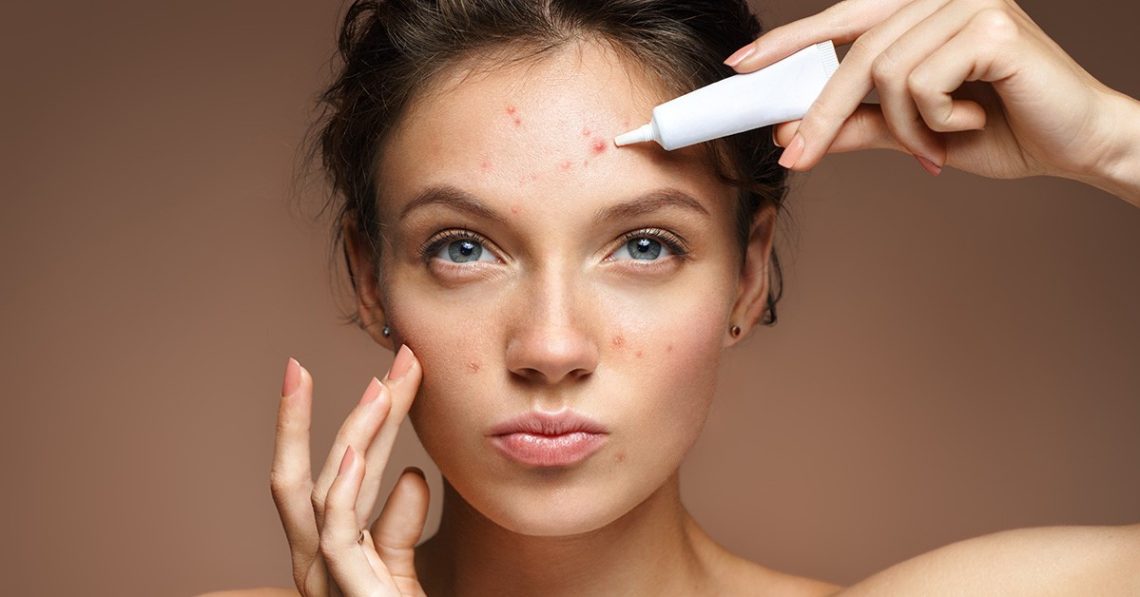
Introduction Glucose oxidase is an enzyme widely used in various industries, including healthcare, food processing, and biotechnology. It plays a crucial role in the breakdown of glucose, a type of sugar, into hydrogen peroxide and gluconic acid. This enzyme has significant applications in medicine, where it is used in diagnostic tests, wound care, and the treatment of certain medical conditions. In addition, it has been explored for its potential in addressing various metabolic disorders. This article delves into the essential details about glucose oxidase, including its definition, mechanism of action, common uses, benefits, risks, and how to use it properly.…
-
-
Introduction Lysozyme is a naturally occurring enzyme found in many bodily fluids such as tears, saliva, and mucus. Known for its antibacterial properties, it serves as a first line of defense in the human immune system. It has applications in medicine, food preservation, and cosmetics due to its antimicrobial action. As a supplement or topical ingredient, lysozyme has gained interest for its safety profile and versatility. What is Lysozyme? Lysozyme is an enzyme that breaks down the cell walls of bacteria, especially Gram-positive types. It is classified as a glycoside hydrolase and was first discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1922.…
-
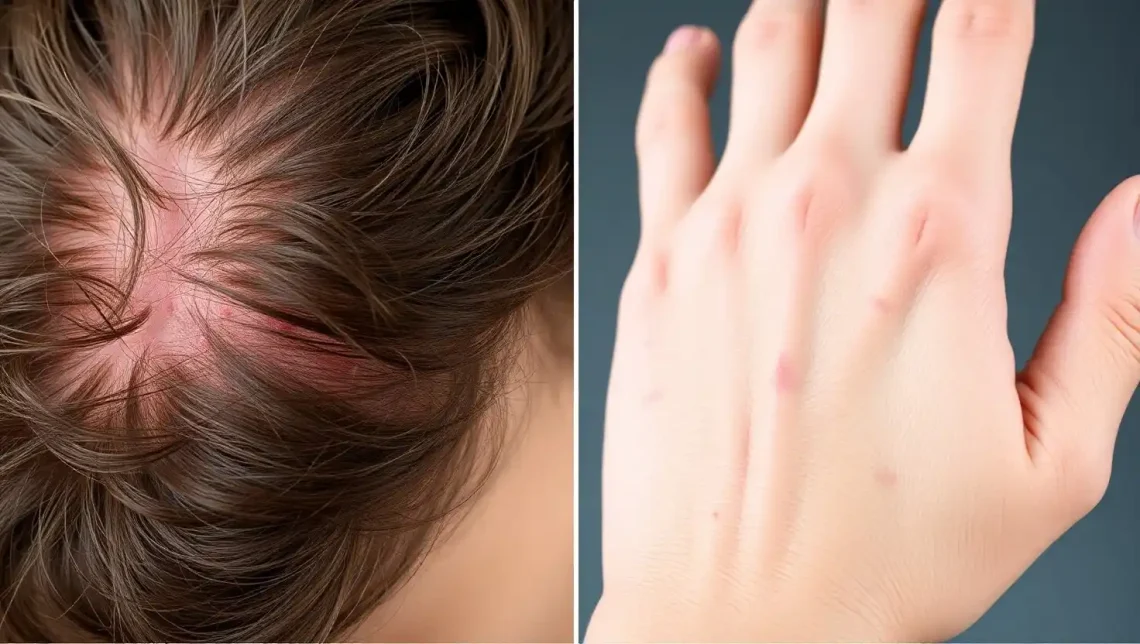
Introduction Lactoperoxidase is a naturally occurring enzyme found in milk, saliva, tears, and other bodily secretions. Known for its antimicrobial properties, it is a key component of the body’s natural defense system. Today, lactoperoxidase is widely used in cosmetics, oral hygiene products, food preservation, and even pharmaceutical formulations. Due to its broad range of uses and natural origin, it is generally considered safe when used appropriately. What is Lactoperoxidase? Lactoperoxidase is a heme-containing peroxidase enzyme, primarily found in mammalian secretions such as cow’s milk and human saliva. It is part of the peroxidase family of enzymes that function by breaking…
-
