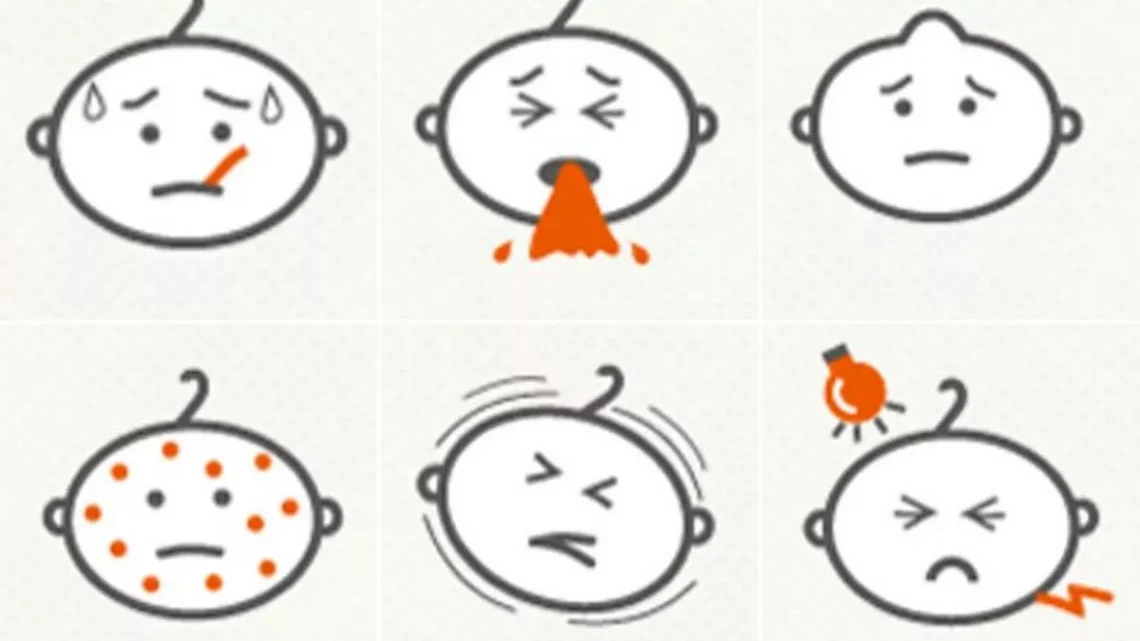
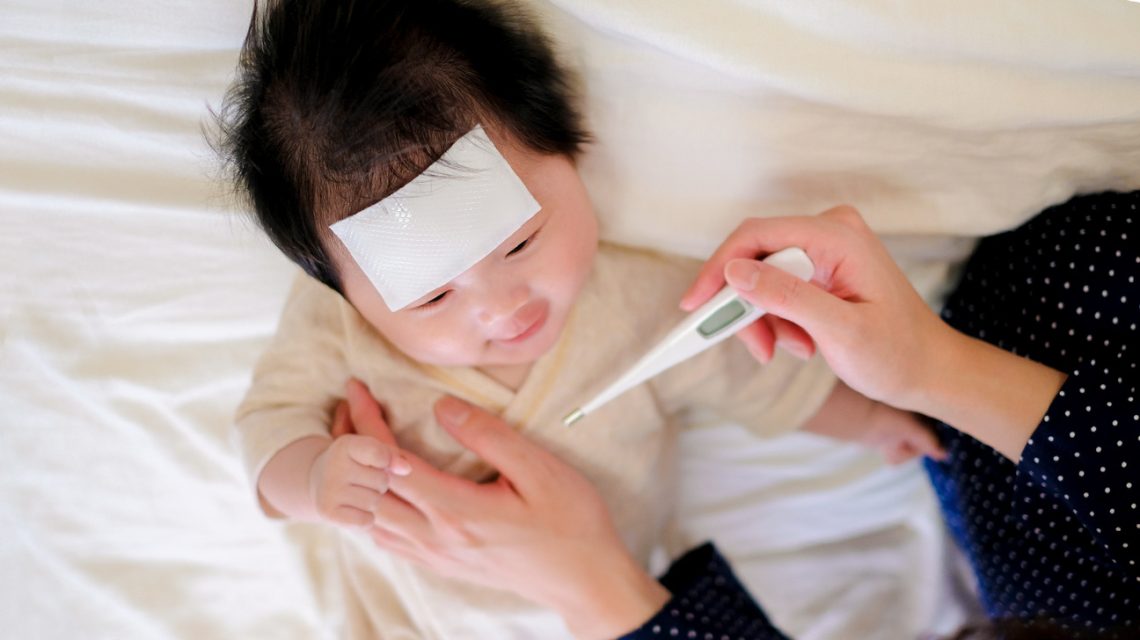
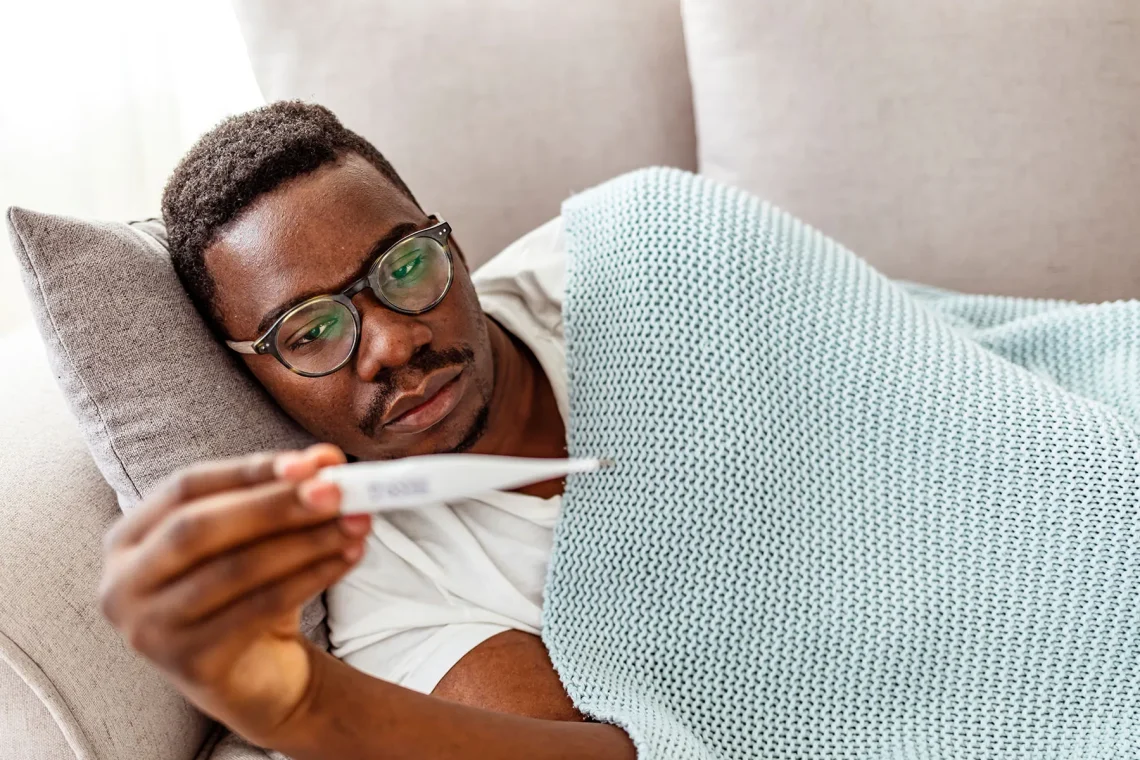
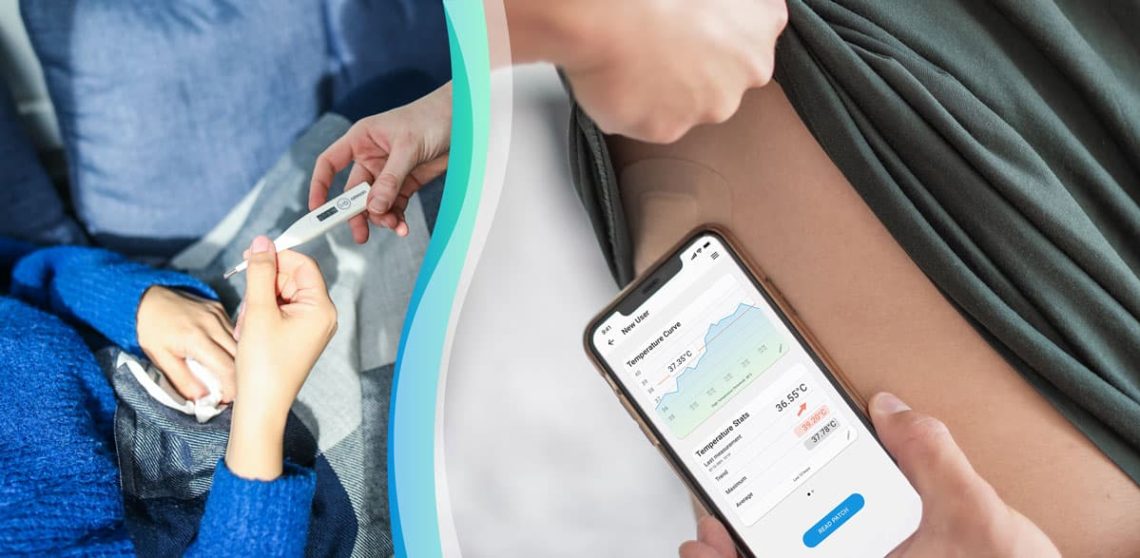
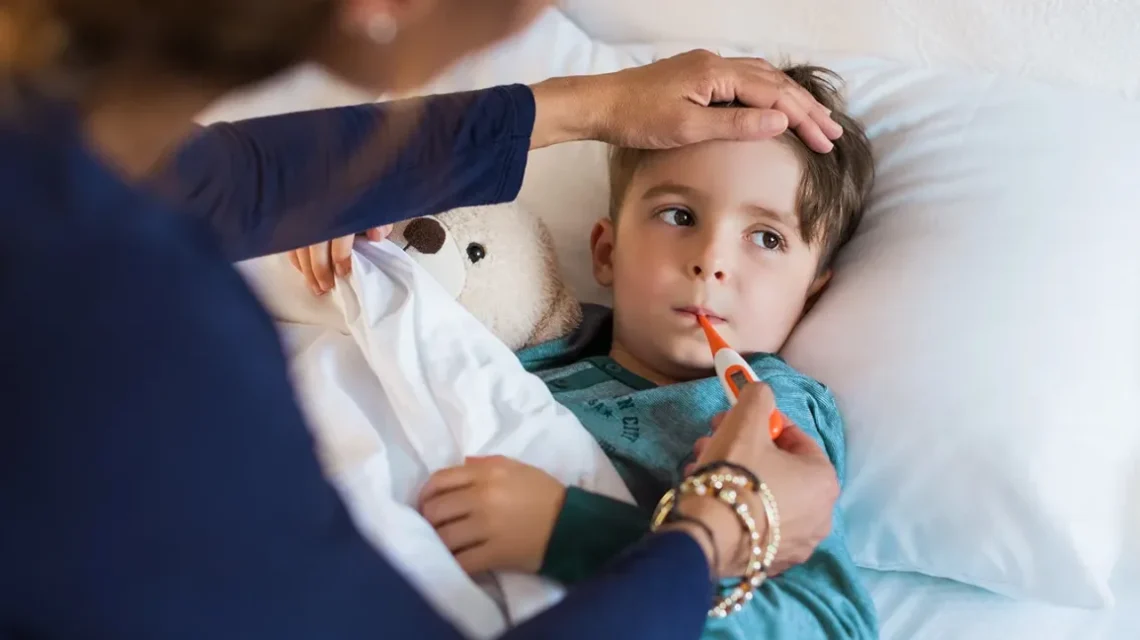
Introduction Fever is a common symptom of illness, signaling that the body is fighting an infection or inflammation. While most fevers are mild and self-limiting, monitoring and tracking fever accurately is essential to: Proper fever monitoring is especially important in infants, elderly individuals, and people with chronic health conditions. Why Monitoring Fever is Important Methods of Measuring Temperature Tip: Always use a calibrated thermometer and follow manufacturer instructions. How Often to Check Fever 1. Infants (<3 months) 2. Children (3 months–5 years) 3. Older Children and Adults General Rule: Monitor more frequently if the fever is high (>102°F / 38.9°C),…
-
-
Introduction Fever is typically a symptom of an identifiable infection or illness. However, in some cases, fever persists without an obvious cause despite initial evaluation. This is known as Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO). FUO presents a diagnostic challenge, requiring a systematic approach to identify underlying conditions, which may include infections, inflammatory disorders, malignancies, or rare diseases. Early recognition and careful evaluation are critical to ensure timely and appropriate treatment. Definition of FUO Traditionally, FUO is defined as: Note: Definitions may vary slightly based on guidelines, but the core concept remains a prolonged, unexplained fever. Common Causes of FUO While…
