Acne is one of the most common skin concerns worldwide, affecting people of all ages and skin types. Even individuals who generally have clear skin may experience occasional pimples due to stress, hormonal fluctuations, diet changes, or environmental triggers. When these breakouts happen, a common question arises: Should you rely on over-the-counter (OTC) products, or is it better to seek prescription treatments? Understanding the differences between OTC and prescription options can help you choose the safest, most effective approach for your skin. This article breaks down how each category works, its strengths and limitations, and factors to consider when deciding…
-
-
Introduction Fever is a common symptom of infection, inflammation, or other illnesses. While mild fevers may not require treatment, high or uncomfortable fevers often prompt the use of over-the-counter (OTC) antipyretics such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) or ibuprofen. Correct dosing is critical for safety and effectiveness, especially in children, infants, and elderly patients. Misuse can lead to serious complications such as liver damage (acetaminophen) or stomach and kidney issues (ibuprofen). Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) for Fever How It Works Dosage Guidelines Age/Weight Dose Frequency Maximum in 24 Hours Infants 0–3 months 10–15 mg/kg Every 4–6 hours Consult doctor Infants/Children 3 months–12 years 10–15…
-
Introduction Nausea is an uncomfortable symptom that can arise from a wide range of conditions, including motion sickness, infections, pregnancy, migraines, gastrointestinal disorders, or medications. When home remedies like hydration, dietary changes, or ginger are insufficient, antiemetic medications can provide relief. Antiemetics work by blocking or modifying the brain and gut signals responsible for nausea and vomiting. Depending on severity and cause, these can range from over-the-counter (OTC) options to prescription medications. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Antiemetics 1. Antihistamines (H1 Receptor Antagonists) 2. Bismuth Subsalicylate Prescription Antiemetics 1. Serotonin (5-HT3) Receptor Antagonists 2. Dopamine Antagonists 3. Anticholinergics 4. Neurokinin-1 (NK1) Receptor Antagonists…
-
Introduction Nausea is an uncomfortable symptom caused by a variety of conditions, including infections, motion sickness, pregnancy, migraines, gastrointestinal disorders, and medications. When home remedies like hydration, dietary adjustments, or ginger are insufficient, antiemetic medications can help relieve symptoms. Antiemetics work by blocking the signals in the brain or gut that trigger nausea and vomiting. Depending on the cause and severity, options range from over-the-counter (OTC) medications to prescription drugs. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Antiemetics 1. Antihistamines (H1 Receptor Antagonists) 2. Bismuth Subsalicylate Prescription Antiemetics 1. Serotonin (5-HT3) Receptor Antagonists 2. Dopamine Antagonists 3. Anticholinergics 4. Neurokinin-1 (NK1) Receptor Antagonists Choosing the…
-
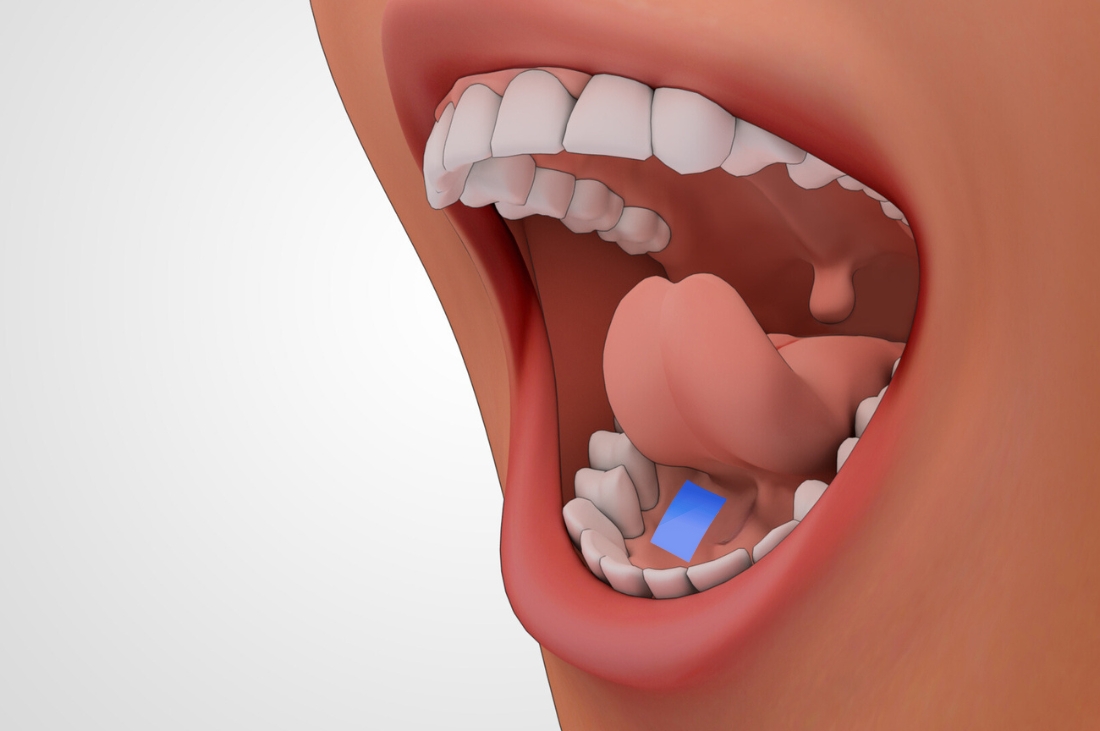
Introduction In recent years, sublingual medications—those designed to dissolve under the tongue—have gained significant attention in the over-the-counter (OTC) drug market. Unlike traditional oral medications that require swallowing and digestion, sublingual drugs leverage the thin mucous membrane under the tongue to deliver active ingredients directly into the bloodstream. This route allows for faster onset of action and improved bioavailability, making sublingual formulations attractive for consumers seeking rapid relief from common ailments. This article explores the mechanisms behind sublingual absorption, current OTC sublingual products, their advantages and limitations, manufacturing challenges, and consumer trends shaping this innovative delivery system. Sublingual Absorption Mechanisms…
-