Introduction Benzocaine is a local anesthetic commonly used to relieve pain and discomfort caused by minor skin irritations, sore throat, dental issues, earaches, and other conditions. Known for its fast-acting numbing effect, it is available in various over-the-counter (OTC) products like gels, sprays, lozenges, and ointments. While effective and generally safe for short-term use, it must be used with caution due to potential side effects and specific warnings. What is Benzocaine? Benzocaine is a topical anesthetic derived from para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). It works by temporarily blocking nerve signals in the body, making it useful for numbing pain and itchiness on…
-
Introduction Hyaluronan, also known as hyaluronic acid, is a naturally occurring substance in the human body, particularly in connective tissues, skin, and eyes. Celebrated for its exceptional moisture-retaining properties, it plays a vital role in maintaining skin hydration, joint lubrication, and wound healing. In recent years, hyaluronan has gained prominence in both medical and cosmetic industries for its versatile therapeutic and rejuvenating effects. What is Hyaluronan? Hyaluronan is a type of glycosaminoglycan, a long-chain sugar molecule that is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It is most abundant in the skin, synovial fluid (around joints), and the vitreous humor…
-
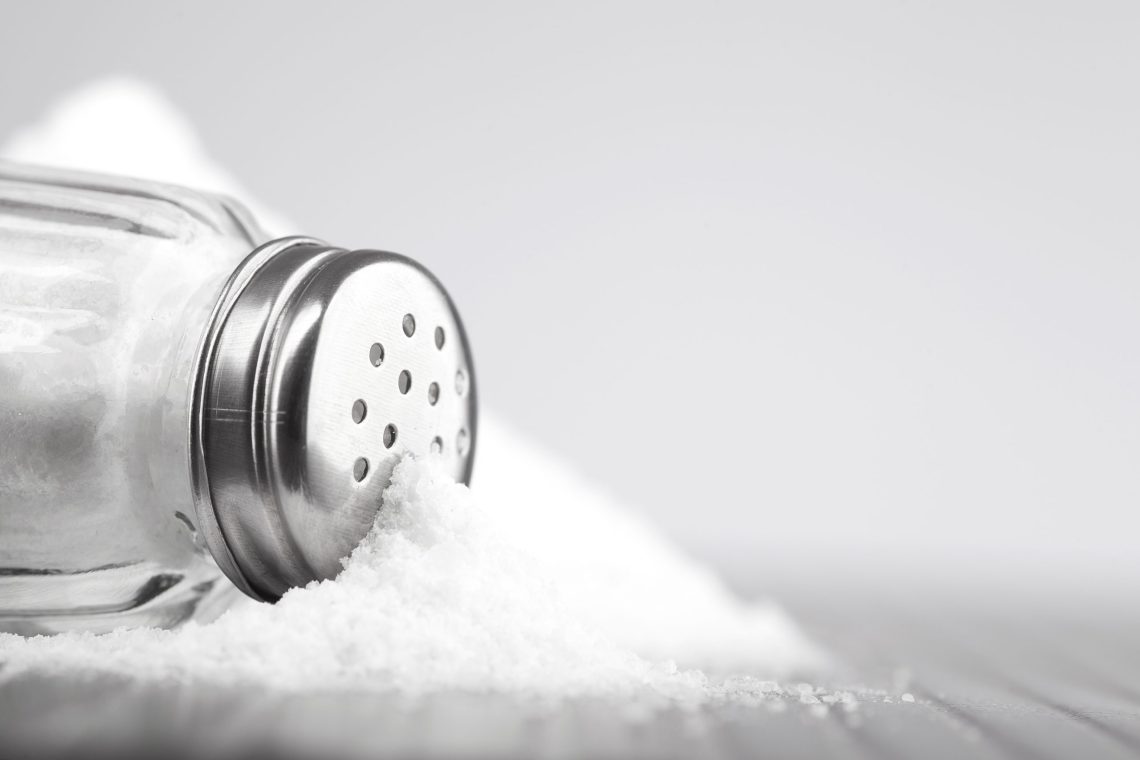
Introduction Sodium chloride, commonly known as salt, is a naturally occurring compound vital for many physiological processes in the body. While best known as a table seasoning, in medical contexts it is a critical agent used in various treatments ranging from rehydration therapy to wound care and intravenous infusions. What is Sodium Chloride? Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an ionic compound made from sodium (Na⁺) and chloride (Cl⁻) ions. It is essential for maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions. Medically, it is often found in solutions used for hydration, flushing, or as a carrier for other medications. How It…
-
Introduction Doxylamine is an antihistamine most commonly used as a short-term treatment for insomnia and as a remedy for allergy symptoms. It also plays a role in managing symptoms of the common cold and is often combined with other medications to treat nausea and vomiting in pregnancy. Known for its sedative properties, doxylamine is available in various over-the-counter and prescription forms. What is Doxylamine? Doxylamine succinate is a first-generation antihistamine belonging to the ethanolamine class. It works by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical involved in allergic reactions, and also has strong sedative effects, which makes it useful as…
