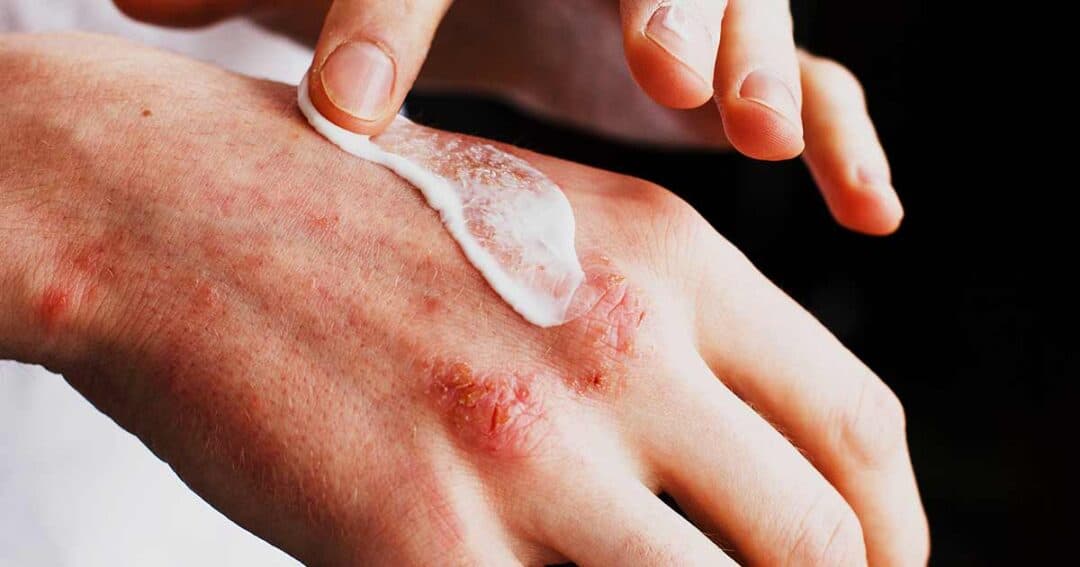
Introduction Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory skin condition that affects both children and adults. It manifests as dry, itchy, red, and sometimes oozing patches. Beyond physical discomfort, eczema can also impact sleep, mental health, and daily activities, particularly in severe cases. While there is no permanent cure, an effective management plan can help: Management revolves around three pillars: moisturizing and skin care, trigger identification and avoidance, and pharmacologic treatment. 1. Moisturizing and Skin Care Moisturizing is the foundation of eczema management. The skin of eczema patients has a weakened barrier, leading to increased water loss and…
-
-
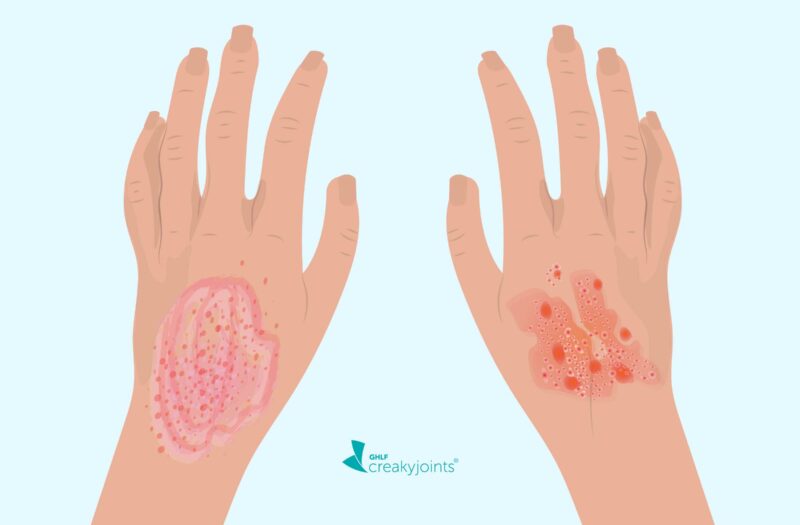
Introduction Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that occurs when the skin reacts to direct contact with irritants or allergens. It often causes redness, itching, and blisters, and while generally not life-threatening, it can significantly impact daily comfort and quality of life. Understanding common triggers such as poison ivy, nickel, and fragrances helps prevent flare-ups and manage symptoms effectively. What is Contact Dermatitis? Contact