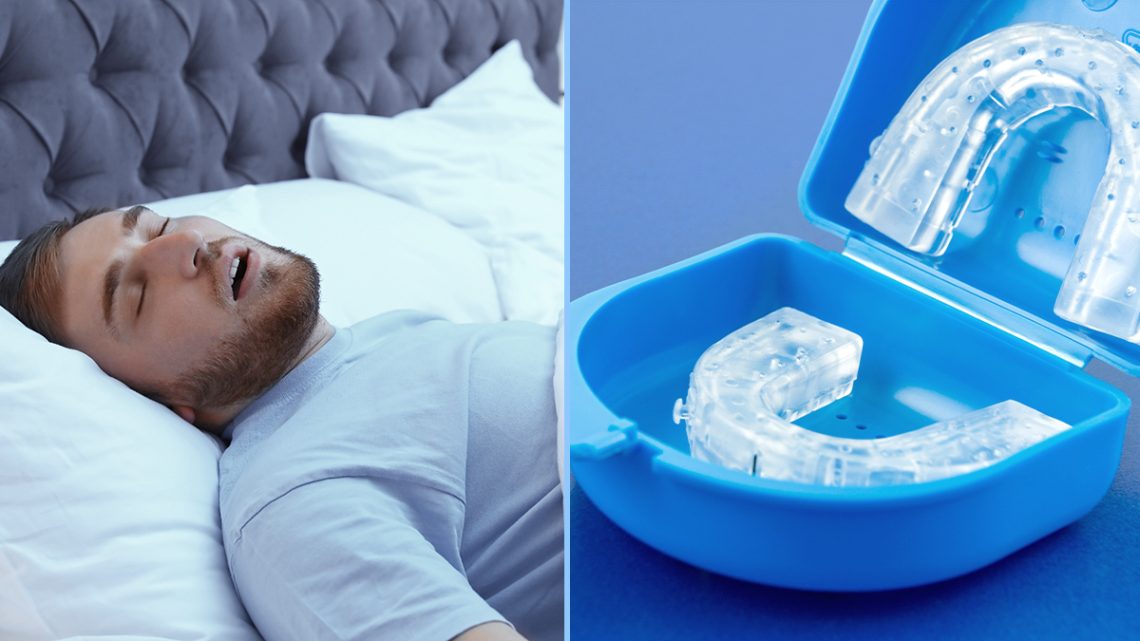
Introduction Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are common sleep-related problems that can affect both health and quality of life. For many people, lifestyle changes, positional therapy, and nasal treatments are helpful, but sometimes additional solutions are needed. Mandibular Advancement Devices (MADs) are one of the most widely used oral appliances designed to reduce snoring and mild-to-moderate sleep apnea. They work by repositioning the lower jaw (mandible) to keep the airway open during sleep. This article explores how MADs work, their benefits, limitations, and important considerations before choosing one. How Mandibular Advancement Devices Work Mechanism of Action Who Typically Benefits…
-
-
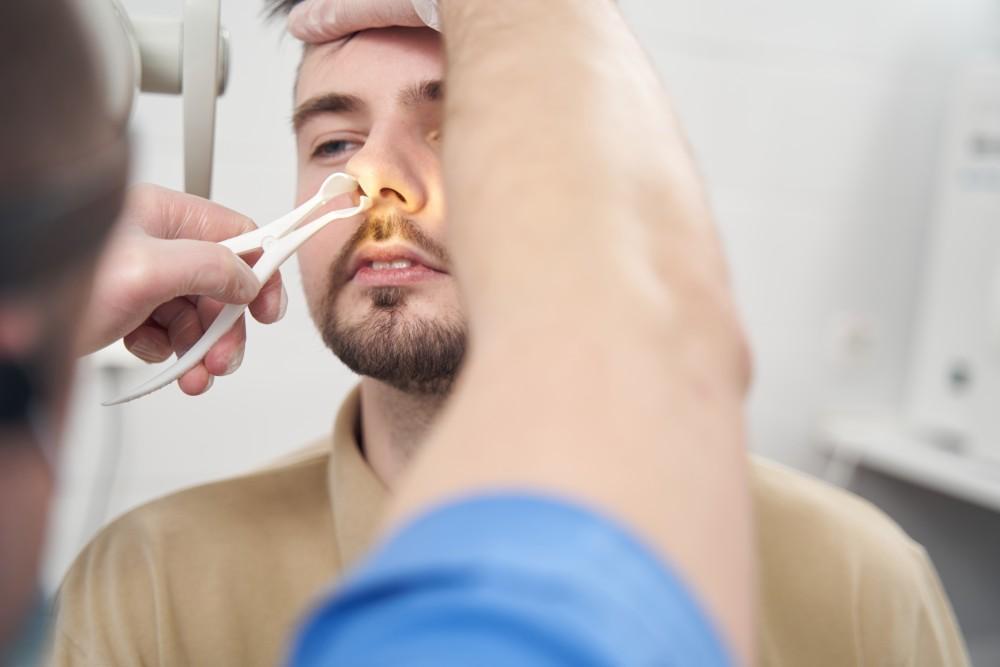
Introduction Nasal congestion is one of the most common contributors to snoring, sleep disturbances, and poor sleep quality. When airflow through the nose is restricted, the body compensates by breathing through the mouth, which can lead to loud snoring, throat dryness, and even exacerbation of sleep apnea. Congestion can arise from temporary issues such as colds, chronic conditions like allergies, or structural problems such as a deviated septum. Addressing nasal obstruction is a crucial step toward clearer airflow, quieter sleep, and better overall health. This article explores the causes of nasal congestion, treatment strategies, and how improving nasal airflow can…
-
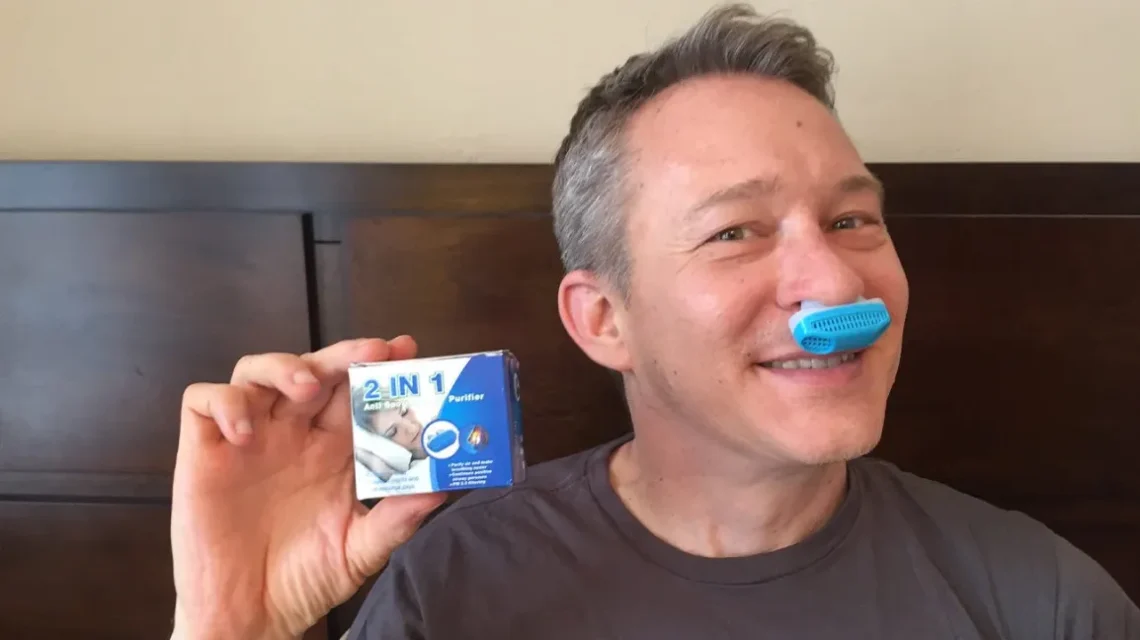
