Introduction Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common cause of lower respiratory tract infections in infants and young children. While most RSV infections are mild, severe cases in infancy, especially those requiring hospitalization, can have long-term consequences. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for parents, caregivers, and healthcare providers to monitor development, manage ongoing health issues, and reduce future complications. 1. Impact on the Respiratory System Bronchial Hyperreactivity and Asthma Risk Chronic Lung Issues 2. Increased Susceptibility to Future Respiratory Infections 3. Hospitalization and Intensive Care Impact 4. Developmental and Immune System Considerations Growth and Nutrition Immune System Sensitization 5.…
-
-
Introduction Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a highly contagious virus that primarily affects the respiratory tract. While it often causes mild cold-like symptoms in older children and adults, RSV can be serious for infants, especially those under 6 months, premature babies, and children with underlying health conditions. Understanding how RSV spreads and taking proactive preventive measures is key to protecting vulnerable infants and reducing the risk of severe illness. 1. How RSV Spreads RSV spreads easily from person to person through direct contact, respiratory droplets, and contaminated surfaces. Common Modes of Transmission: Who Can Spread RSV? 2. Why Babies Are…
-
Introduction Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common viral infection that primarily affects the respiratory system. While many cases in infants, toddlers, and older adults are mild and manageable at home, RSV can become severe, particularly in young infants, premature babies, older adults, or those with chronic health conditions. Recognizing the warning signs of severe RSV infection is crucial for timely medical intervention and preventing complications such as respiratory distress, pneumonia, or dehydration. 1. Who is at Higher Risk for Severe RSV Certain groups are more likely to develop severe RSV illness requiring hospitalization: High-risk individuals should be monitored closely…
-
Introduction Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common viral infection in infants and young children, often causing cold-like symptoms such as runny nose, cough, and mild fever. While most cases are mild and manageable at home, RSV can sometimes lead to lower respiratory tract infections like bronchiolitis, particularly in infants under 6 months or children with underlying health conditions. Proper home care focuses on maintaining hydration, clearing nasal passages, and monitoring symptoms for signs of deterioration. Early attention can prevent complications and reduce the need for hospitalization. 1. Hydration Maintaining adequate fluid intake is crucial because RSV can cause reduced…
-
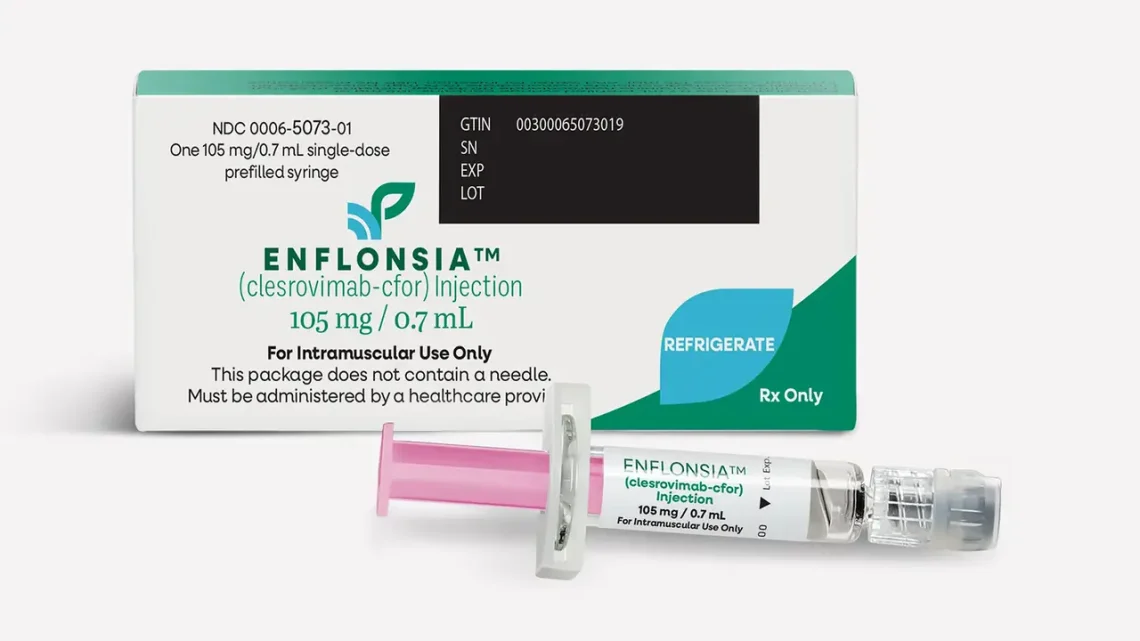
Introduction Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a leading cause of severe respiratory illness in infants and young children. Each year, RSV leads to numerous hospitalizations worldwide, especially in babies under 6 months of age. While vaccines for older adults and pregnant women help protect some populations, infants themselves can now be directly protected through Beyfortus (nirsevimab), a monoclonal antibody specifically designed for RSV prevention. Beyfortus represents a major advance in infant care, offering passive immunity during the first months of life, when babies are most vulnerable to severe RSV complications. What is Beyfortus? Beyfortus is a long-acting monoclonal antibody that…