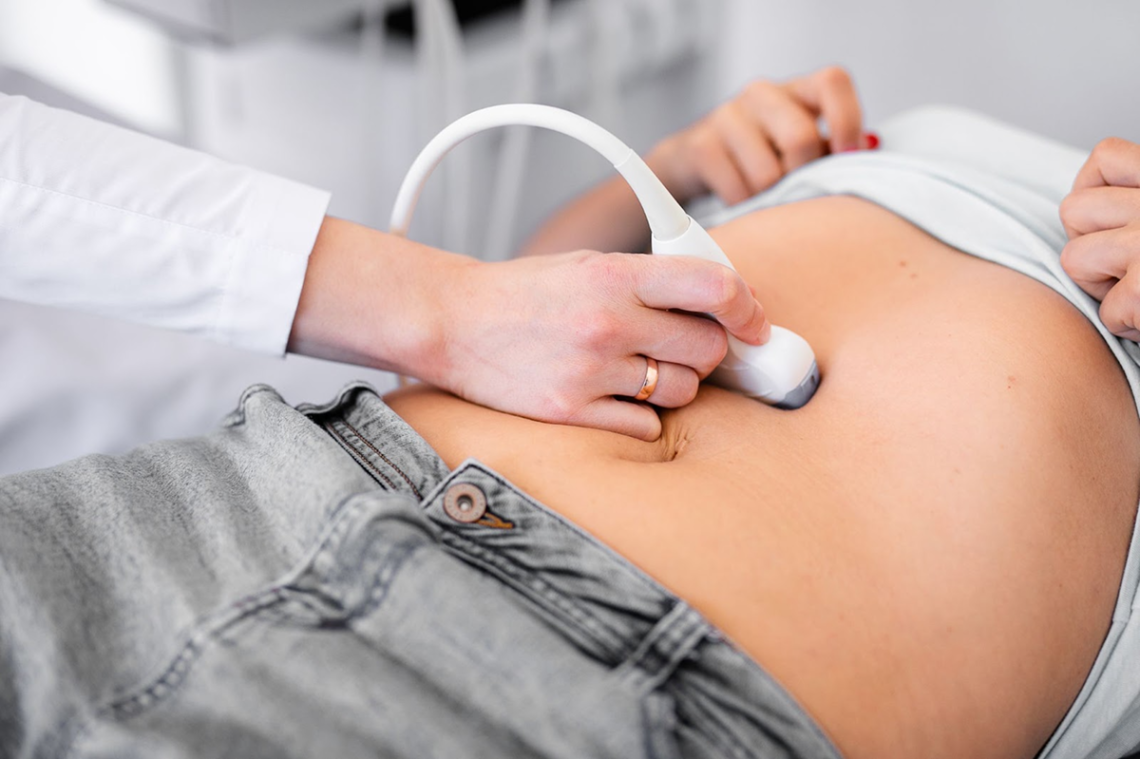
Introduction Abdominal pain is one of the most common complaints in healthcare, ranging from mild discomfort to severe, urgent conditions. Because the abdomen contains many vital organs—the stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, and reproductive organs—pinpointing the exact cause is not always simple. When the cause of pain isn’t obvious through history and physical examination alone, doctors may order diagnostic tests. These include laboratory studies, imaging scans, and endoscopic procedures (scopes). This article explains the common tests used to diagnose abdominal pain and what to expect from them. Initial Evaluation: History and Physical Exam Before ordering tests, your doctor will…
-
-
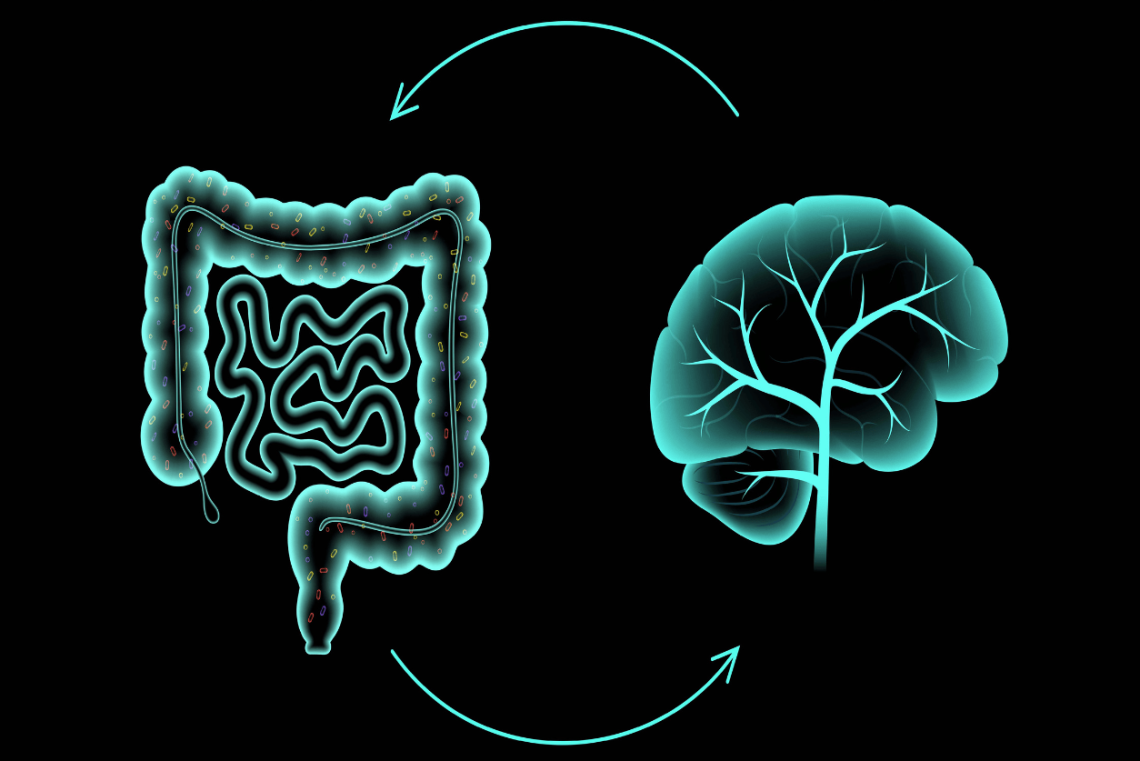
Introduction Many people notice that abdominal pain and digestive discomfort often worsen during stressful times. This is not just a coincidence—the gut and the brain are deeply interconnected through what scientists call the gut-brain axis. Stress can directly influence how the digestive system functions, while gut issues can also affect mood and mental health. Understanding this two-way relationship helps explain why conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are often linked with stress and anxiety, and why managing emotional health can play a vital role in reducing abdominal pain. What Is the Gut-Brain Axis? The gut-brain axis is the communication network…
-
Introduction Gas and bloating are common digestive complaints that can cause discomfort, embarrassment, and even pain. While occasional gas is normal, excessive bloating or persistent discomfort often relates to diet, lifestyle habits, or underlying digestive sensitivities. Fortunately, simple adjustments in eating patterns and daily routines can bring significant relief. This article explores effective dietary and lifestyle tips to help manage gas and bloating naturally. Understanding Gas and Bloating Dietary Tips for Gas and Bloating Relief 1. Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals 2. Limit Gas-Producing Foods 3. Try a Low-FODMAP Diet 4. Reduce Carbonated Drinks 5. Eat Slowly and Chew Thoroughly…
-
