Introduction Dandruff is a common scalp condition characterized by flaking, itching, and irritation. While over-the-counter shampoos and natural remedies are effective for many people, some cases are stubborn or severe. Persistent dandruff may be a result of seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, or fungal overgrowth, requiring prescription-strength treatments. This article explores prescription options for managing stubborn dandruff, including topical and oral medications, how they work, and guidelines for safe use. When Is Prescription Treatment Needed? Topical Prescription Treatments 1. Ketoconazole 2% or 4% 2. Ciclopirox 3. Topical Corticosteroids 4. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors Oral Prescription Treatments (For Severe or Refractory Cases) 1. Oral…
-
-
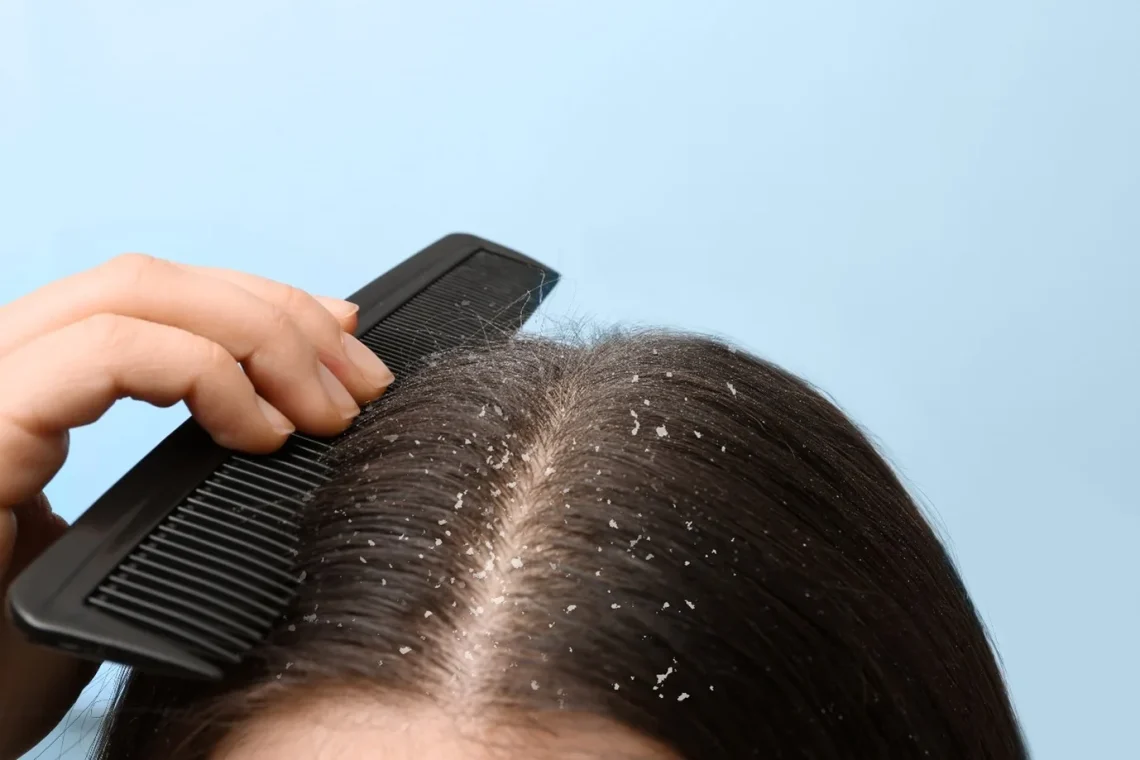
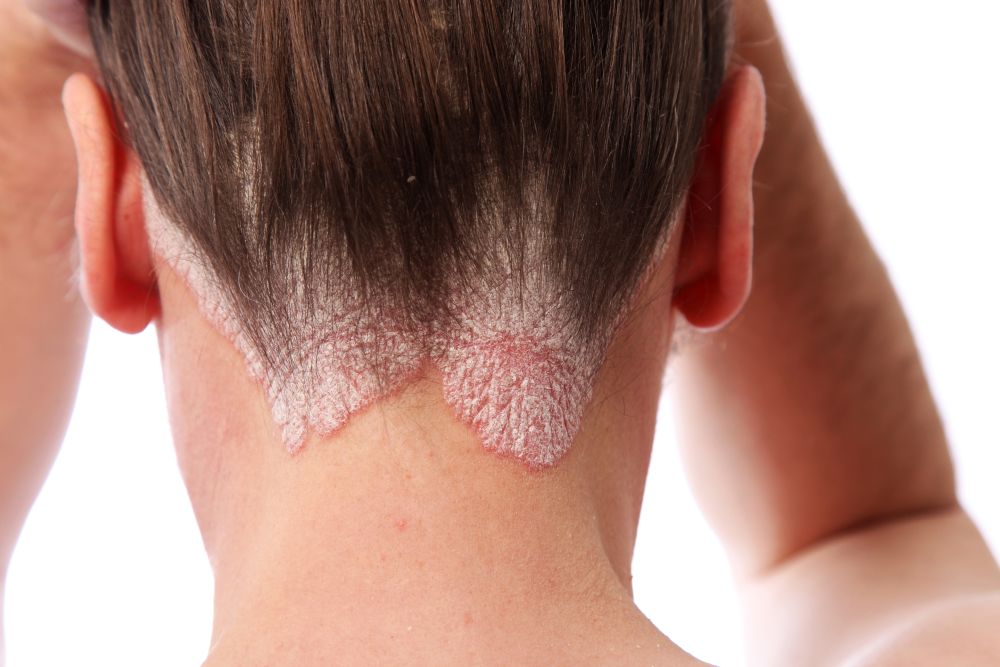
Introduction Dandruff is often perceived as a minor cosmetic concern, but in many cases, it is caused by a medical condition called seborrheic dermatitis (SD). This chronic inflammatory skin disorder affects areas rich in oil glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. On the scalp, SD can lead to flaking, redness, itching, and irritation, often mistaken for ordinary dandruff. Understanding seborrheic dermatitis is key to choosing the right treatments and managing symptoms effectively. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches for seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp. What is Seborrheic Dermatitis? Causes and Triggers 1. Fungal Overgrowth…
-
Introduction Dandruff is a common scalp condition that causes itching, flaking, and irritation. While medicated shampoos are effective, many people prefer natural remedies to manage mild to moderate dandruff. Two of the most popular natural treatments are tea tree oil and apple cider vinegar (ACV) rinses. These remedies are believed to help control fungal growth, balance scalp pH, and reduce inflammation. This article explores how tea tree oil and apple cider vinegar work, how to use them safely, and additional tips for maintaining a healthy, flake-free scalp. Tea Tree Oil for Dandruff How It Works How to Use Tips Apple…
-