Introduction Snoring is a common sleep concern that can disturb both the snorer and their bed partner. Many people look for quick solutions to reduce snoring, and over-the-counter products like nasal strips, nasal dilators, and nasal sprays are popular choices. These products aim to improve airflow through the nose and reduce vibrations in the throat that cause snoring. But do they actually work, and who benefits most from them? This article explores the science behind these nasal aids, how they function, their effectiveness, and how to incorporate them into a comprehensive snoring management plan. Understanding Snoring and Nasal Resistance Snoring…
-
Introduction Many people rely on alcohol or sedatives in the evening to unwind or fall asleep. While these substances may seem to help you relax, they can actually disrupt sleep quality, worsen snoring, and increase the risk of sleep apnea. Understanding how alcohol and sedatives affect the airway and sleep cycles is crucial for improving rest, reducing nighttime breathing problems, and promoting overall health. This article explores the effects of alcohol and sedatives on sleep, why avoiding them before bed matters, and strategies for healthier nighttime routines. How Alcohol Affects Sleep and Snoring 1. Muscle Relaxation and Airway Collapse Alcohol…
-
Introduction Snoring is one of the most common sleep complaints worldwide, affecting both the person who snores and the people who share their sleeping environment. While snoring can occur for many reasons—such as nasal congestion, sleep position, or anatomy—excess weight is one of the most influential and modifiable factors. Even a modest amount of weight loss can significantly reduce snoring frequency, loudness, and severity. This article explains how weight affects the airway, why even small changes make a big difference, and how weight loss can improve not only snoring but also overall sleep quality and long-term health. Understanding the Link…
-
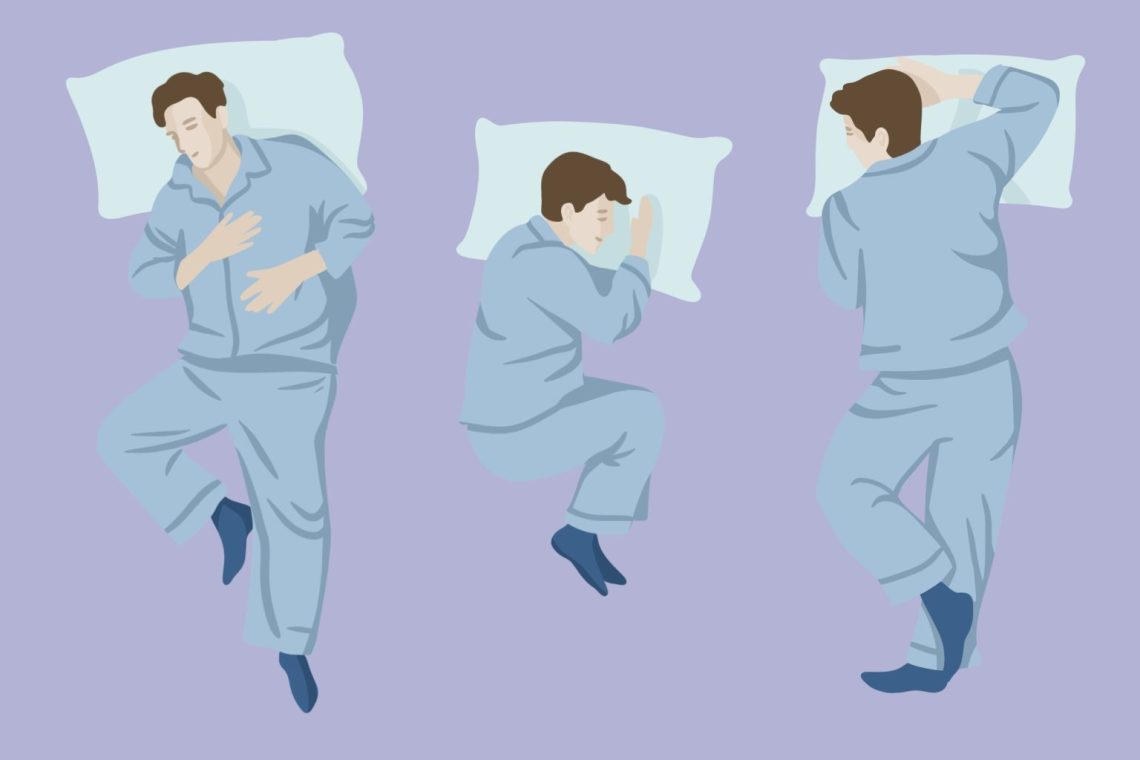