-
Introduction Fever is a natural immune response and often a sign of a mild illness, such as a viral infection. However, in certain situations, fever can be a warning sign of a serious, potentially life-threatening condition. Rapid recognition of these “red flag” fevers—especially those caused by meningitis or sepsis—can save lives. This article explains how to identify dangerous fever, the associated symptoms, and when to seek urgent medical care. Serious Causes of Fever 1. Meningitis 2. Sepsis Urgency: Sepsis requires immediate medical attention and hospitalization, often in an intensive care setting. Other Red Flag Situations Immediate Actions for Serious Fever…
-
Introduction Fever is one of the most common symptoms prompting people to seek medical attention. It occurs when the body temperature rises above its normal range, usually as a response to infection, inflammation, or other triggers. Fever is not a disease itself but a signal that the body is fighting something. Understanding the underlying causes of fever, including common misconceptions like teething, helps in effective management and timely medical care. 1. Infections The most frequent cause of fever is infection. These can be: A. Viral Infections B. Bacterial Infections C. Other Infections 2. Inflammatory Conditions Fever can arise from non-infectious…
-
Introduction Fever is the body’s natural response to infection or inflammation, helping the immune system fight pathogens. While mild fevers are generally beneficial, high or uncomfortable fevers can cause discomfort, dehydration, and fatigue. Along with medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, non-medication cooling techniques—such as sponging, light clothing, and hydration—can help manage fever safely. These strategies are especially important for children, elderly individuals, and anyone with prolonged or high fever. Why Cooling Techniques Matter Cooling techniques do not replace medications when needed but complement fever management. Sponging or Tepid Water Baths Tips: Light Clothing and Bedding Rationale: Reduces heat retention and…
-
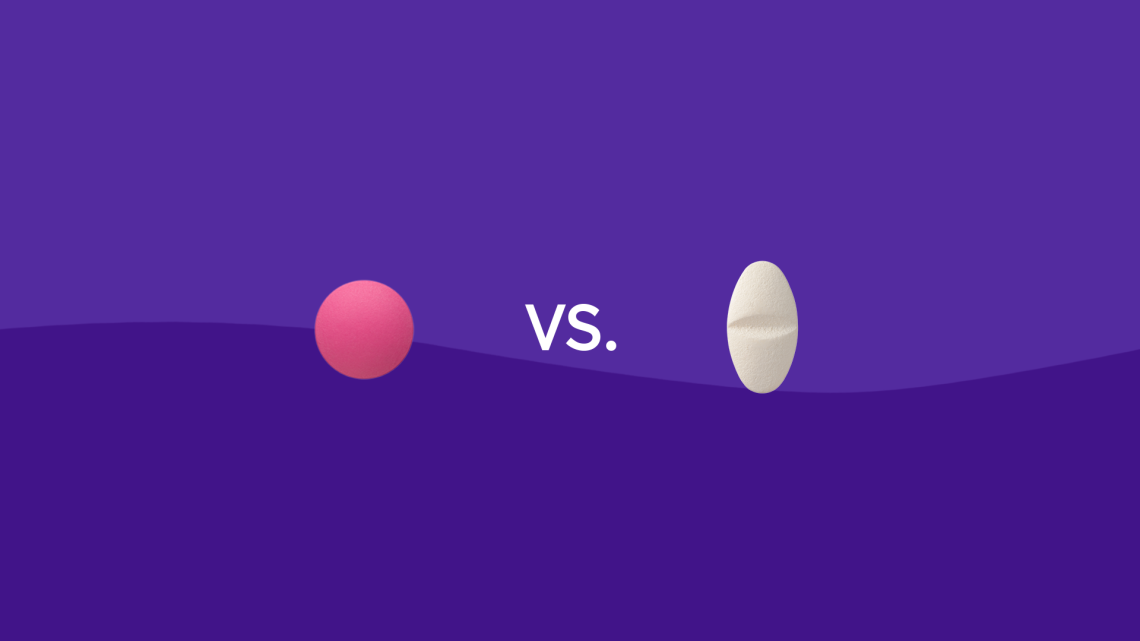
Introduction Fever is a common symptom of infection, inflammation, or other illnesses. While mild fevers may not require treatment, high or uncomfortable fevers often prompt the use of over-the-counter (OTC) antipyretics such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) or ibuprofen. Correct dosing is critical for safety and effectiveness, especially in children, infants, and elderly patients. Misuse can lead to serious complications such as liver damage (acetaminophen) or stomach and kidney issues (ibuprofen). Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) for Fever How It Works Dosage Guidelines Age/Weight Dose Frequency Maximum in 24 Hours Infants 0–3 months 10–15 mg/kg Every 4–6 hours Consult doctor Infants/Children 3 months–12 years 10–15…
