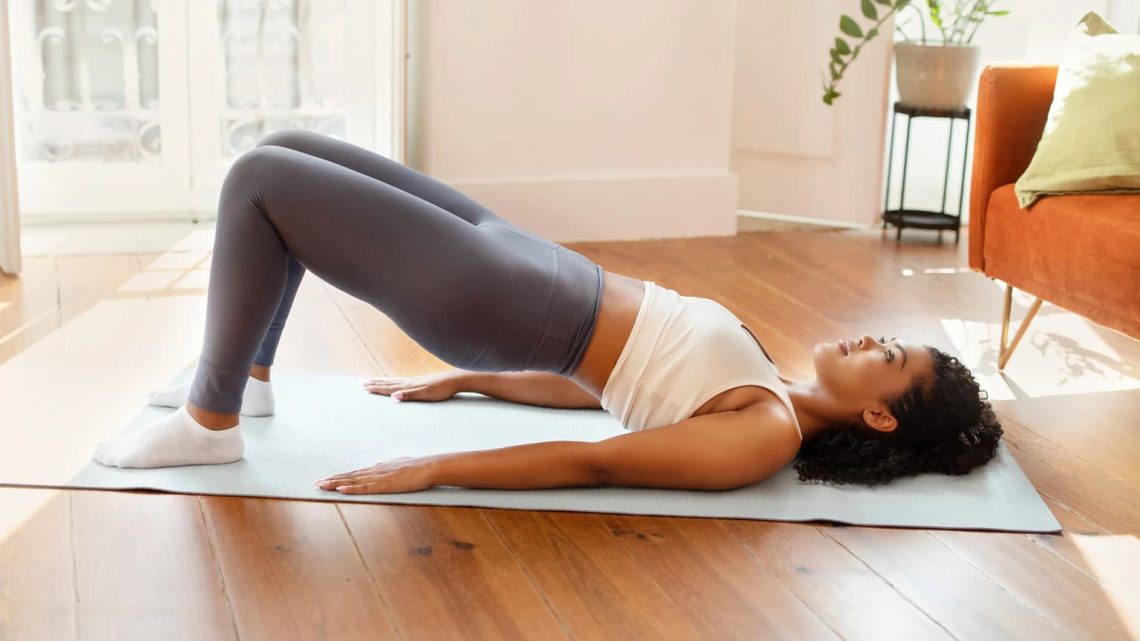
Introduction The pelvic floor is a group of muscles that support the bladder, bowel, and (in women) the uterus. These muscles play a vital role in controlling urination, bowel movements, and sexual function. Over time, factors like pregnancy, childbirth, aging, surgery, obesity, and chronic coughing can weaken the pelvic floor, leading to issues such as urinary incontinence or reduced sexual satisfaction. Pelvic floor exercises—commonly called Kegel exercises—strengthen these muscles and improve control. The best part? They’re simple, effective, and can be done anywhere without special equipment. This step-by-step guide will show men and women how to properly perform Kegels, avoid…
-
-
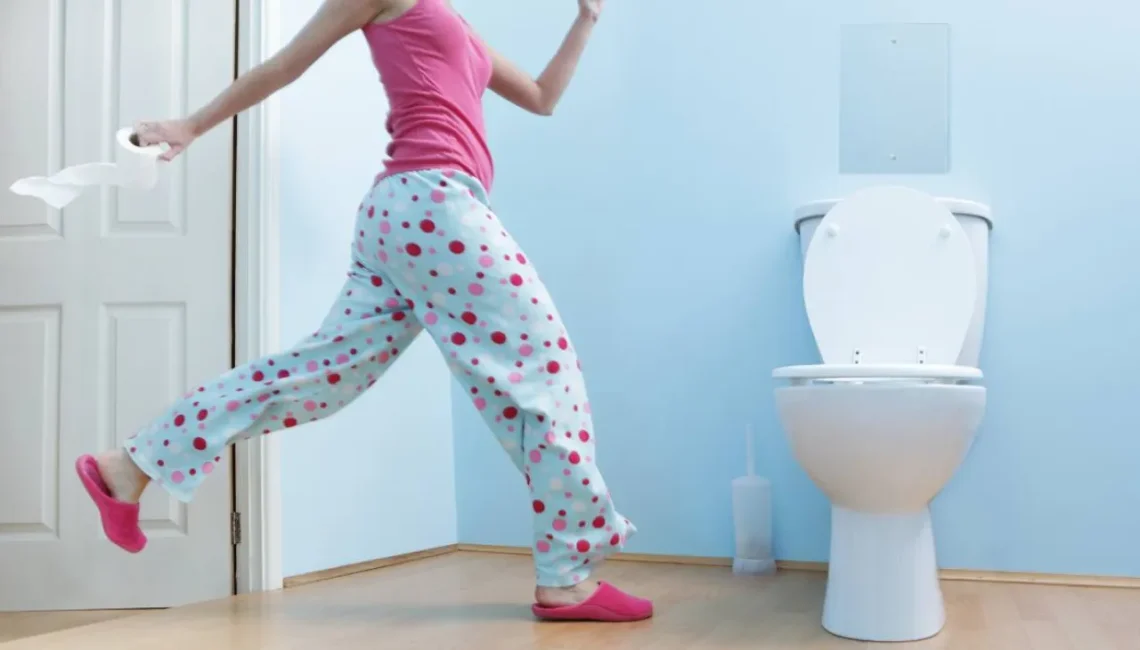
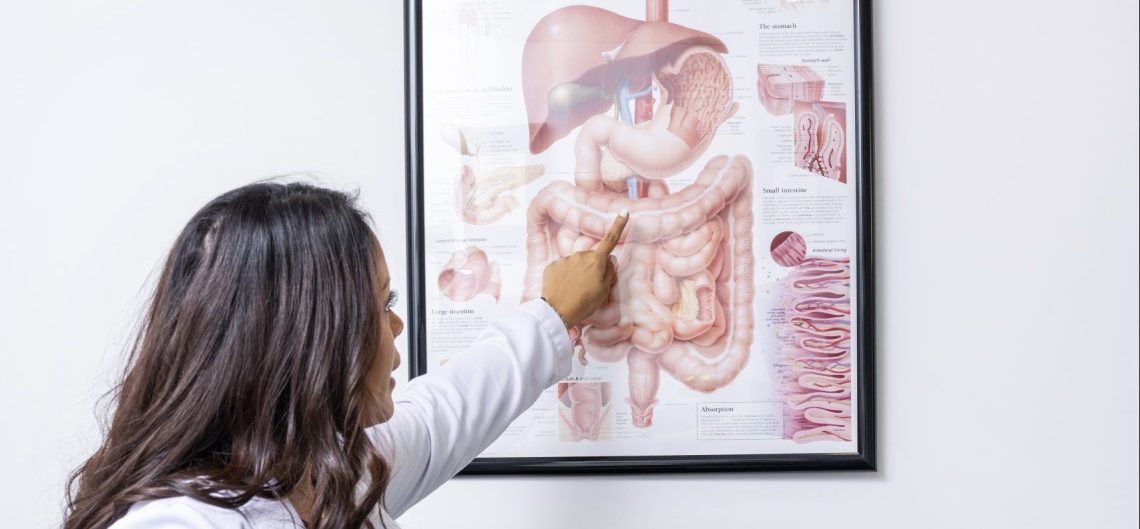
Introduction Urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of bladder control, leading to accidental leakage of urine. While it is more common in older adults and women, it can affect people of any age or gender. Incontinence is not a disease itself but a symptom of underlying health issues. Understanding the different types—stress, urge, overflow, and functional incontinence—can help individuals identify causes, recognize symptoms, and seek appropriate medical support. 1. Stress Incontinence Causes Symptoms 2. Urge Incontinence (Overactive Bladder) Causes Symptoms 3. Overflow Incontinence Causes Symptoms 4. Functional Incontinence Causes Symptoms Conclusion Urinary incontinence can be distressing and affect quality of…
-
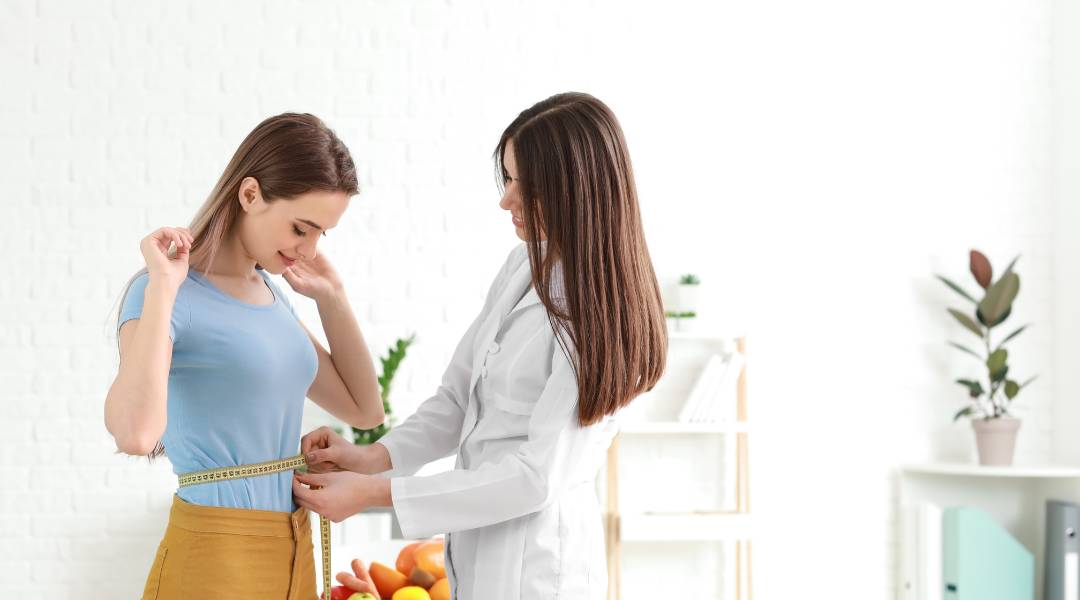