Introduction Dandruff is a common scalp condition that causes itching, flaking, and irritation. While medicated shampoos are effective, many people prefer natural remedies to manage mild to moderate dandruff. Two of the most popular natural treatments are tea tree oil and apple cider vinegar (ACV) rinses. These remedies are believed to help control fungal growth, balance scalp pH, and reduce inflammation. This article explores how tea tree oil and apple cider vinegar work, how to use them safely, and additional tips for maintaining a healthy, flake-free scalp. Tea Tree Oil for Dandruff How It Works How to Use Tips Apple…
-
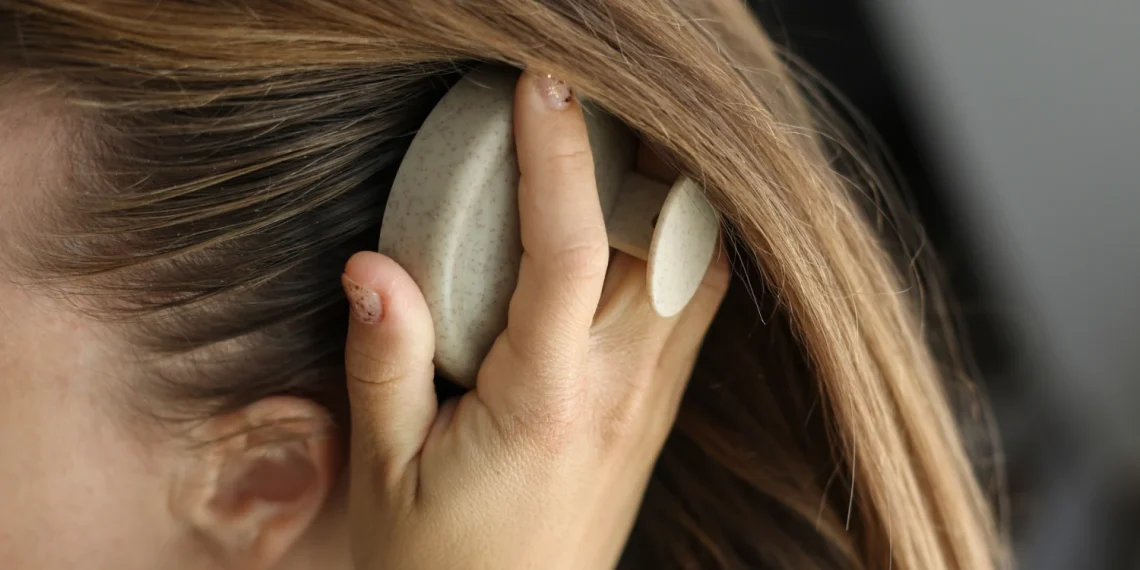
Introduction A healthy scalp is the foundation of healthy hair and can play a key role in managing dandruff, dryness, and irritation. One of the most effective ways to enhance scalp health is through regular scalp massage. Not only does massage improve blood circulation, but it also helps loosen dead skin flakes, distribute natural oils, and prepare the scalp for better absorption of shampoos and treatments. This article explores the benefits of scalp massage and provides step-by-step techniques to help you maintain a clean, healthy, and flake-free scalp. Benefits of Scalp Massage 1. Loosens Flakes 2. Improves Blood Circulation 3.…
-
Introduction Dandruff is a common scalp condition characterized by flaking, itching, and sometimes redness. One of the most effective ways to manage dandruff is through regular shampooing, which helps remove excess oil, dead skin, and fungal buildup. However, the frequency of hair washing can vary depending on the severity of dandruff, scalp type, and the shampoo used. Washing too often or too little can either irritate the scalp or fail to control flakes. This article provides guidance on how often to wash your hair to keep dandruff under control while maintaining a healthy scalp. Understanding the Role of Hair Washing…
-
Introduction Dandruff is a common scalp condition characterized by flaking, itching, and irritation. While mild cases can sometimes be managed with regular hair washing, persistent dandruff often requires medicated shampoos. Anti-dandruff shampoos contain active ingredients that target the underlying causes, such as fungal overgrowth, excess oil, or scalp irritation. This article provides an in-depth guide to the most common active ingredients—Zinc Pyrithione, Selenium Sulfide, Ketoconazole, and Coal Tar—and how to choose the right shampoo for your scalp needs. Understanding Dandruff and Its Causes Key Anti-Dandruff Shampoo Ingredients 1. Zinc Pyrithione How It Works Benefits Considerations 2. Selenium Sulfide How It…