Introduction Hearing loss affects millions worldwide, impacting communication, social interaction, and quality of life. Traditionally, hearing aids have been expensive, requiring professional fitting and prescription. However, recent regulatory shifts and technological advancements have ignited a revolution: over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids. These devices promise easier access, affordability, and user autonomy. This article explores how OTC hearing aids are reshaping the landscape, the technology behind them, potential challenges, and what consumers should consider when navigating this emerging market. FDA Regulatory Changes and Market Opening In 2017, the U.S. Congress passed the Over-the-Counter Hearing Aid Act, which the FDA implemented by creating a…
-
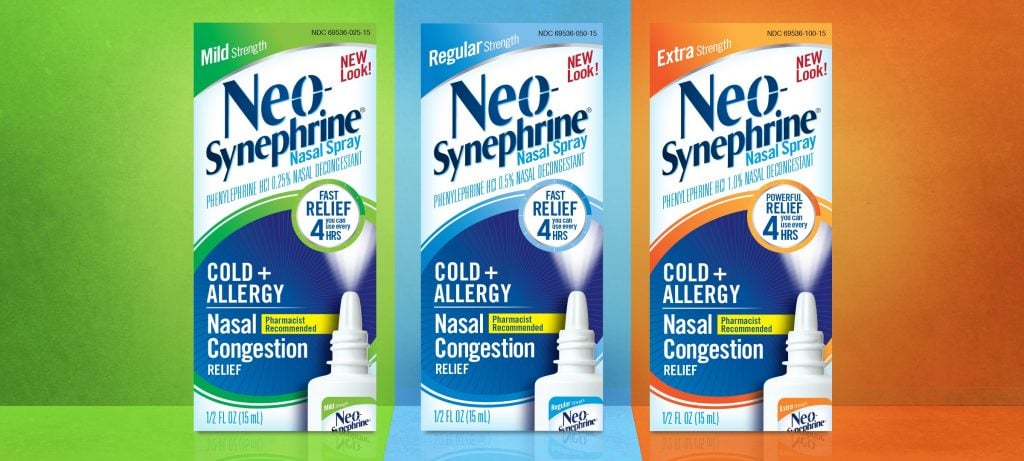
Introduction For decades, oral phenylephrine has been a staple in over-the-counter (OTC) cold and allergy medications marketed as nasal decongestants. However, recent evaluations by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and independent researchers have concluded that oral phenylephrine is largely ineffective at relieving nasal congestion. As a result, consumers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies are urgently exploring alternatives. This article delves into the emerging innovations and options that promise more effective and safer relief for nasal congestion in the post-phenylephrine era. Current Effective Alternatives to Oral Phenylephrine With the diminishing credibility of oral phenylephrine, many are turning to well-established alternatives…
-
Introduction Probiotics have exploded in popularity over the last decade, marketed as over-the-counter (OTC) solutions for everything from bloating and diarrhea to immunity and mental clarity. These “good bacteria” promise to restore balance to the gut microbiome, particularly after disruptions caused by antibiotics. With increasing consumer awareness about gut health’s connection to overall wellness, the market is now flooded with probiotic supplements in pills, powders, gummies, and fermented foods. However, despite their growing presence on pharmacy shelves, not all probiotics are created equal—and their benefits are highly strain-specific, dosage-dependent, and subject to numerous regulatory and scientific challenges. Understanding Probiotic Strains…
-
Introduction In an evolving healthcare landscape that emphasizes accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and patient empowerment, Rx-to-OTC drug switches have emerged as a key strategy for expanding self-care options. These switches occur when medications once available only by prescription gain approval for over-the-counter (OTC) sale. The shift reflects growing trust in consumer health literacy and demand for greater convenience in managing common health conditions. From allergy relief to heartburn treatment, many once-prescription drugs have made successful transitions to the pharmacy shelf. However, this transformation involves rigorous evaluation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), as well as ongoing concerns about safety, affordability,…
-
Introduction In recent years, cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive compound derived from the cannabis plant, has made significant waves in the health and wellness industry. Among its many applications, topical CBD products—creams, balms, lotions, and salves—have emerged as popular options for managing localized pain, inflammation, and even certain skin conditions. These over-the-counter (OTC) solutions offer a non-invasive, non-intoxicating alternative to traditional pain relievers, particularly for those seeking to avoid oral NSAIDs or opioids. As CBD-infused topicals fill shelves in pharmacies, wellness stores, and online markets, questions around their efficacy, regulation, safety, and appropriate usage continue to spark debate. This article explores…