-
Introduction Ketoconazole is an antifungal medication that is used to treat a variety of fungal infections. It belongs to the class of medications known as azoles, which inhibit the growth of fungi by interfering with the synthesis of ergosterol, a crucial component of the fungal cell membrane. Ketoconazole can be applied topically or taken orally, and it is available in various forms such as creams, shampoos, and tablets. It is commonly prescribed to treat conditions such as dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, fungal skin infections, and systemic fungal infections. While ketoconazole is effective in treating fungal infections, its use must be monitored…
-
Introduction Permethrin is a synthetic chemical that belongs to the class of insecticides known as pyrethroids. It is widely used to control various types of pests, including head lice, scabies mites, and other external parasites. Permethrin is also employed in agriculture and veterinary medicine for pest control. It works by disrupting the nervous system of insects, leading to paralysis and death. Permethrin is available in both prescription and over-the-counter formulations, including creams, lotions, shampoos, and sprays. Its use is considered safe when applied according to guidelines, but it is essential to be aware of potential side effects and precautions. What…
-
Introduction Nicotine is a naturally occurring alkaloid found primarily in the tobacco plant, Nicotiana tabacum. It is the main addictive substance in tobacco products, including cigarettes, cigars, and smokeless tobacco. Beyond its recreational use, nicotine is also utilized in medical treatments to help individuals quit smoking, though it is notorious for its addictive properties. As a stimulant, nicotine acts on the nervous system and has both therapeutic and detrimental effects on health. This article provides a detailed examination of nicotine, its uses, benefits, side effects, and guidelines for its use. What is Nicotine? Nicotine is a colorless, odorless alkaloid that…