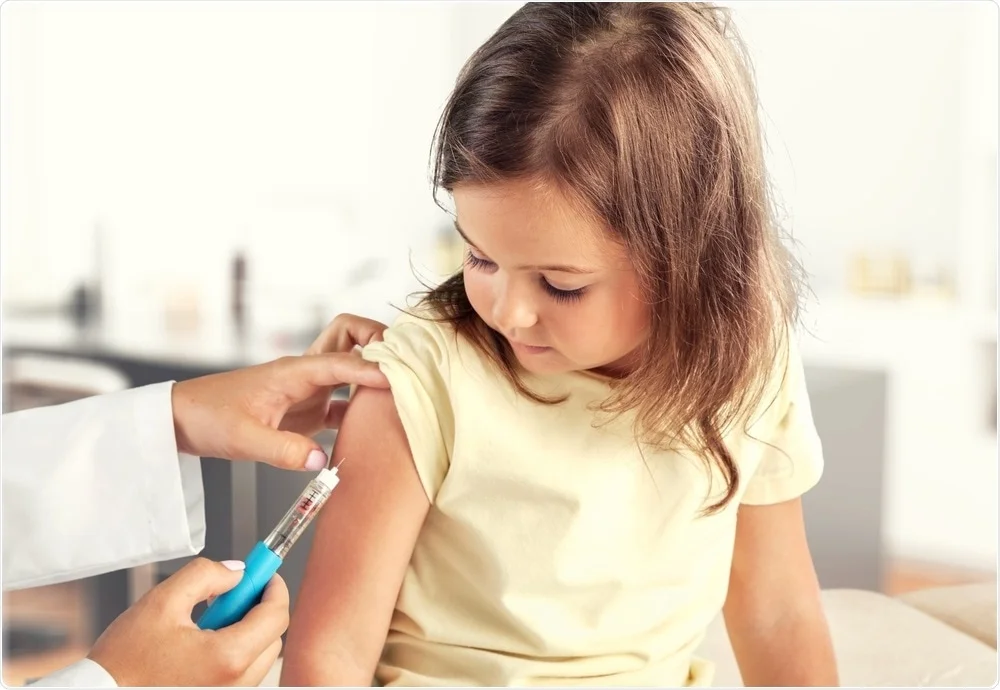
Introduction Global travel can bring adventure, opportunity, and cultural enrichment—but it can also expose travelers to infectious diseases like measles. Measles outbreaks continue to occur worldwide, including in countries where it was once eliminated. Because measles is among the most contagious viruses known, travelers to outbreak regions must take preventive measures to protect themselves and avoid spreading the disease upon return. Why Travel Increases Measles Risk Precautions Before Traveling 1. Check Your Immunization Status 2. Special Recommendations for Infants 3. Consider Health Conditions Precautions During Travel 1. Practice Good Hygiene 2. Minimize Close Contact 3. Stay Informed Precautions After Returning…
-
-
Introduction Measles has plagued humanity for centuries, causing countless deaths—especially among children—before the arrival of modern medicine. The introduction of the measles vaccine in the 20th century marked a turning point in global public health. Today, measles is a vaccine-preventable disease, yet its history serves as a reminder of what can happen when vaccination rates decline. Early History of Measles Ancient Origins Global Epidemics Scientific Breakthroughs Virus Identification First Measles Vaccine Vaccination Success Global Implementation Dramatic Decline in Cases Elimination Achievements Challenges and Setbacks Conclusion The history of measles is a story of both tragedy and triumph. From centuries of…
-
Introduction Measles is often thought of as a childhood disease, but adults are not immune to its dangers—especially if they have never been vaccinated or previously infected. Measles in adults can be more severe than in children, with a higher likelihood of complications and longer recovery times. Global travel, declining vaccination rates, and occasional outbreaks mean that unprotected adults remain at significant risk. Why Adults Can Still Get Measles Risks of Measles in Adults 1. Increased Complication Rates 2. Higher Mortality Risk 3. Greater Impact on Daily Life Severity of Measles in Adults 1. Symptom Intensity 2. Common Adult Complications…
-
Introduction Measles is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the measles virus. While there is no specific antiviral cure, most patients recover with proper supportive care. However, measles can lead to serious complications such as pneumonia, encephalitis, and dehydration—especially in children under 5, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals. Effective treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, preventing complications, and supporting recovery. Supportive Care for Measles Since measles is caused by a virus, antibiotics are not used unless a bacterial complication develops. Supportive care aims to ease symptoms and help the immune system fight the infection. 1. Rest and Hydration 2. Fever…
