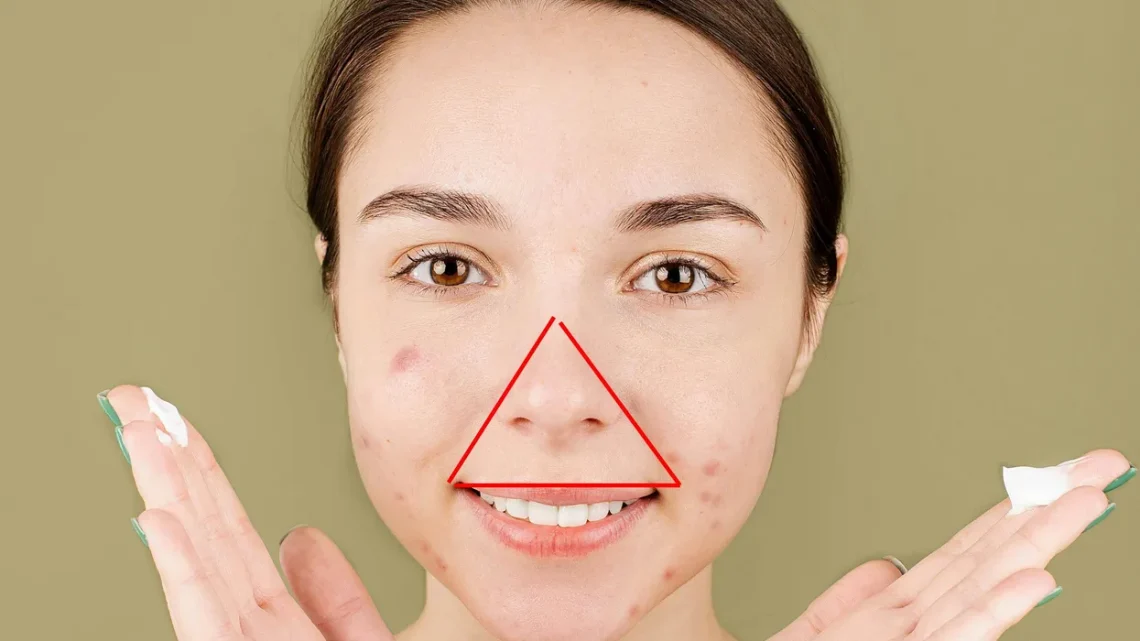
Introduction: Pimples can appear at the most inconvenient times, and while occasional breakouts are normal, the good news is that many of them can be prevented with a consistent skincare routine and smart habits. Three of the most effective preventive strategies—proper cleansing, using non-comedogenic products, and hands-off behavior—are simple yet powerful approaches that work for all skin types. This article explores why these three pillars matter, how to apply them correctly, and what mistakes to avoid for clear, healthy-looking skin. Why Prevention Matters Treating pimples after they appear can be frustrating, especially because many breakouts can be avoided in the…
-
-
Acne is one of the most common skin concerns worldwide, affecting people of all ages and skin types. Even individuals who generally have clear skin may experience occasional pimples due to stress, hormonal fluctuations, diet changes, or environmental triggers. When these breakouts happen, a common question arises: Should you rely on over-the-counter (OTC) products, or is it better to seek prescription treatments? Understanding the differences between OTC and prescription options can help you choose the safest, most effective approach for your skin. This article breaks down how each category works, its strengths and limitations, and factors to consider when deciding…
-
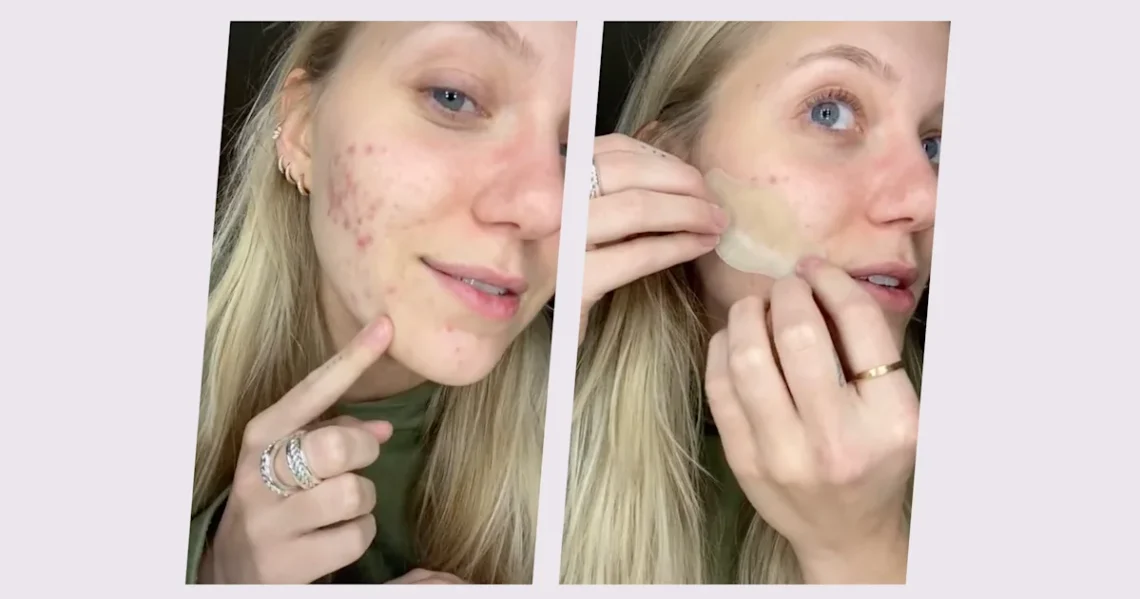
Introduction Pimples can be painful, inflamed, and hard to ignore—especially when they appear unexpectedly. In recent years, pimple patches, also known as hydrocolloid bandages, have become one of the most popular and effective spot treatments for reducing inflammation, absorbing pus, and speeding up healing. These tiny stickers may look simple, but they rely on medical-grade technology originally used for wound care. This article explains what pimple patches are, how they work, their different types, when to use them, and important safety tips. Whether you’re dealing with an overnight breakout or want a cleaner way to manage pimples, hydrocolloid patches offer…
-
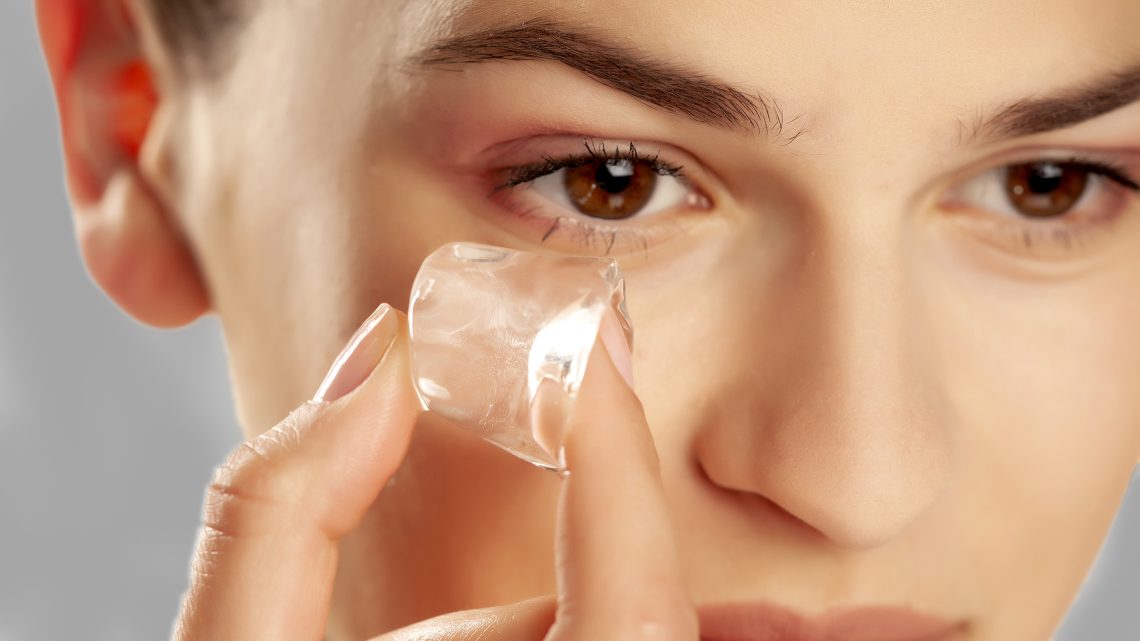