dermatitis is divided into two main types: 1. Irritant Contact Dermatitis 2. Allergic Contact Dermatitis Common Triggers 1. Poison Ivy, Oak, or Sumac 2. Nickel 3. Fragrances and Cosmetics Identifying Your Triggers Treatment and Management…
-
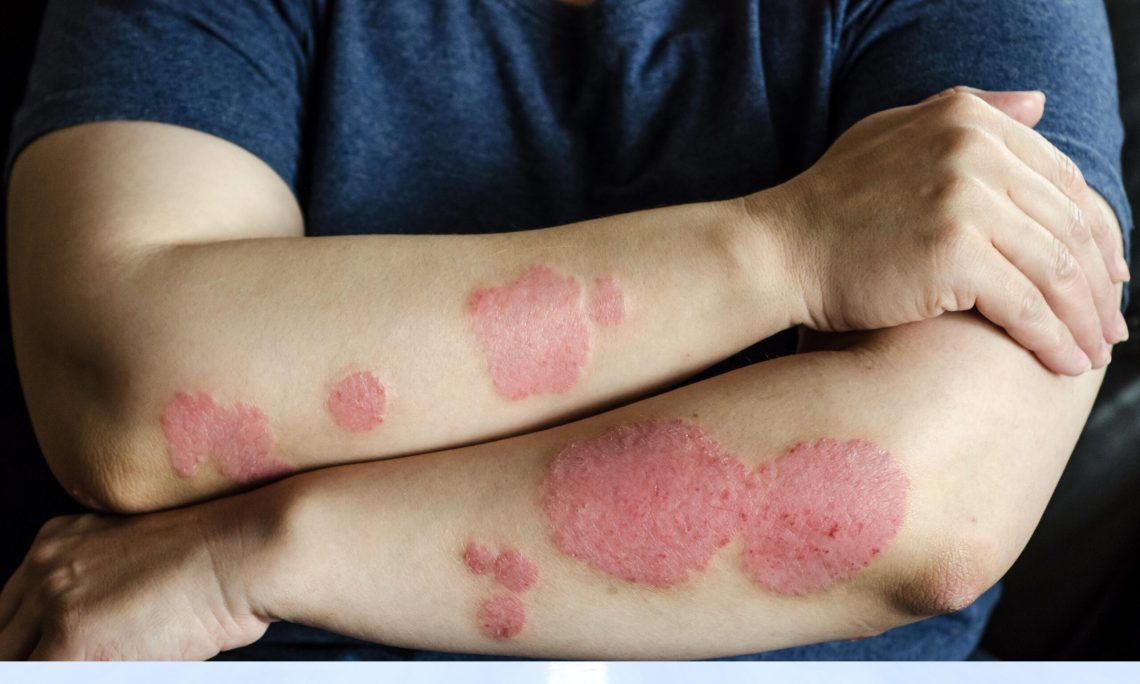
Introduction Rashes are a frequent skin complaint and can be caused by a variety of conditions, ranging from allergic reactions and infections to chronic skin disorders. Identifying the type of rash is essential for appropriate management and to distinguish harmless rashes from those requiring urgent care. This guide covers common types of rashes, their characteristics, triggers, and basic management tips, along with suggested images for visual identification. 1. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) 2. Psoriasis 3. Hives (Urticaria) 4. Contact Dermatitis 5. Chickenpox (Varicella) 6. Ringworm (Tinea) 7. Shingles (Herpes Zoster) Tips for Rash Identification When to Seek Medical Care: Conclusion Rashes…
-
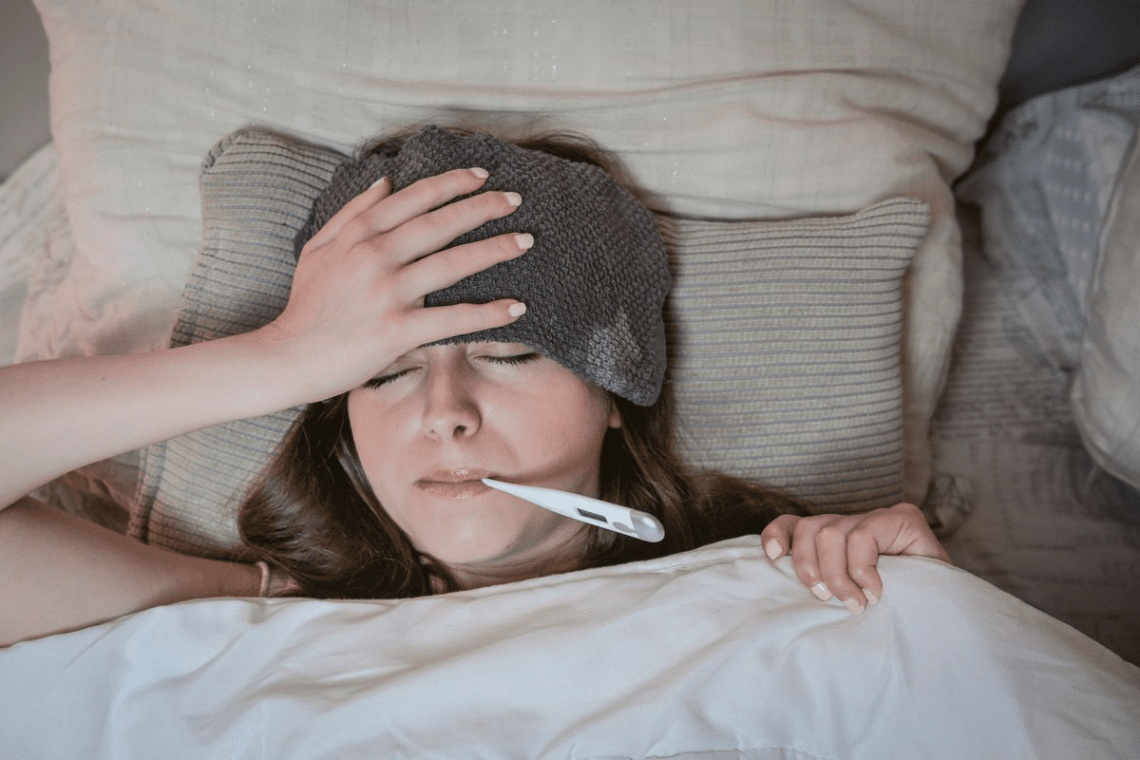
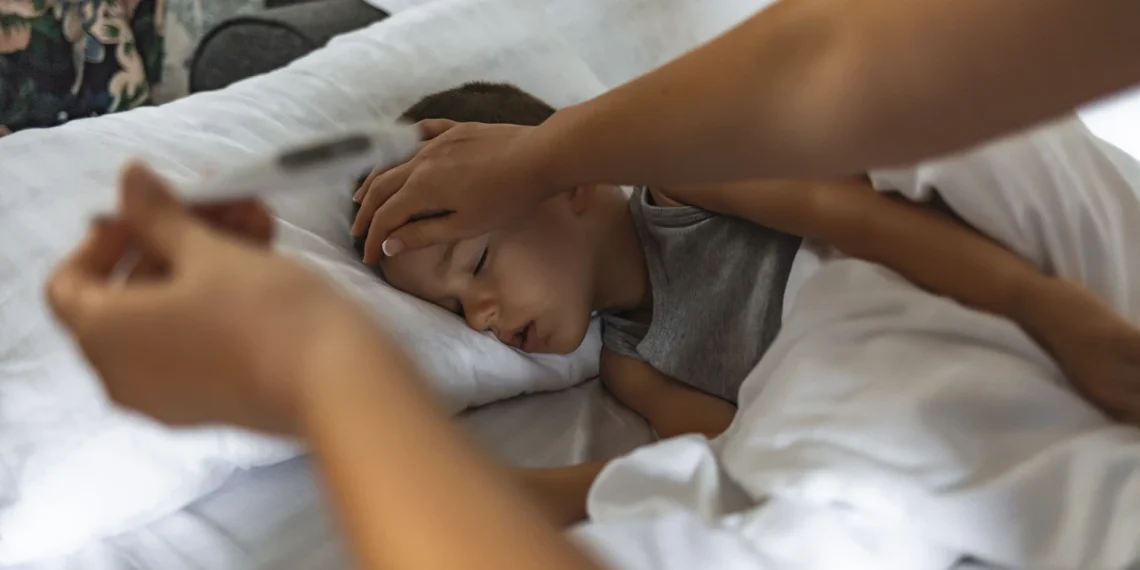
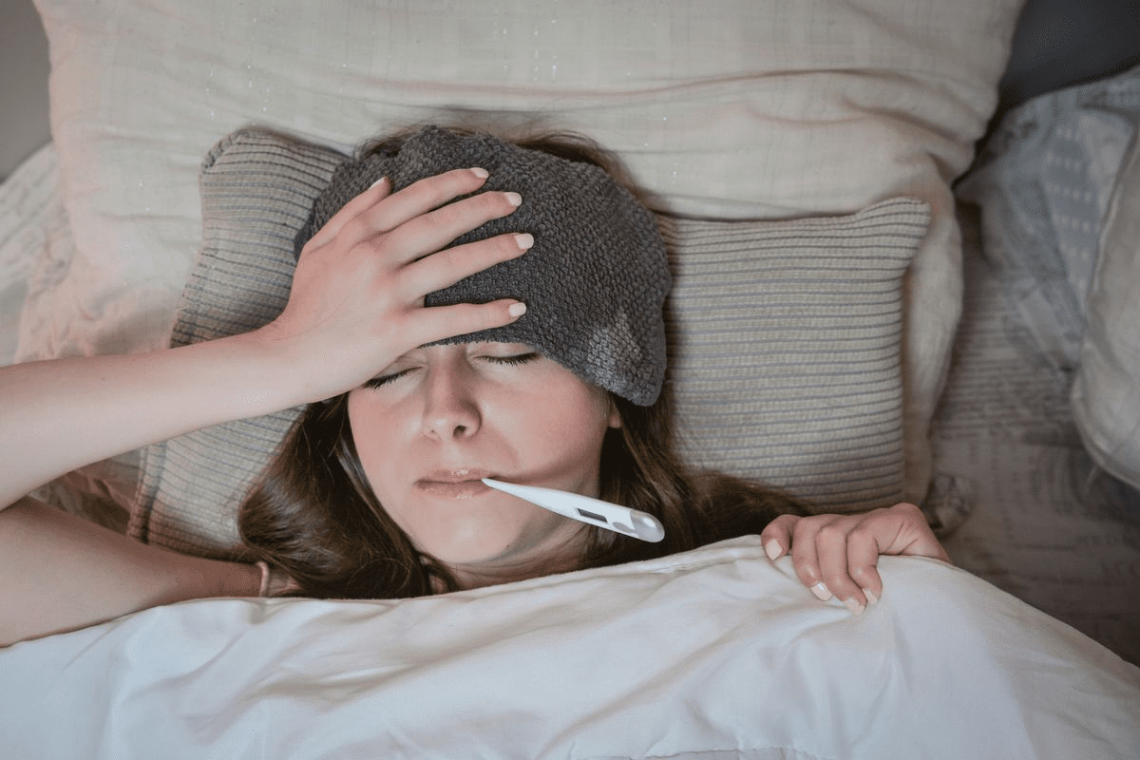
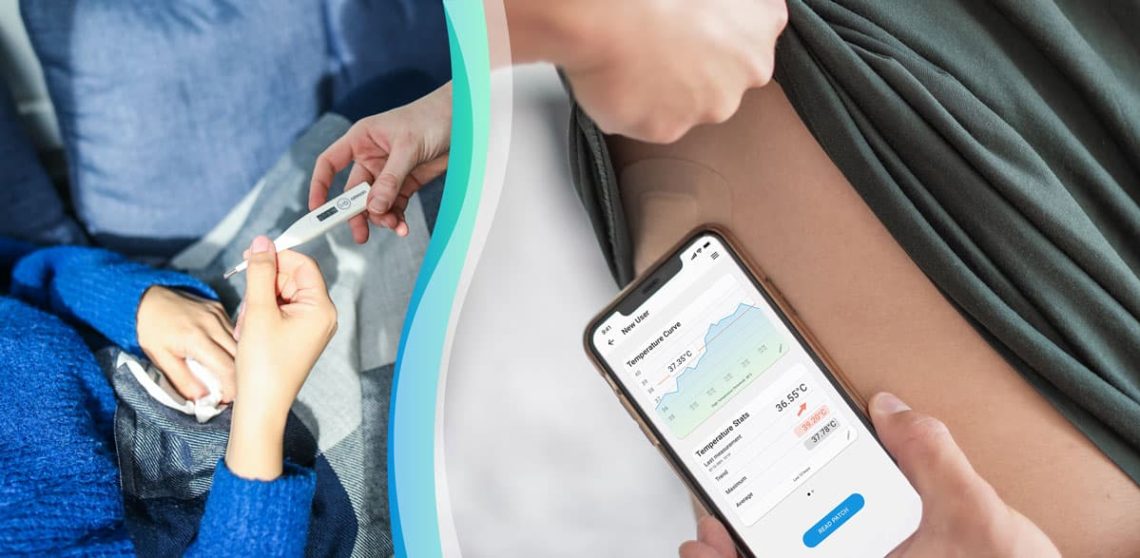
