Introduction Most people associate heart attacks with chest pain, but heart attacks can present in less obvious ways. Symptoms such as jaw pain, back pain, or stomach discomfort are sometimes the only warning signs, particularly in women, older adults, and diabetics. Recognizing these atypical presentations is critical, as delayed treatment increases the risk of heart muscle damage, complications, or death. This article explores unusual heart attack symptoms, why they occur, and what actions to take immediately. Jaw Pain as a Heart Attack Symptom Back Pain as a Heart Attack Symptom Stomach Pain or Abdominal Discomfort Why Heart Attacks Present Atypically…
-
-
Introduction Sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, and palpitations can be alarming. These symptoms may indicate a heart attack, but they can also occur during a panic attack. Distinguishing between the two is crucial, as a heart attack is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention, whereas a panic attack, though frightening, is not immediately life-threatening. Misinterpreting the signs can delay critical care or cause unnecessary panic. This article explains key differences, warning signs, risk factors, and when to seek help. Heart Attack Symptoms Heart attacks occur when blood flow to the heart is blocked, usually due to a clot in…
-
Introduction When it comes to strokes and heart attacks, time is critical. The faster a person receives treatment, the better the chances of minimizing long-term damage and improving survival. The acronym FAST is widely used to help recognize stroke symptoms quickly, enabling prompt medical attention. Understanding FAST and the urgency of early action can save lives and reduce complications. What Does FAST Stand For? FAST is a simple tool to identify stroke symptoms quickly: Why Time is Critical Recognizing Symptoms Beyond FAST While FAST is highly effective, other warning signs may occur: For Stroke For Heart Attack Recognizing these symptoms…
-
Introduction People with diabetes are at higher risk of heart disease and heart attacks compared to the general population. One of the challenges is that heart attack symptoms in diabetics can be atypical or subtle, often leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Understanding how diabetes affects symptom presentation is crucial for early recognition and timely medical intervention. This article explains why diabetics may experience silent or atypical heart attacks, the common and subtle symptoms, risk factors, and strategies for prevention and early detection. Why Heart Attack Symptoms Can Be Different in Diabetics Common and Atypical Heart Attack Symptoms in Diabetics…
-
Introduction A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, usually conjures images of sudden chest pain. However, some heart attacks occur without noticeable symptoms, and are known as silent heart attacks. Despite the absence of classic warning signs, silent heart attacks are serious and can cause permanent heart damage or even be fatal. Recognizing risk factors and subtle symptoms is essential for prevention and early intervention. What is a Silent Heart Attack? Causes of Silent Heart Attacks Risk Factors for Silent Heart Attacks Subtle Symptoms to Watch For Even without chest pain, silent heart attacks may present with mild or unusual symptoms,…
-