-
Introduction Measles is one of the most contagious viral diseases in the world, caused by the measles virus from the Paramyxoviridae family. Despite the availability of a safe and effective vaccine, measles continues to cause outbreaks in both developing and developed countries. These outbreaks often result in severe illness, preventable deaths, and significant strain on healthcare systems. Understanding the causes of measles outbreaks and their global impact is critical to strengthening public health measures and preventing future epidemics. Causes of Measles Outbreaks 1. Declining Vaccination Coverage 2. International Travel and Importation of Cases 3. Weak Healthcare Infrastructure 4. Crowded Living…
-
Introduction Measles is not just another childhood illness—it’s one of the most contagious diseases known to humans. Its ability to spread rapidly through communities has led to explosive outbreaks in areas with low vaccination coverage. The secret to its high transmissibility lies in a concept called R₀ (basic reproduction number). Understanding R₀ helps explain why controlling measles requires extremely high levels of immunity in a population. What is R₀ (Basic Reproduction Number)? For measles, the R₀ is estimated between 12 and 18, making it one of the highest among all infectious diseases.This means that one person with measles can infect…
-
Introduction Measles is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the measles virus (a member of the Paramyxoviridae family). While most cases resolve within a couple of weeks, measles is far from harmless. The virus can weaken the immune system for several weeks or even months, leaving the body vulnerable to other infections. In some cases, measles leads to serious and potentially fatal complications. Three of the most severe are pneumonia, encephalitis, and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE).Understanding these complications is crucial for recognizing the importance of vaccination and early medical care. Pneumonia: The Leading Cause of Measles-Related Deaths Pneumonia is…
-
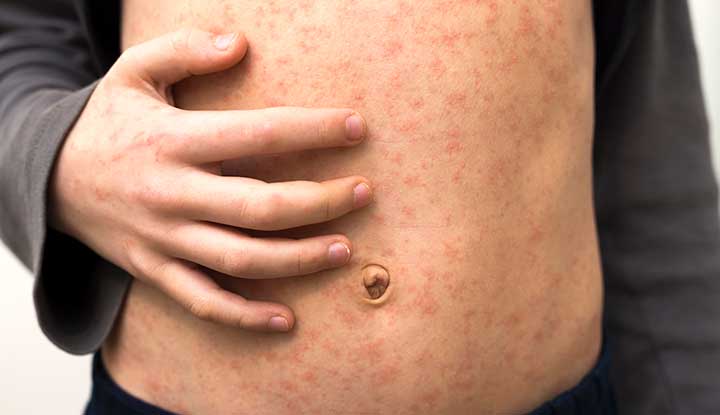
Introduction Measles is a highly contagious viral illness that spreads through respiratory droplets and can lead to serious complications—especially in unvaccinated children and adults. While vaccines have dramatically reduced its global burden, measles outbreaks still occur, often due to low vaccination coverage. Recognizing the early and classic symptoms of measles—including the hallmark rash, fever, cough, and Koplik’s spots—can help with early diagnosis and prevent further spread. What Causes Measles? Measles is caused by the measles virus, a member of the paramyxovirus family. It spreads through: Measles is extremely contagious—up to 90% of unvaccinated people in close contact with an infected…