Introduction Snoring is often dismissed as a minor annoyance, but it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious condition: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Sleep apnea occurs when the airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep, leading to interrupted breathing, low oxygen levels, and fragmented sleep. While not all snorers have sleep apnea, loud, frequent snoring is one of the most common warning signs. Understanding the link between snoring and sleep apnea—and knowing when to get tested—is crucial for long-term health and well-being. This article explores the connection between snoring and sleep apnea, key symptoms, risk factors, and…
-
-
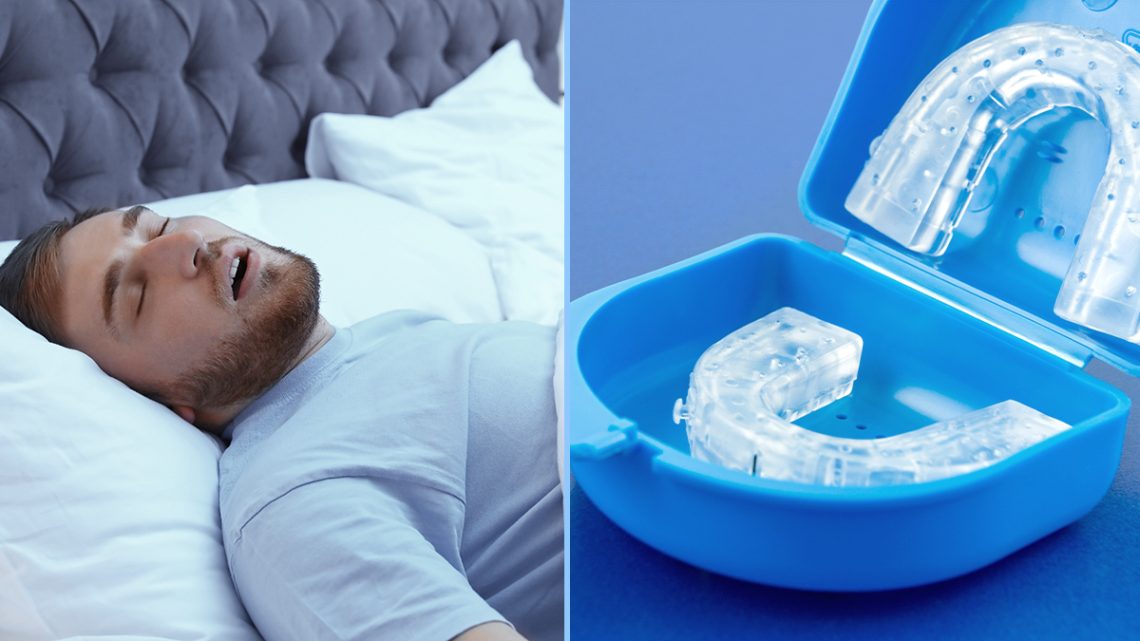
Introduction Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are common sleep-related problems that can affect both health and quality of life. For many people, lifestyle changes, positional therapy, and nasal treatments are helpful, but sometimes additional solutions are needed. Mandibular Advancement Devices (MADs) are one of the most widely used oral appliances designed to reduce snoring and mild-to-moderate sleep apnea. They work by repositioning the lower jaw (mandible) to keep the airway open during sleep. This article explores how MADs work, their benefits, limitations, and important considerations before choosing one. How Mandibular Advancement Devices Work Mechanism of Action Who Typically Benefits…
-
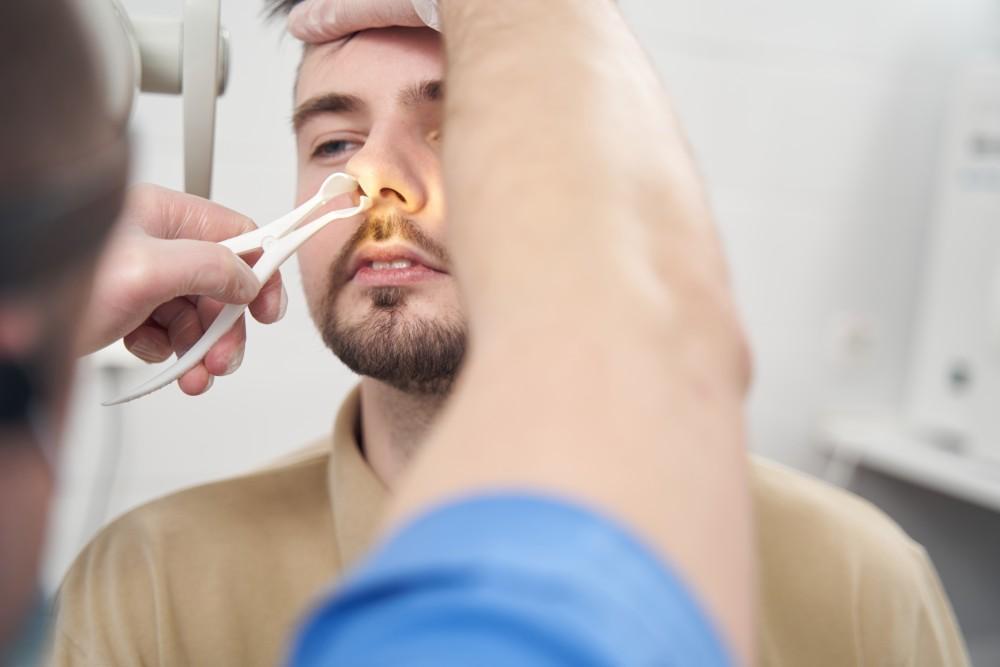
Introduction Nasal congestion is one of the most common contributors to snoring, sleep disturbances, and poor sleep quality. When airflow through the nose is restricted, the body compensates by breathing through the mouth, which can lead to loud snoring, throat dryness, and even exacerbation of sleep apnea. Congestion can