Introduction Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, occurs when your blood glucose drops below 70 mg/dL. It’s a common but potentially serious issue, especially for people with diabetes who use insulin or other glucose-lowering medications. If untreated, it can lead to confusion, unconsciousness, seizures, or even death. This guide explains what hypoglycemia is, why it happens, how to spot it early, and how to treat it safely and effectively. What Is Hypoglycemia? Hypoglycemia happens when the level of glucose (sugar) in your blood drops too low to fuel your body’s activities—especially the brain, which depends heavily on glucose. Blood Sugar Levels…
-
-
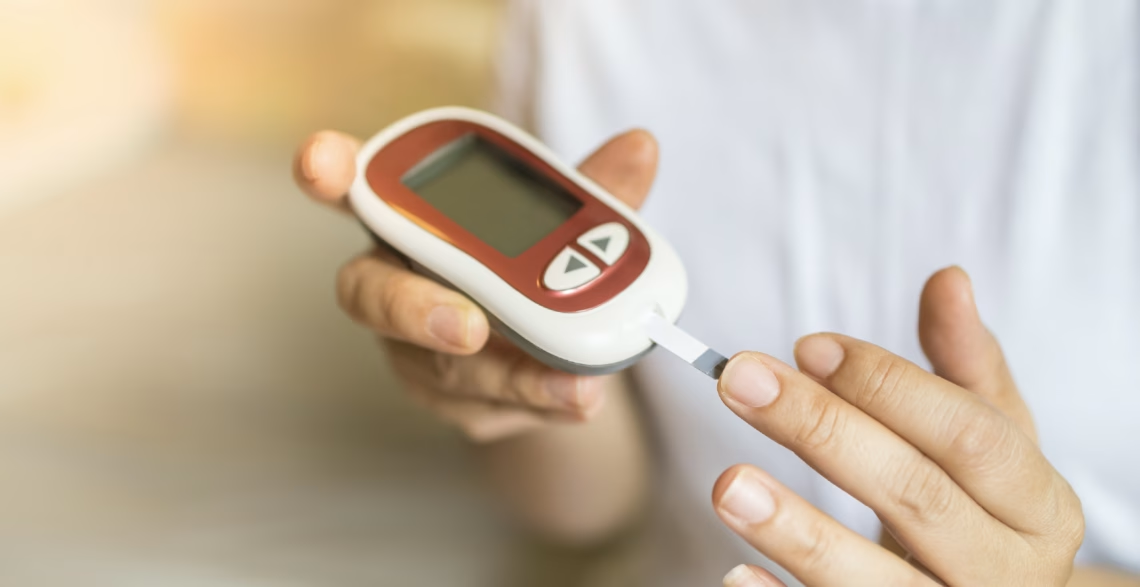
Introduction For individuals living with diabetes or at risk, blood sugar monitoring is one of the most important tools in managing their condition. Whether you’re using a traditional glucose meter or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM), tracking your glucose levels helps prevent complications and guides daily decisions on diet, activity, and medication. Understanding the available monitoring tools and knowing your target ranges is essential for effective diabetes management. 1. Why Monitor Blood Sugar? Regular monitoring helps: Monitoring is recommended for: 2. Blood Glucose Monitoring Methods Traditional Blood Glucose Meters (BGM) How it works: Pros: Cons: Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) How…
-
Introduction Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). There are two primary forms: Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. While both result in elevated blood sugar levels, they have different causes, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment approaches. Understanding the differences between these two types is crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and long-term health. 1. What Is Diabetes? Diabetes occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin properly. Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that helps glucose enter the cells to be used for energy.…
-
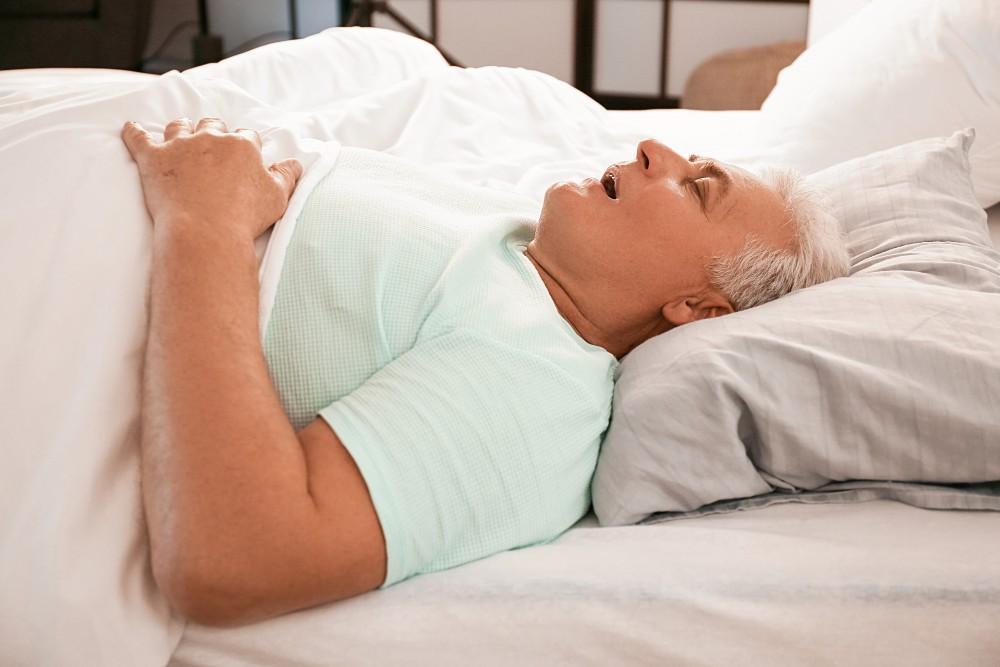