Introduction Heart attacks, or myocardial infarctions, are a leading cause of death among women worldwide. Unlike men, who often experience classic symptoms such as chest pain and left arm discomfort, women frequently present with atypical or subtle symptoms. Awareness of these signs is critical, as delayed recognition can lead to serious complications or death. This article explores the common atypical symptoms of heart attacks in women, risk factors, and preventive strategies. Atypical Heart Attack Symptoms in Women 1. Shortness of Breath 2. Unusual Fatigue 3. Nausea or Vomiting 4. Pain in Jaw, Neck, or Back 5. Sweating and Dizziness 6.…
-
Introduction Heart attacks, also known as myocardial infarctions, occur when blood flow to the heart is blocked, often by a blood clot or plaque buildup in the coronary arteries. Early recognition of symptoms is crucial, as timely medical intervention can save lives and reduce heart damage. Men may experience classic heart attack signs, but symptoms can sometimes be subtle or mistaken for other conditions. Understanding these signs helps in rapid identification and immediate response. Classic Heart Attack Symptoms in Men 1. Chest Pain or Discomfort 2. Pain in the Arm, Shoulder, or Jaw 3. Shortness of Breath 4. Sweating 5.…
-
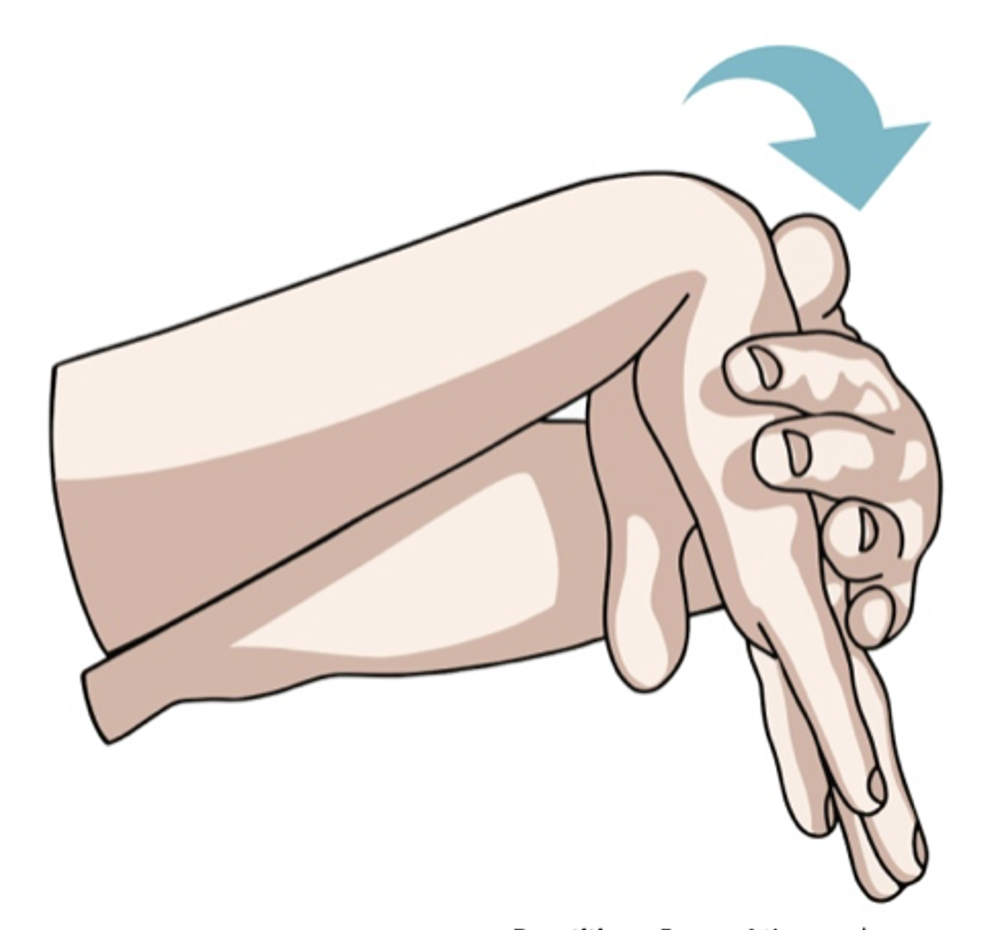
Introduction Pregnancy is often associated with well-known symptoms such as nausea, fatigue, and frequent urination. However, many women experience less common symptoms that can be surprising or uncomfortable. Nosebleeds, skin changes, and carpal tunnel syndrome are among these symptoms, caused by hormonal fluctuations, increased blood volume, and physical changes. Understanding these symptoms, why they occur, and how to manage them can help expectant mothers feel more prepared and comfortable throughout pregnancy. Nosebleeds During Pregnancy Why They Occur Managing Nosebleeds Skin Changes During Pregnancy Common Skin Changes Managing Skin Changes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Pregnancy Why It Happens Managing Carpal Tunnel…
-
Introduction Pregnancy is a time of profound physical transformation, and it is accompanied by emotional changes and mood swings. Hormonal shifts, physical discomfort, life adjustments, and anticipation of motherhood can all influence a pregnant woman’s mood and mental well-being. While mood swings are a normal part of pregnancy, understanding them helps women manage emotions, communicate with loved ones, and seek help when needed. This article explores the causes, common patterns, coping strategies, and warning signs related to emotional changes during pregnancy. Why Emotional Changes Occur During Pregnancy 1. Hormonal Fluctuations 2. Physical Discomfort 3. Psychological Adjustments 4. Social and Environmental…
-
Introduction During pregnancy, women often experience uterine contractions, which can cause confusion about whether labor has started. Some contractions are practice contractions, known as Braxton Hicks, while others indicate true labor. Recognizing the difference between these two types is essential for timely preparation, reducing anxiety, and knowing when to seek medical attention. This article explains the differences between Braxton Hicks contractions and real labor contractions, their characteristics, and practical tips for monitoring them. What Are Braxton Hicks Contractions? What Are Real Labor Contractions? Key Differences Between Braxton Hicks and Real Labor Contractions Feature Braxton Hicks Contractions Real Labor Contractions Timing/Regularity…