arise from temporary issues such as colds, chronic conditions like allergies, or structural problems such as a deviated septum. Addressing nasal obstruction is a crucial step toward clearer airflow, quieter sleep, and better overall health. This article explores the causes of nasal congestion, treatment strategies, and how improving nasal airflow can…
-
Introduction Acne is more than a skin-deep problem. While clogged pores, oil production, and bacteria are involved, many internal factors—including stress, gut health, diet, and micronutrient imbalances—can influence how often you break out and how your skin heals. A holistic approach doesn’t replace medical acne treatments but supports the body from within, helping reduce inflammation, balance hormones, and build skin resilience. This comprehensive article explores three major holistic pillars—stress management, gut health, and supplements—that play a scientifically supported role in clearer, healthier skin. Understanding Holistic Acne Management A holistic approach focuses on the whole body, not just the skin. Acne…
-
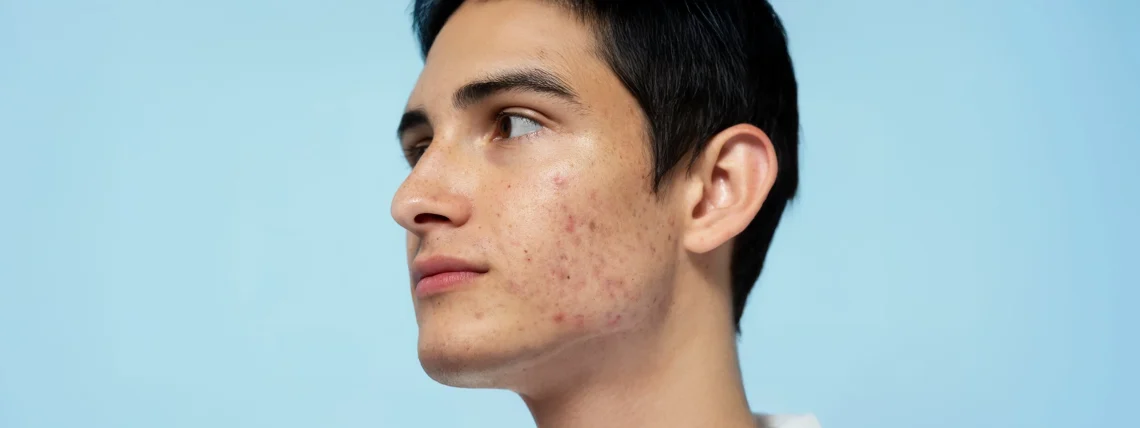
Introduction While acne is commonly associated with teenagers, a significant number of adults—especially women—continue to struggle with persistent breakouts well into their 20s, 30s, 40s, and even 50s. Adult acne can be frustrating because its causes are more complex, often tied to internal factors such as hormones, stress, or medical conditions. It can also be stubborn, requiring a more personalized and layered treatment approach than adolescent acne. This detailed guide explains why acne happens in adults, the key differences from teenage acne, and the most effective treatment strategies to regain clear, healthy skin. Understanding Adult Acne How Adult Acne Differs…
-