Introduction For decades, weight loss has been viewed as the central measure of health, with medical advice often centered on dieting, calorie restriction, and achieving a “healthy” body size. However, a growing body of research challenges this weight-centric approach, suggesting that health is not defined solely by numbers on a scale. Instead, the Health at Every Size (HAES) movement promotes a holistic framework that emphasizes overall well-being, self-acceptance, and sustainable health behaviors—regardless of body size or weight. HAES is not about denying the health risks associated with obesity; rather, it aims to reduce weight stigma while focusing on long-term, achievable…
-
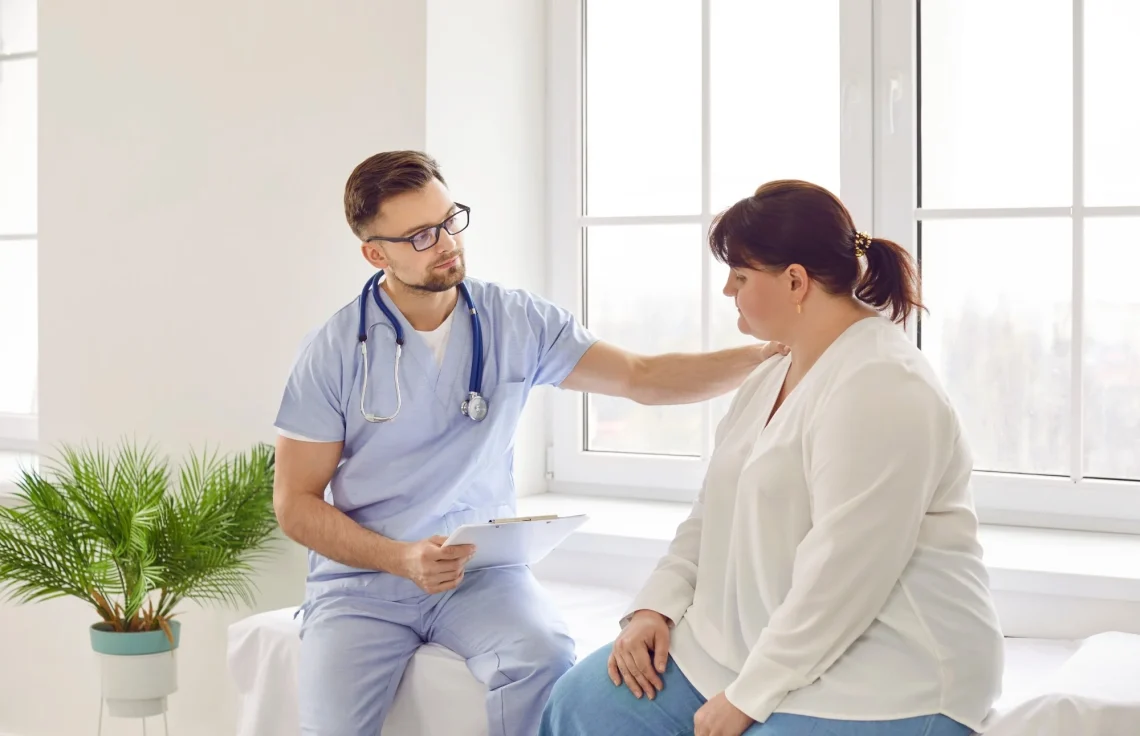
Introduction Obesity and overweight affect millions of people worldwide, but those living with higher body weights often face more than just physical health challenges—they also encounter weight bias and stigma. In healthcare settings, this can result in patients feeling judged, dismissed, or overlooked, which may prevent them from seeking medical care. Addressing weight bias is not just about kindness; it’s a matter of improving health outcomes, trust, and equality in medical treatment. What is Weight Bias and Stigma? In healthcare, these biases may show up as: The Impact of Weight Bias in Healthcare How Healthcare Professionals Can Address Weight Bias…
-
Introduction Weight management is not just about diet and exercise—it’s also about motivation, accountability, and emotional well-being. While individual determination plays an important role, research consistently shows that people are more successful in reaching and maintaining a healthy weight when they have a strong support system. Having people to encourage, guide, and celebrate progress with can make the journey less overwhelming and more sustainable. This article explores why a support system is essential, the types of support available, and how to build one that works for your lifestyle and goals. Why a Support System Matters in Weight Management Types of…