Introduction Fever is a common symptom of illness, signaling that the body is fighting an infection or inflammation. While most fevers are mild and self-limiting, monitoring and tracking fever accurately is essential to: Proper fever monitoring is especially important in infants, elderly individuals, and people with chronic health conditions. Why Monitoring Fever is Important Methods of Measuring Temperature Tip: Always use a calibrated thermometer and follow manufacturer instructions. How Often to Check Fever 1. Infants (<3 months) 2. Children (3 months–5 years) 3. Older Children and Adults General Rule: Monitor more frequently if the fever is high (>102°F / 38.9°C),…
-
Introduction Fever is typically a symptom of an identifiable infection or illness. However, in some cases, fever persists without an obvious cause despite initial evaluation. This is known as Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO). FUO presents a diagnostic challenge, requiring a systematic approach to identify underlying conditions, which may include infections, inflammatory disorders, malignancies, or rare diseases. Early recognition and careful evaluation are critical to ensure timely and appropriate treatment. Definition of FUO Traditionally, FUO is defined as: Note: Definitions may vary slightly based on guidelines, but the core concept remains a prolonged, unexplained fever. Common Causes of FUO While…
-
Introduction Fever is a natural immune response and often a sign of a mild illness, such as a viral infection. However, in certain situations, fever can be a warning sign of a serious, potentially life-threatening condition. Rapid recognition of these “red flag” fevers—especially those caused by meningitis or sepsis—can save lives. This article explains how to identify dangerous fever, the associated symptoms, and when to seek urgent medical care. Serious Causes of Fever 1. Meningitis 2. Sepsis Urgency: Sepsis requires immediate medical attention and hospitalization, often in an intensive care setting. Other Red Flag Situations Immediate Actions for Serious Fever…
-
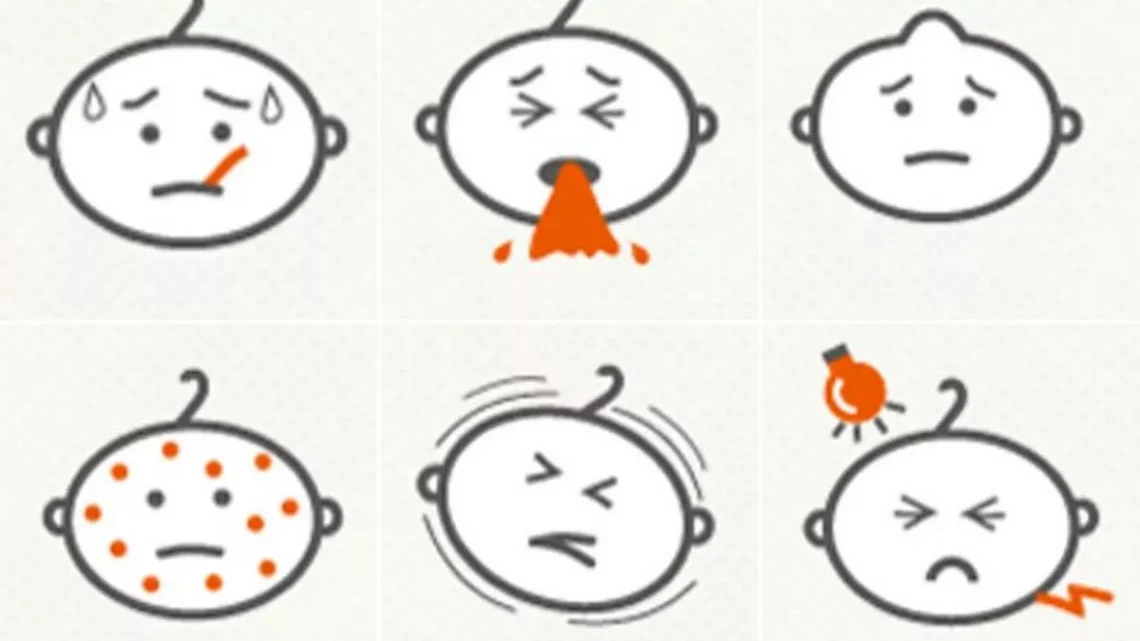
Introduction Fever is one of the most common symptoms prompting people to seek medical attention. It occurs when the body temperature rises above its normal range, usually as a response to infection, inflammation, or other triggers. Fever is not a disease itself but a signal that the body is fighting something. Understanding the underlying causes of fever, including common misconceptions