Introduction Snoring is a common sleep disturbance affecting millions of people worldwide. While often viewed as a harmless annoyance, persistent snoring can disrupt sleep quality, strain relationships, and sometimes signal underlying issues such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). One of the simplest and most effective behavioral strategies for managing snoring is positional therapy—a method that encourages sleeping on the side rather than on the back. This approach can significantly minimize airway obstruction, reduce vibration in the throat, and promote smoother breathing during sleep. This article explores why sleeping position matters, how positional therapy works, who can benefit from it, and…
-
Introduction Acne is more than a skin-deep problem. While clogged pores, oil production, and bacteria are involved, many internal factors—including stress, gut health, diet, and micronutrient imbalances—can influence how often you break out and how your skin heals. A holistic approach doesn’t replace medical acne treatments but supports the body from within, helping reduce inflammation, balance hormones, and build skin resilience. This comprehensive article explores three major holistic pillars—stress management, gut health, and supplements—that play a scientifically supported role in clearer, healthier skin. Understanding Holistic Acne Management A holistic approach focuses on the whole body, not just the skin. Acne…
-
Introduction Acne is often seen as a simple skin problem, but at its core, it is deeply influenced by hormonal activity. Whether you’re a teenager going through puberty or an adult dealing with breakouts in your 30s or 40s, hormones play a major role in triggering, worsening, and sustaining acne. Understanding how hormones