Introduction Sleep is essential for overall health, but when it’s interrupted by breathing problems, it can have serious consequences—especially for the heart. Sleep apnea, a common and often undiagnosed sleep disorder, does more than just cause fatigue. Research has clearly shown a strong link between sleep apnea and heart disease, including high blood pressure, arrhythmias, heart failure, stroke, and even sudden cardiac death. Understanding this connection is vital for early diagnosis and treatment, potentially reducing the risk of life-threatening cardiovascular complications. 1. What is Sleep Apnea? Sleep apnea is a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. There…
-
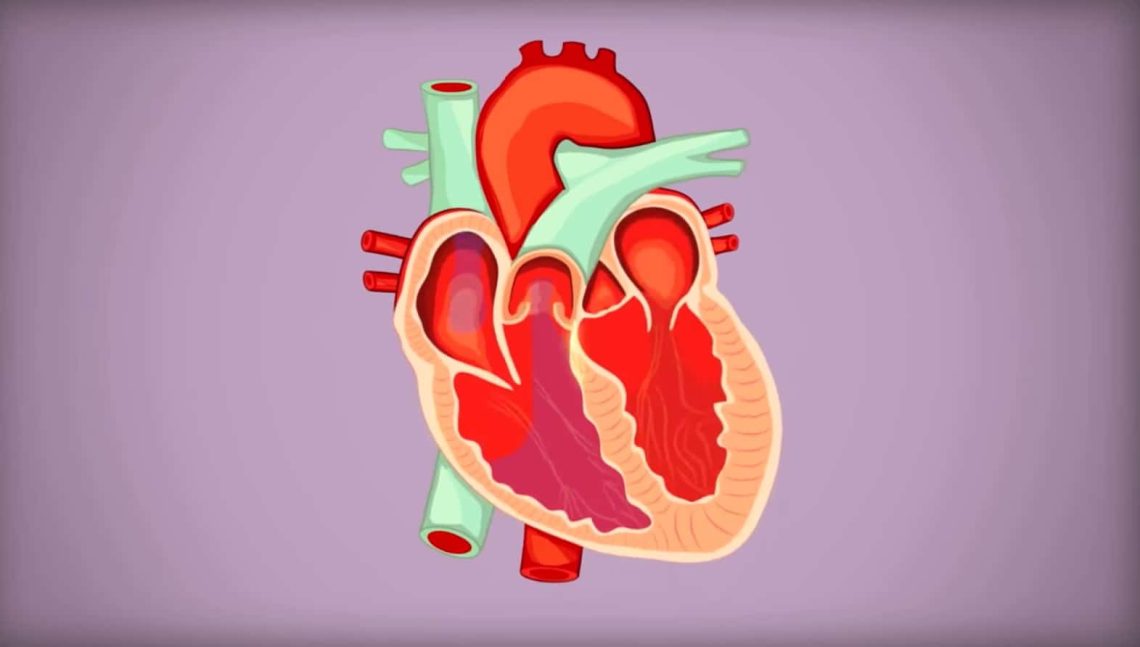
Introduction A healthy heart beats in a steady, rhythmic pattern—about 60 to 100 times per minute at rest. But when that rhythm becomes irregular, too fast, or too slow, it’s known as an arrhythmia. While some arrhythmias are harmless and go unnoticed, others can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Understanding the different types of arrhythmias—from atrial fibrillation (AFib) to premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)—is key to recognizing symptoms early and managing treatment effectively. This article provides a comprehensive overview of common arrhythmias, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. 1. What Is an Arrhythmia? An arrhythmia is an abnormal…
-
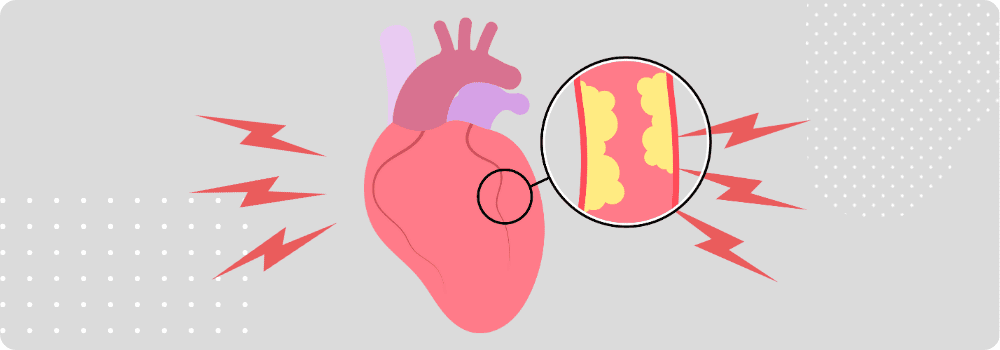
Introduction Angina, often described as chest discomfort or pressure, is a symptom of underlying heart disease rather than a disease itself. It occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood, usually due to narrowed coronary arteries. Recognizing angina is critical because it can signal coronary artery disease (CAD) or an increased risk of heart attack. This article delves into the different types of angina, their triggers, and effective treatment strategies, helping readers understand how to manage this condition and protect heart health. What is Angina? Angina is characterized by discomfort, pressure, or tightness in the chest that…
-
Introduction Heart disease remains the leading cause of death globally, and heart attacks (myocardial infarctions) are a critical manifestation of this condition. Traditionally, chest pain has been considered the hallmark symptom of a heart attack. However, research and clinical observations reveal that symptoms often vary, especially in women, whose experiences can differ significantly from the classic presentations. Recognizing these non-traditional symptoms can be life-saving, as early intervention dramatically improves outcomes. This article explores the broader spectrum of heart attack symptoms, with a focus on understanding gender-specific differences. Understanding Heart Attacks A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to a…