-
Introduction Food is not just fuel—it’s also tied to emotions, comfort, and social experiences. While enjoying food is natural, problems arise when eating becomes a coping mechanism for stress, sadness, boredom, or anxiety. This behavior, often called emotional eating, can lead to overeating and, in some cases, escalate into binge eating disorder (BED). Unlike occasional indulgence, emotional or binge eating can disrupt physical health, contribute to weight gain, and negatively affect mental well-being. The good news is that both emotional eating and binge eating can be managed with awareness, practical strategies, and professional support. Understanding Emotional Eating What Is Emotional…
-
Introduction Weight management is often thought of as a simple equation of calories in versus calories out. While energy balance is certainly important, the body’s internal hormonal system plays a major role in regulating appetite, metabolism, and fat storage. Among these hormones, leptin and ghrelin are two of the most critical players. Often referred to as the “hunger hormones,” they act as messengers between the gut, fat stores, and the brain to help control food intake and body weight. Understanding how leptin and ghrelin function—and how imbalances can affect weight—can provide valuable insight into why weight loss is so challenging…
-
Introduction For individuals struggling with severe obesity, traditional weight-loss methods such as diet, exercise, and medications may not always be effective. In such cases, bariatric surgery (also known as weight-loss surgery) can be a life-changing option. These surgical procedures are designed to help individuals lose weight by altering the digestive system, leading to reduced food intake, nutrient absorption, or both. Beyond weight loss, bariatric surgery can significantly improve or even resolve obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea. This article explores the main types of bariatric surgery, eligibility requirements, potential risks, and what long-term success looks…
-
Introduction Obesity is a complex, chronic health condition that affects millions worldwide. It is not merely about weight gain—it is associated with serious health risks such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, sleep apnea, and certain cancers. While lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, exercise, and behavioral therapy remain the foundation of weight management, some individuals may require additional support to achieve and maintain weight loss. For people who struggle despite consistent efforts, medication can play a vital role in obesity treatment. This article explores the most commonly prescribed weight-loss medications, how they work, and important considerations for…
-
Introduction Weight loss is one of the most common health goals across the globe, yet many people struggle to achieve lasting results. Quick-fix diets, extreme exercise regimens, and unrealistic expectations often lead to short-term success followed by discouraging setbacks. True, sustainable weight loss requires more than shedding pounds quickly—it’s about creating long-term lifestyle changes that support both physical and mental well-being. At the heart of this process is setting realistic goals. When goals are practical, measurable, and personalized, they pave the way for consistent progress and lasting success. Why Setting Realistic Goals Matters Many people begin their weight loss journey…