like teething, helps in effective management and timely medical care. 1. Infections The most frequent cause of fever is infection. These can be: A. Viral Infections B. Bacterial Infections C. Other Infections 2. Inflammatory Conditions Fever can arise from non-infectious…
-
Introduction Febrile seizures are convulsions triggered by a rapid rise in body temperature, most commonly in children between 6 months and 5 years of age. They can be alarming for parents, but are usually benign and self-limiting. Understanding what febrile seizures are, why they happen, and how to respond is essential for parents and caregivers to provide safe care and reduce anxiety. What Are Febrile Seizures? Causes and Risk Factors Important: Most febrile seizures are harmless and do not indicate epilepsy or long-term neurological problems. Signs and Symptoms During a febrile seizure, you may notice: Duration: Typically less than 5…
-
Introduction Fever is the body’s natural response to infection or inflammation, helping the immune system fight pathogens. While mild fevers are generally beneficial, high or uncomfortable fevers can cause discomfort, dehydration, and fatigue. Along with medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, non-medication cooling techniques—such as sponging, light clothing, and hydration—can help manage fever safely. These strategies are especially important for children, elderly individuals, and anyone with prolonged or high fever. Why Cooling Techniques Matter Cooling techniques do not replace medications when needed but complement fever management. Sponging or Tepid Water Baths Tips: Light Clothing and Bedding Rationale: Reduces heat retention and…
-
Introduction Fever is a common symptom of infection, inflammation, or other illnesses. While mild fevers may not require treatment, high or uncomfortable fevers often prompt the use of over-the-counter (OTC) antipyretics such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) or ibuprofen. Correct dosing is critical for safety and effectiveness, especially in children, infants, and elderly patients. Misuse can lead to serious complications such as liver damage (acetaminophen) or stomach and kidney issues (ibuprofen). Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) for Fever How It Works Dosage Guidelines Age/Weight Dose Frequency Maximum in 24 Hours Infants 0–3 months 10–15 mg/kg Every 4–6 hours Consult doctor Infants/Children 3 months–12 years 10–15…