-
Introduction Facing a serious illness such as cancer, heart failure, or advanced lung disease can be overwhelming—not just physically but emotionally and psychologically. Supportive care services like palliative care and hospice are designed to improve the quality of life for patients and families coping with serious health challenges. Although often confused, palliative care and hospice serve distinct roles and apply at different stages of illness. This article explores the differences and similarities between palliative care and hospice, when each is appropriate, and how they help patients and caregivers throughout the healthcare journey. What is Palliative Care? Palliative care is specialized…
-
Introduction Completing cancer treatment marks a significant milestone, but it also ushers in a new phase known as cancer survivorship. Survivors often face unique physical, emotional, and social challenges as they transition from active treatment to post-treatment life. Understanding these challenges and adopting strategies to maintain health and well-being is essential for a fulfilling life after cancer. This article explores the concept of cancer survivorship, common physical and emotional issues faced by survivors, and practical approaches to promote long-term health. What is Cancer Survivorship? Cancer survivorship begins at diagnosis and continues through the remainder of a person’s life. It encompasses:…
-
Introduction Chemotherapy is a powerful cancer treatment that uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. While effective, it often comes with side effects due to its impact on both cancerous and healthy cells. Among the most common and challenging side effects are nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. Managing these symptoms is essential to maintain quality of life, ensure treatment adherence, and support overall well-being. This article explores why these side effects occur, strategies for managing them, and tips for patients undergoing chemotherapy. Why Do Chemotherapy Side Effects Occur? Chemotherapy drugs target rapidly dividing cells, which include cancer cells but also affect…