Introduction Pimples often appear with redness, swelling, and pain—especially inflammatory acne like papules, pustules, and cysts. While many skincare treatments target bacteria or oil buildup, one of the fastest ways to calm a pimple’s appearance is ice therapy. This simple, inexpensive method uses cold temperature to shrink blood vessels, reduce swelling, and numb the area for instant relief. Ice therapy is not a cure for acne, but it is a highly effective emergency treatment to reduce visible redness and discomfort. This article explains how ice therapy works, the correct way to use it, the mistakes to avoid, and when it’s…
-
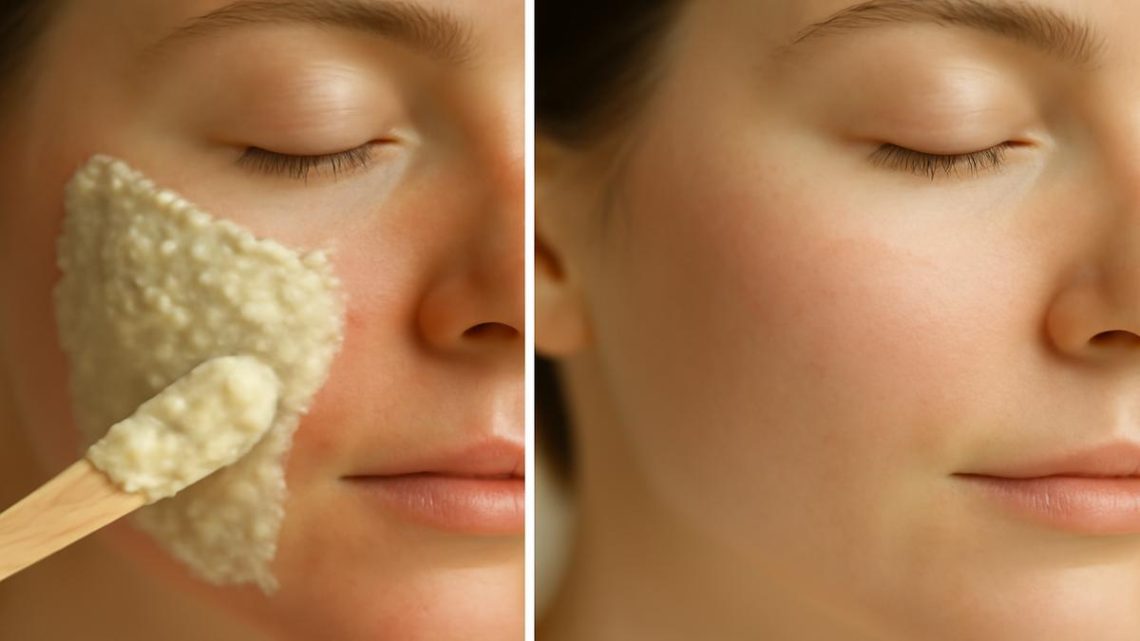
Introduction Pimples can appear suddenly and often at the most inconvenient times. While many over-the-counter treatments exist, some people prefer gentle, natural remedies—especially for mild, occasional breakouts. DIY skincare masks made from ingredients like honey, aloe vera, or tea tree oil have become increasingly popular due to their soothing, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties. However, natural does not always mean safe. Certain ingredients, particularly essential oils like tea tree oil, must be used with caution to avoid irritation, burns, or allergic reactions. This article explores effective DIY pimple-reduction remedies, how to use them safely, and when to avoid them. Why Consider…
-
Introduction When a patient presents with symptoms, determining the exact cause is not always straightforward. Many illnesses share overlapping signs, making diagnosis a complex process rather than a single step. This is where differential diagnosis becomes essential. It is a systematic method doctors use to narrow down possible conditions, eliminate unlikely causes, and ultimately reach the most accurate diagnosis. Understanding how differential diagnosis works empowers patients, improves communication with healthcare providers, and ensures more precise and effective treatment. This article explains the importance of differential diagnosis, how it’s performed, and why it plays a crucial role in modern medicine. What…
-