-
Introduction Fever in infants under 3 months of age is considered a medical emergency. Unlike older children and adults, young infants have immature immune systems and may not show typical signs of illness. Even a mild temperature elevation in this age group can indicate a serious bacterial or viral infection, such as sepsis, urinary tract infection, or meningitis. Prompt medical evaluation is essential to prevent complications, identify the underlying cause, and initiate timely treatment. Understanding Fever in Young Infants Causes of Fever in Infants Under 3 Months Fever may indicate serious or minor conditions, but all cases should be evaluated…
-
Introduction Fever is a common physiological response defined as an elevation of body temperature above the normal range, typically due to infection or inflammation. It is a sign that the body’s immune system is active, fighting off harmful pathogens like viruses, bacteria, or other disease triggers. While fever is often uncomfortable, it is not always harmful; in fact, a mild to moderate fever can be beneficial, enhancing immune defense. However, fever can sometimes be dangerous or extremely uncomfortable, particularly in infants, the elderly, or individuals with underlying medical conditions. Knowing when to treat a fever and when it is safe…
-
Introduction A fever is a temporary rise in body temperature, usually as a response to infection, inflammation, or other medical conditions. While commonly associated with illness, not all temperature elevations indicate a serious problem. Understanding normal body temperature ranges by age and what constitutes a fever is essential for proper monitoring and timely medical care. Body temperature can vary by age, time of day, activity level, and measurement method (oral, rectal, ear, forehead, or axillary). Normal Body Temperature Ranges by Age Age Group Normal Body Temperature Newborns (0–3 months) 97.9–100.4°F (36.6–38°C) Infants (3–12 months) 99–100.4°F (37.2–38°C) Toddlers (1–3 years) 98.6–100.4°F…
-
Introduction Strep throat is widely recognized as a bacterial infection characterized by a sudden sore throat accompanied by fever, swollen lymph nodes, and white patches on the tonsils. Fever is often considered one of the hallmark symptoms. However, can you have strep throat without a fever? This question is important because missing or misinterpreting symptoms can delay diagnosis and treatment, potentially leading to complications. This article explores the possibility of strep throat without a fever, how it presents, the importance of accurate diagnosis, and what to do if you suspect you have strep throat without the classic symptom of fever.…