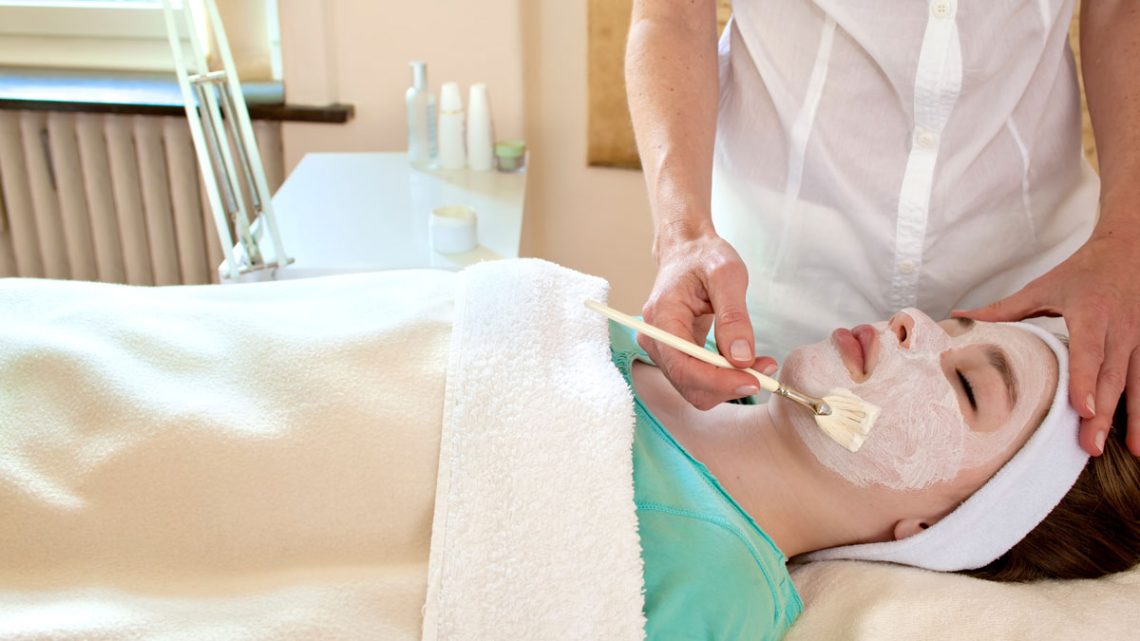
Introduction While topical products and oral medications form the foundation of acne treatment, professional in-clinic procedures can significantly enhance results—especially for stubborn, moderate, or persistent acne. Dermatologists and licensed estheticians offer targeted therapies that help reduce breakouts, unclog pores, minimize inflammation, and improve skin texture.This article explores the three most effective professional acne treatments: chemical peels, laser therapy, and extractions. Understanding how each works, who they’re suitable for, and what results to expect can help you choose the best treatment for your skin. Why Professional Acne Treatments Matter Professional treatments offer benefits that at-home skincare cannot achieve: They are especially…
-
Introduction For many people, topical treatments alone are not enough to control moderate to severe acne. When breakouts are persistent, painful, widespread, or cause scarring, dermatologists often turn to oral prescription medications. These systemic treatments work from the inside out to reduce inflammation, regulate hormones, control bacteria, and shrink oil glands.The most commonly used oral medications include antibiotics, birth control pills, and isotretinoin (Accutane). Each targets acne differently and is recommended for specific situations.This comprehensive guide explains how each medication works, who needs it, how long treatment lasts, possible side effects, and when to consult a dermatologist. Why Oral Medications…
-
Introduction Acne is one of the most common skin concerns globally, affecting both teenagers and adults. While pimples may appear similar at first glance, acne actually comes in several types, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. Understanding your acne type is crucial