Introduction In today’s complex medical landscape, seeking a second opinion has become an empowering and essential step in making informed healthcare decisions. A second opinion allows you to confirm a diagnosis, explore alternative treatments, and gain clarity—especially when facing major, life-altering medical choices. Contrary to common belief, asking for another professional’s perspective is not disrespectful to your original doctor. Instead, it is a smart, proactive approach to protect your health, understand your options, and feel confident in your treatment plan. This article explains when a second opinion is necessary, how to get one, and what benefits it can bring to…
-
Introduction Many people are tempted to pop pimples when they appear, hoping for instant relief. While it can be tempting, popping acne often worsens inflammation, increases the risk of infection, and can lead to scarring. Understanding why dermatologists advise against it and how to safely manage pimples is essential for maintaining healthy skin. 1. Why You Should Avoid Popping Pimples A. Risk of Infection B. Inflammation and Scarring C. Delayed Healing D. Acne Spread 2. When It Might Be Safe to Pop 3. How to Pop a Pimple Safely (If You Must) Step 1: Wash Your Hands Step 2: Clean…
-
Introduction Acne breakouts are frustrating, but targeted spot treatments can help reduce inflammation, unclog pores, and speed healing. Two of the most popular and effective over-the-counter ingredients are Benzoyl Peroxide (BP) and Salicylic Acid (SA). Understanding how they work, when to use each, and potential side effects can help you choose the right treatment for your skin. 1. How Spot Treatments Work Spot treatments are applied directly to active pimples, aiming to: Unlike full-face treatments, spot treatments target specific problem areas, minimizing irritation to surrounding skin. 2. Benzoyl Peroxide (BP) How It Works Strengths Precautions 3. Salicylic Acid (SA) How…
-
Introduction Falling asleep quickly can be a challenge, especially for people dealing with stress, anxiety, or irregular sleep schedules. The Military Method is a sleep technique developed to help soldiers fall asleep in as little as two minutes, even in less-than-ideal conditions. This method combines physical relaxation and mental focus, training the body and mind to transition rapidly into sleep. It has gained popularity for its simplicity, effectiveness, and suitability for anyone, whether in a noisy environment or trying to reset a disrupted sleep pattern. 1. The Concept Behind the Military Method 2. Step-by-Step Military Method Step 1: Relax Your…