-
Introduction A restful night’s sleep is influenced not only by our bodies but also by our sleep environment. For people prone to snoring, obstructive sleep apnea, or mild airway obstructions, the bedroom setup can either aggravate or reduce nighttime breathing difficulties. Creating a sleep-friendly environment can help minimize snoring, improve oxygen flow, and promote deeper, more restorative sleep. This article explores practical strategies to optimize your sleep environment for quieter breathing. 1. Optimize Bedroom Temperature and Humidity a. Temperature b. Humidity 2. Reduce Allergens and Irritants a. Bedding and Fabrics b. Air Quality c. Pets 3. Strategic Bed Positioning a.…
-
Introduction Snoring occurs when airflow through the airway causes vibration of soft tissues in the throat. While factors like obesity, nasal congestion, alcohol, and sleep position play a role, weak or flabby throat and tongue muscles are a major contributor to snoring. Strengthening these muscles can improve airway stability, reduce vibration, and promote quieter sleep. This article explores the science behind tongue and throat exercises, specific techniques to try, and how regular practice can help reduce snoring. How Tongue and Throat Muscles Affect Snoring 1. Muscle Weakness and Airway Collapse 2. Benefits of Muscle Training Effective Tongue and Throat Exercises…
-
Introduction Snoring is often dismissed as a minor annoyance, but it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious condition: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Sleep apnea occurs when the airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep, leading to interrupted breathing, low oxygen levels, and fragmented sleep. While not all snorers have sleep apnea, loud, frequent snoring is one of the most common warning signs. Understanding the link between snoring and sleep apnea—and knowing when to get tested—is crucial for long-term health and well-being. This article explores the connection between snoring and sleep apnea, key symptoms, risk factors, and…