to selecting the most effective skincare routine or medical treatment. The three primary categories of acne are comedonal, inflammatory, and cystic. Each type varies in severity, causes, and appearance, making accurate identification the first step in successful acne management. 1. Comedonal Acne: Blackheads and Whiteheads What It Is Comedonal acne is the mildest form of acne. It…
-
Introduction Pimples are extremely common, and most people experience breakouts at some point in their lives. Occasional pimples can usually be managed with simple skincare routines and over-the-counter (OTC) treatments. However, when pimples become persistent, painful, or start affecting your confidence, it may be time to involve a dermatologist. Dermatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating all types of acne, from mild comedones to severe cystic lesions. This article explains how to recognize when pimples need professional attention, what a dermatologist can do, and what to expect during your visit. Understanding Persistent Pimples Persistent pimples are breakouts that: Chronic or recurrent…
-
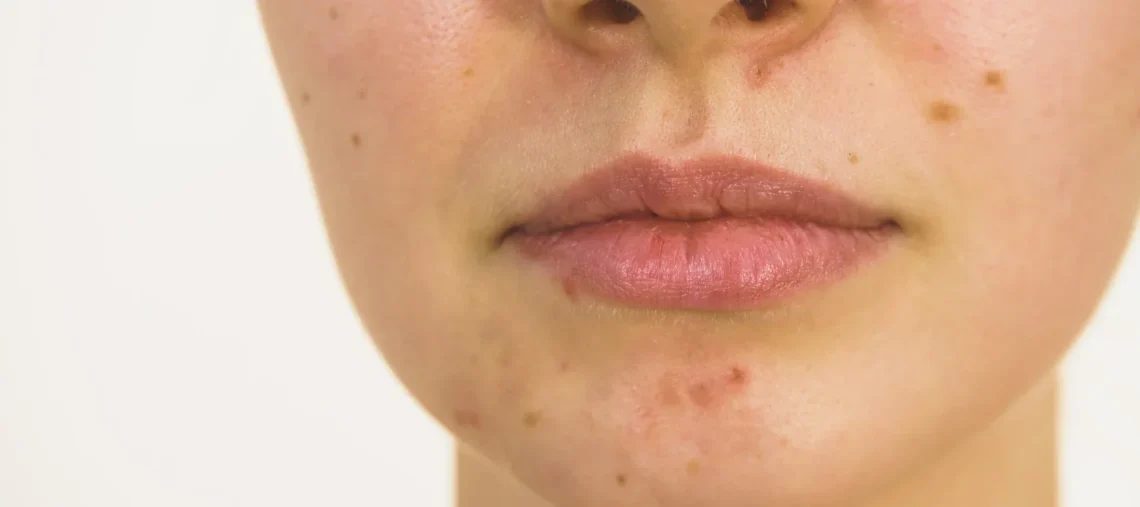
Introduction Under-the-skin pimples—also known as cystic pimples or cystic acne—are among the most painful and stubborn types of breakouts. Unlike surface pimples, they form deep within the skin, causing swelling, tenderness, and inflammation. These pimples often never develop a visible “head,” which is why they feel like hard, painful bumps under the surface. Cystic pimples can be emotionally frustrating because they last longer, resist simple treatments, and can leave behind scars or dark marks. Understanding why they form and how to manage them safely can make a huge difference in preventing damage and speeding up healing. Introduction: What Are Under-the-Skin…