Introduction Abdominal pain is one of the most frequent complaints in children and a leading reason for pediatric doctor visits. While it is often caused by minor and temporary issues like indigestion or constipation, sometimes abdominal pain can signal something more serious that requires urgent medical care. Parents and caregivers often struggle to determine when to wait, when to treat symptoms at home, and when to seek professional help. Understanding the common causes of abdominal pain in children, as well as the warning signs of serious illness, can help ensure timely and appropriate care. Common Causes of Abdominal Pain in…
-
Introduction Abdominal pain is one of the most common reasons people seek medical care. In most cases, it is caused by minor issues such as indigestion, gas, or mild infections. However, sometimes abdominal pain signals a serious underlying condition that requires immediate medical attention. Recognizing red flag symptoms can be lifesaving, as they often point to urgent problems like appendicitis, bowel obstruction, perforated ulcers, internal bleeding, or even cancer. This article will help you understand when abdominal pain is an emergency, what warning signs to watch for, and when to seek medical help without delay. Why Abdominal Pain Can Be…
-
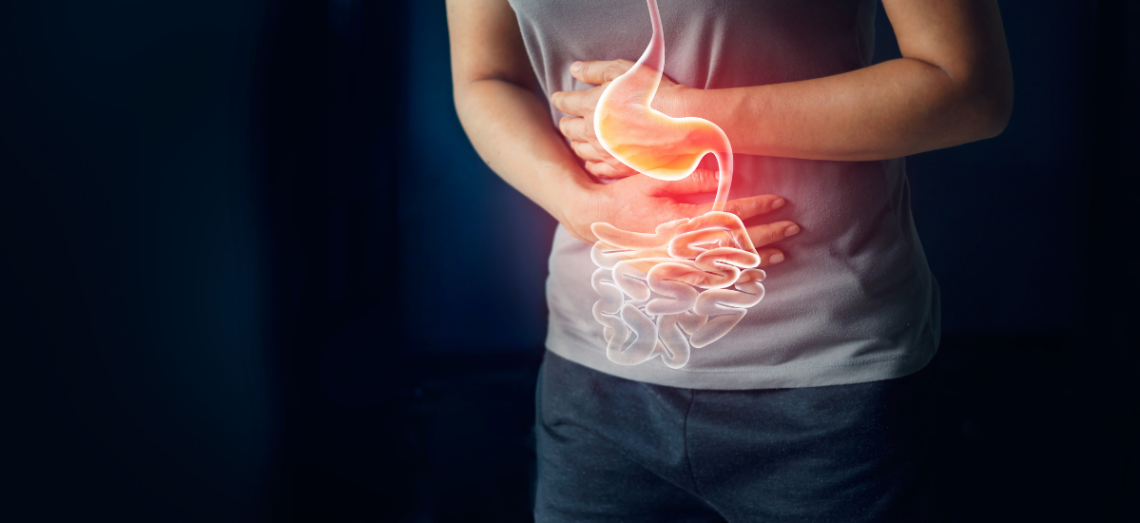
Introduction Chronic abdominal pain is a persistent and often distressing symptom that affects millions of people worldwide. Unlike acute abdominal pain, which typically comes on suddenly and resolves with treatment, chronic abdominal pain lasts for weeks, months, or even years. It can interfere with daily activities, negatively impacting one’s quality of life. Chronic abdominal pain can be caused by a range of gastrointestinal conditions, including Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), and functional disorders. These conditions often present with overlapping symptoms, making accurate diagnosis and treatment essential for effective management. In this article, we…
-
Introduction Hiccups are usually short-lived and harmless, resolving without any treatment. However, when hiccups persist for more than 48 hours (persistent hiccups) or even longer than 2 months (intractable hiccups), they can significantly disrupt eating, sleeping, and overall well-being. Persistent hiccups often indicate an underlying medical condition and may require professional medical interventions. This article explores the medical approaches used to evaluate and manage persistent hiccups, including diagnostic steps, medications, and more advanced treatments. Step 1: Medical Evaluation Before treating hiccups, doctors aim to identify the underlying cause. A thorough evaluation may include: Once the cause is determined, treatment focuses…