affect the skin helps explain why acne becomes chronic in some people and why certain treatments—especially hormonal therapies—work so effectively. This article explores how hormones contribute to acne, why hormonal acne is so common, and the treatment options that target these internal imbalances. How Hormones Contribute to…
-
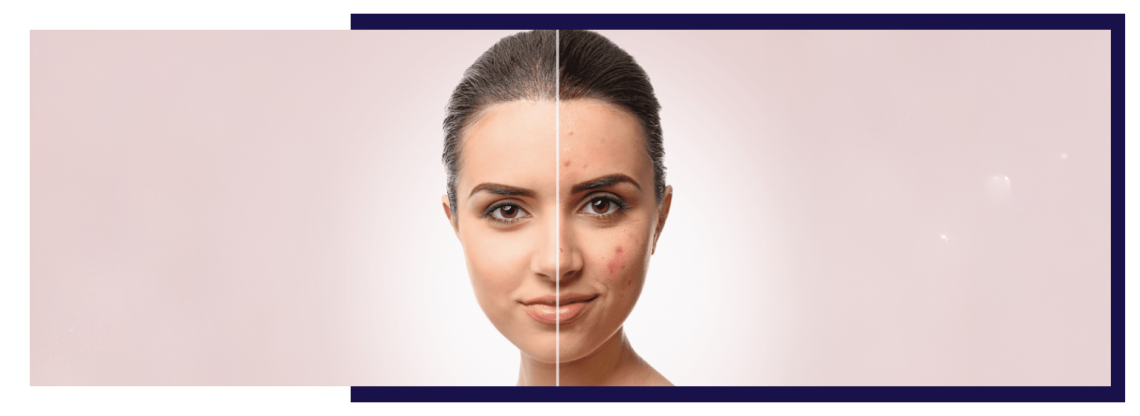
Introduction While acne is commonly associated with teenagers, a significant number of adults—especially women—continue to struggle with persistent breakouts well into their 20s, 30s, 40s, and even 50s. Adult acne can be frustrating because its causes are more complex, often tied to internal factors such as hormones, stress, or medical conditions. It can also be stubborn, requiring a more personalized and layered treatment approach than adolescent acne. This detailed guide explains why acne happens in adults, the key differences from teenage acne, and the most effective treatment strategies to regain clear, healthy skin. Understanding Adult Acne How Adult Acne Differs…
-
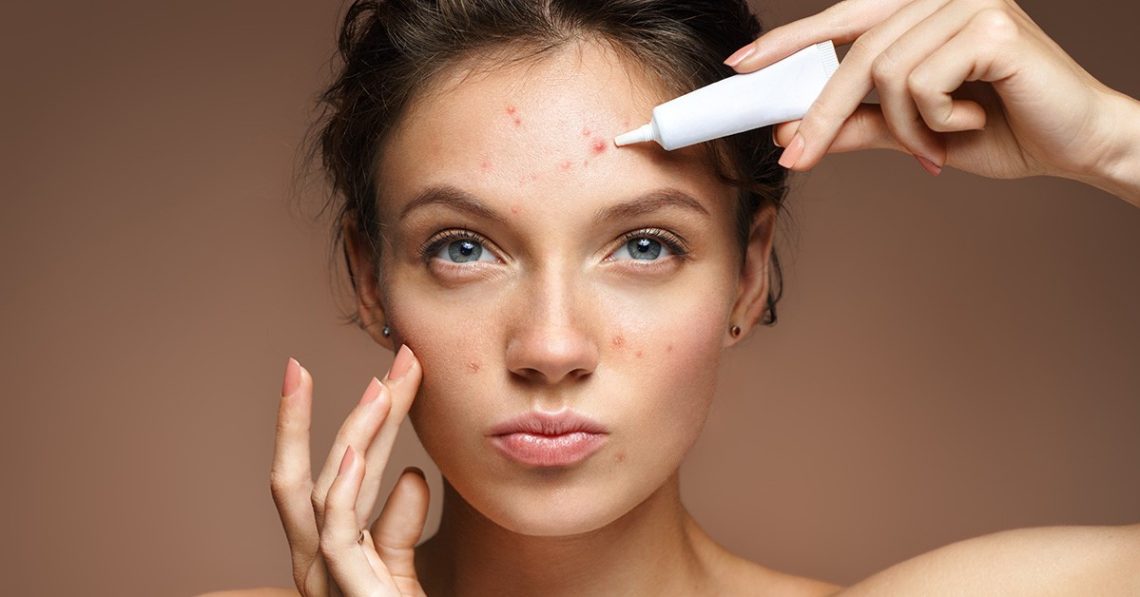
Introduction Acne is a common skin condition, but for many, its aftereffects linger long after active breakouts have faded. Acne scarring can impact confidence, texture, and skin tone, making the skin appear uneven or pitted. Understanding how scars form—and the wide range of treatments available today—can help you make informed decisions about prevention and correction.This comprehensive guide covers the types of acne scars, how to prevent them, and the most effective professional and at-home treatment options. What Causes Acne Scarring? Acne scarring occurs when inflammation damages the skin’s deeper layers. The healing process triggers collagen production, but if too much…