-
Introduction Hiccups are a quirky, involuntary reflex that almost everyone has experienced. They usually start when the diaphragm contracts suddenly, often triggered by eating too quickly, swallowing air, or drinking carbonated beverages. While most hiccups resolve on their own, people throughout history have developed countless remedies—some unusual, yet surprisingly effective. These folk remedies may not always have strong scientific backing, but many are rooted in practical logic or traditional wisdom. In this article, we’ll explore some of the most unusual but effective hiccup remedies from around the world. 1. Drinking Water in Strange Ways Drinking Upside Down Sipping Ice-Cold Water…
-
Introduction Hiccups, or singultus, are involuntary contractions of the diaphragm followed by a sudden closure of the vocal cords. Most hiccups are harmless and short-lived, but persistent hiccups can be irritating. Among the many home remedies, the sugar swallow trick is a classic and widely used method. But how does it work, and why might it stop hiccups? Let’s explore the science behind this simple remedy. 1. How to Perform the Sugar Swallow Trick Step-by-Step Instructions Note: Avoid using powdered sugar or sugar substitutes, as the texture may not provide the same effect. 2. Why It Might Work The sugar…
-
Introduction Hiccups, medically known as singultus, are involuntary contractions of the diaphragm, followed by a sudden closure of the vocal cords. While most hiccups are harmless, they can be uncomfortable and disruptive. One effective, non-invasive way to stop hiccups is through diaphragmatic breathing, a technique that directly targets the muscle responsible for the hiccup reflex. By calming and controlling the diaphragm, this method can often resolve hiccups quickly. 1. Understanding the Diaphragm and Hiccups The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located beneath the lungs, essential for breathing. Hiccups occur when the diaphragm spasms involuntarily, triggering the characteristic “hic” sound. Techniques…